Physics is a very important subject for students. It may be hard for some students. For helping students here we have shared NCERT Class 12 Physics Chapter 1 Electric Charges and Fields Handwritten Notes.
The Electric Charges and Fields notes is a best resource for students who are preparing for their board exam because it compile the entire lesson in short and include every important topic.
NCERT Class 12 Physics Chapter 1 Electric Charges and Fields Notes























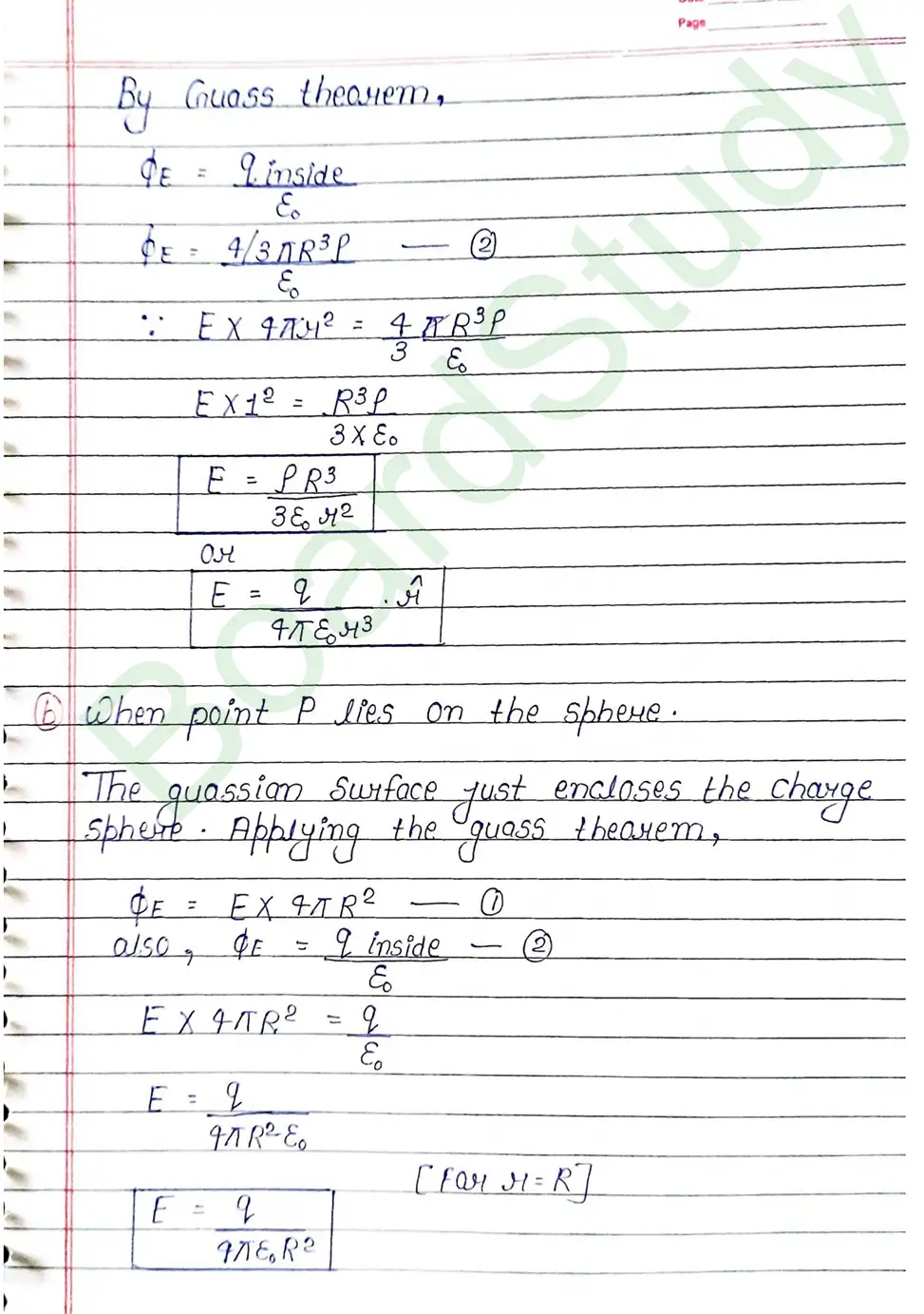

Next Chapter: Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance
Other Subjects:
Class 12 Biology Notes
Class 12 Chemistry Notes
Students who are studying physics in class 12 should definitely use this note and you can access this notes anytime on our website for free of cost. If you found notes helpful, you can also help your friends by sharing with them
Electric Charges and Fields Notes PDF
We have also shared the PDF of Electric Charges and Fields Notes so students don’t feel any difficulty in reading the notes. You can ask your doubts in the comment section. We will be happy to help you.
Key Points: Electric Charges and Fields Notes PDF
Electric charge: Electric change is a fundamental property of elementary particles that causes them to exert electric forces on each other. It is scalar quantity. It is denoted by Q or q. Its magnitude is equal to product of current and time.
Types of charge :
- Positive charge – If a body looses electron then charge amperes at the body is called positive charge! So, positive change = loss of electron = decrease in electron = Small decrease in mass.
- Negative charge – If a body gains electron, then charge of the body is called negative charge. So, Negative charge = Gain of electron = Increase of electron = Small increase in mass.
Conductor: Conductors are materials that allow electric charge to flow easily through them. They have a large number of free electrons, which facilitate the easy movement of charge, making them good conductors of electricity. eg : Metals, human and animal bodies etc
Insulator : Insulators are materials that resist the flow of electric change because they lack free electrons. As a result, they offer very high electrical resistance and do not conduct electricity. eg: Non metals like glass, diamond, plastic.
Basic properties of electric charge
- Additivity
- Quantisation
- Conservation
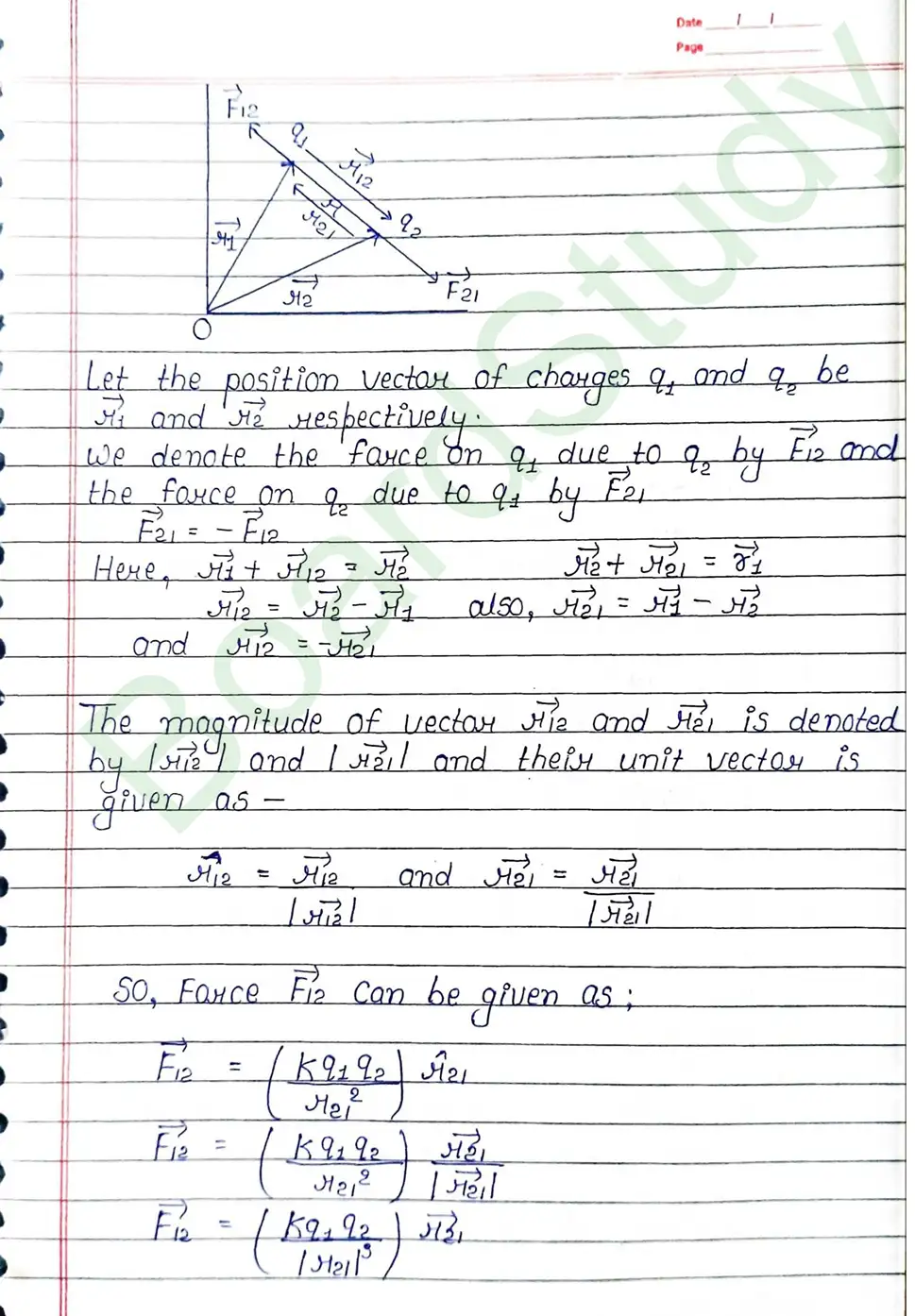
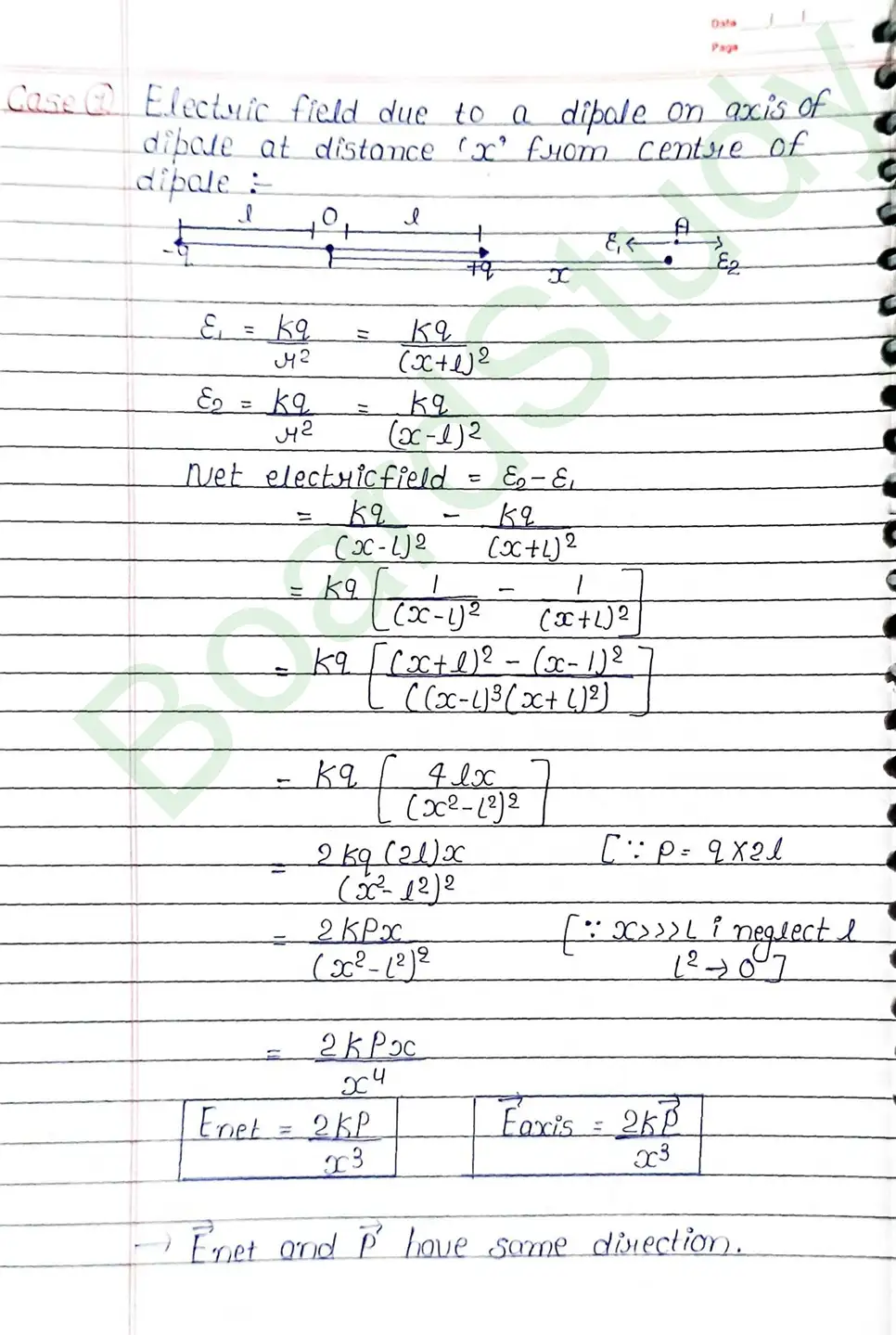
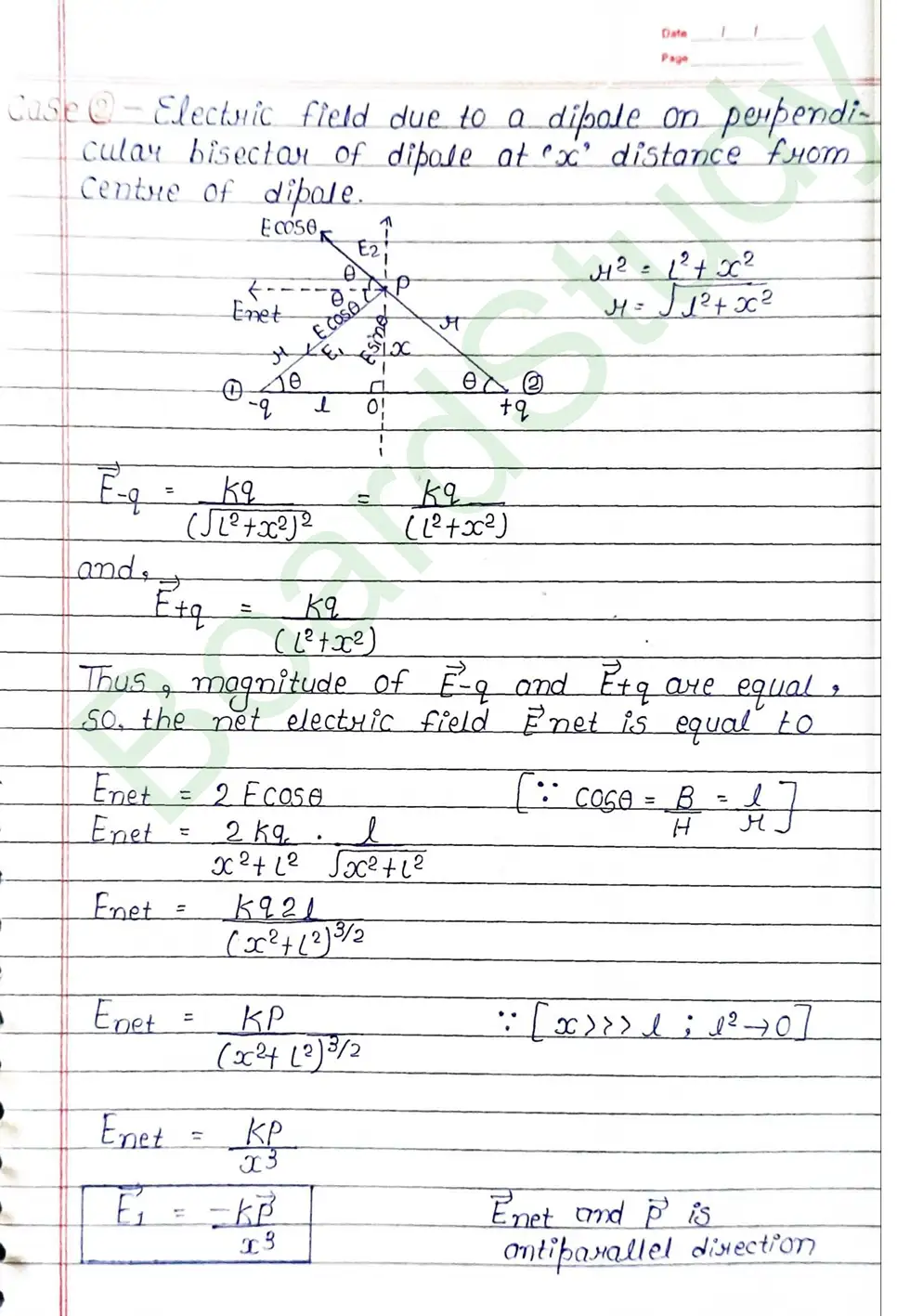
Coulomb’s Law : The electrostatic force acting between two charges is directly proportional to product of charge and inversaly proportional to square of distance between them.
Limitation of coulomb’s law :
- The electric charge must be at rest.
- The electric charge must be point charges ie; the extension of charges must be much smaller than separation between the charges.
- The separation between charge must be greater than nuclear size () because strong nuclear force dominates the electrostatic force.
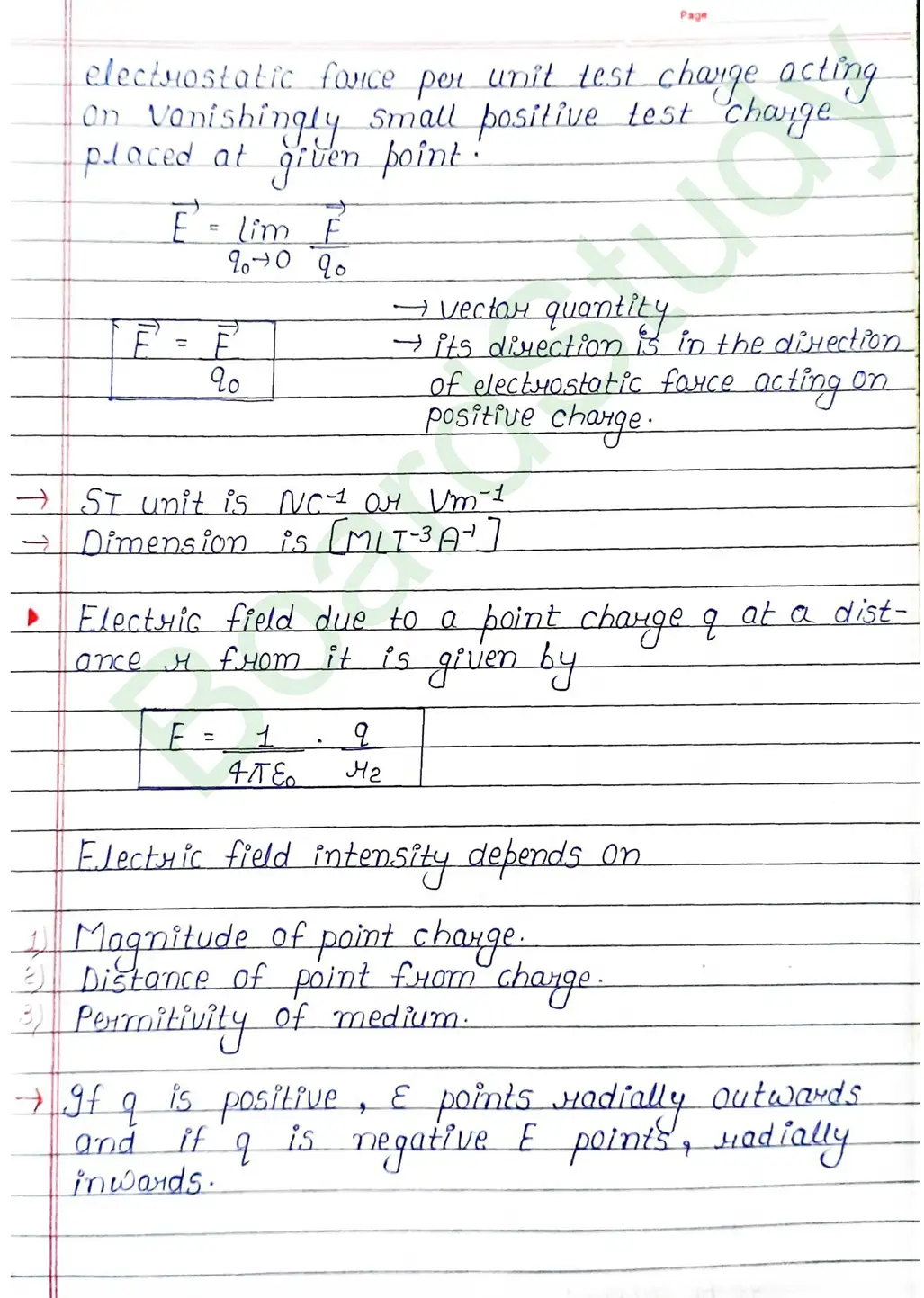
Electric field : The region or space around a charge in which another charge experience electrostatic force of attraction or repulsion is known as electric field. 161The extension of electric field of a charge is upto infinity (∞).
Properties of Electric field lines of force
- Lines of force are continuous curves without any breaks.
- No two lines of force can cross each other.
- They start at positive charges and ends at negative charge – they cannot form closed loops.
- The relative closeness of the lines of force indicates the strength of electric field at different points.
- They are always normal to the surface of the conductor.
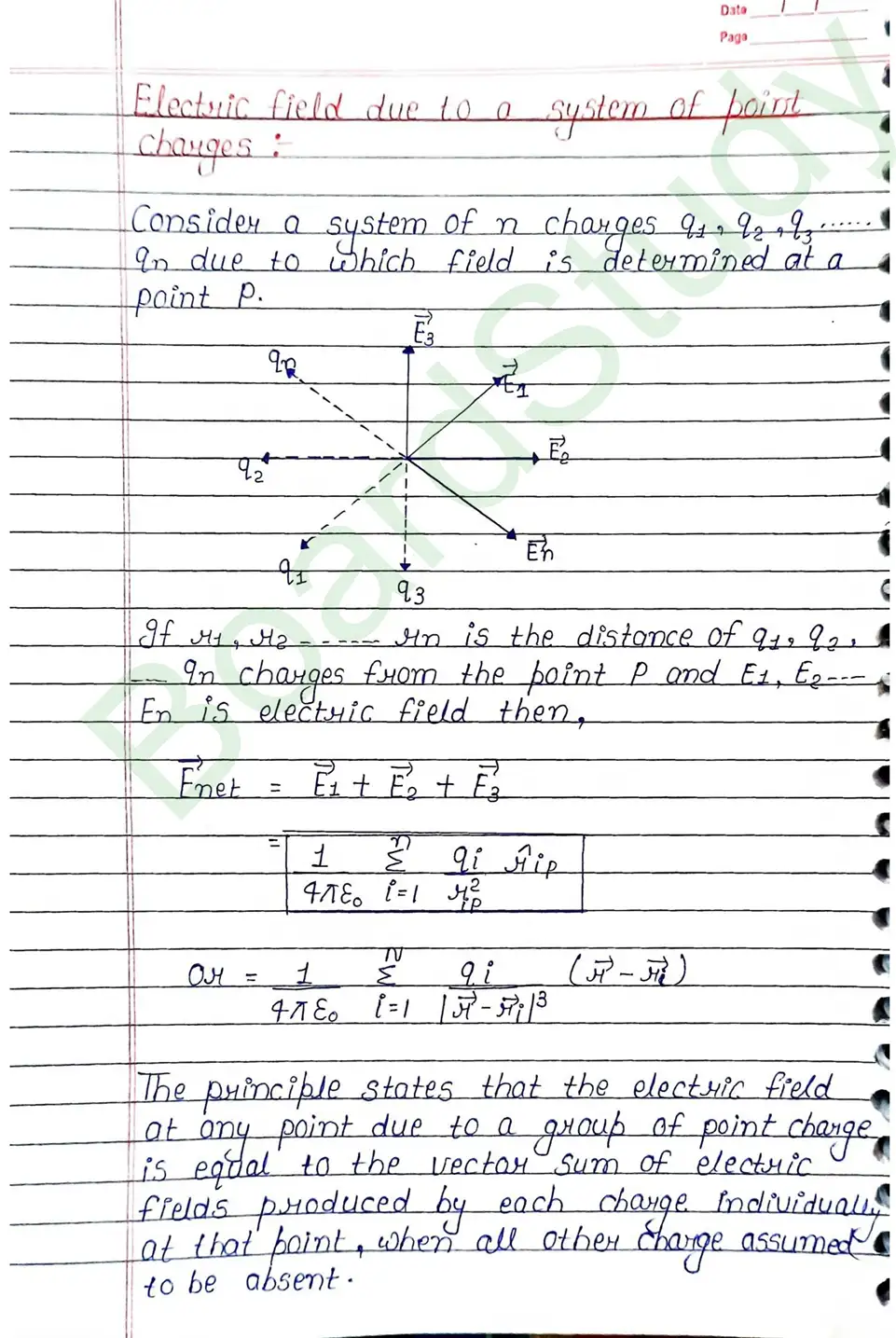
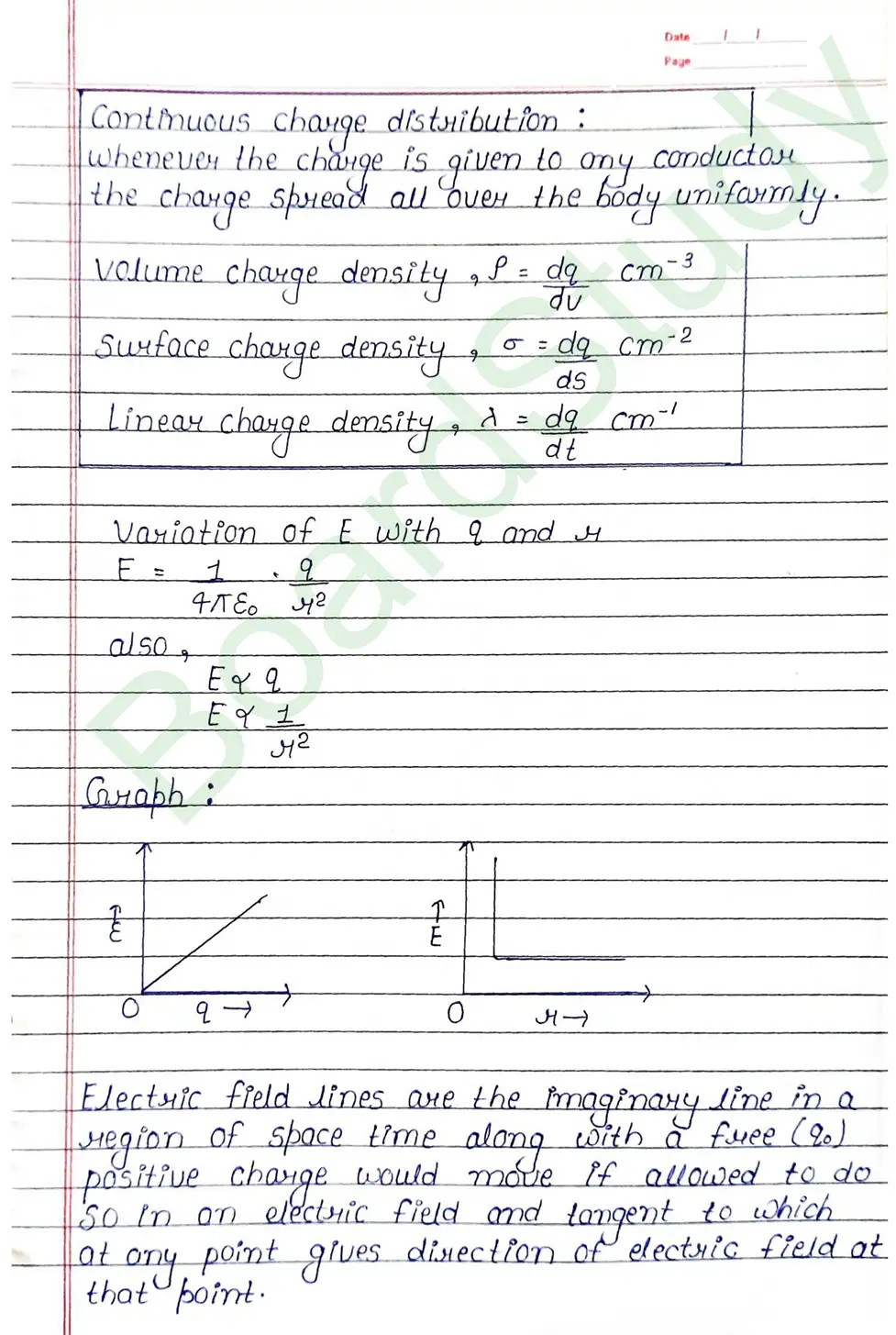
Electric Flux: The electric flux through a given area held inside an electric field is the measure of total number of electric lines of force passing normally through that area.
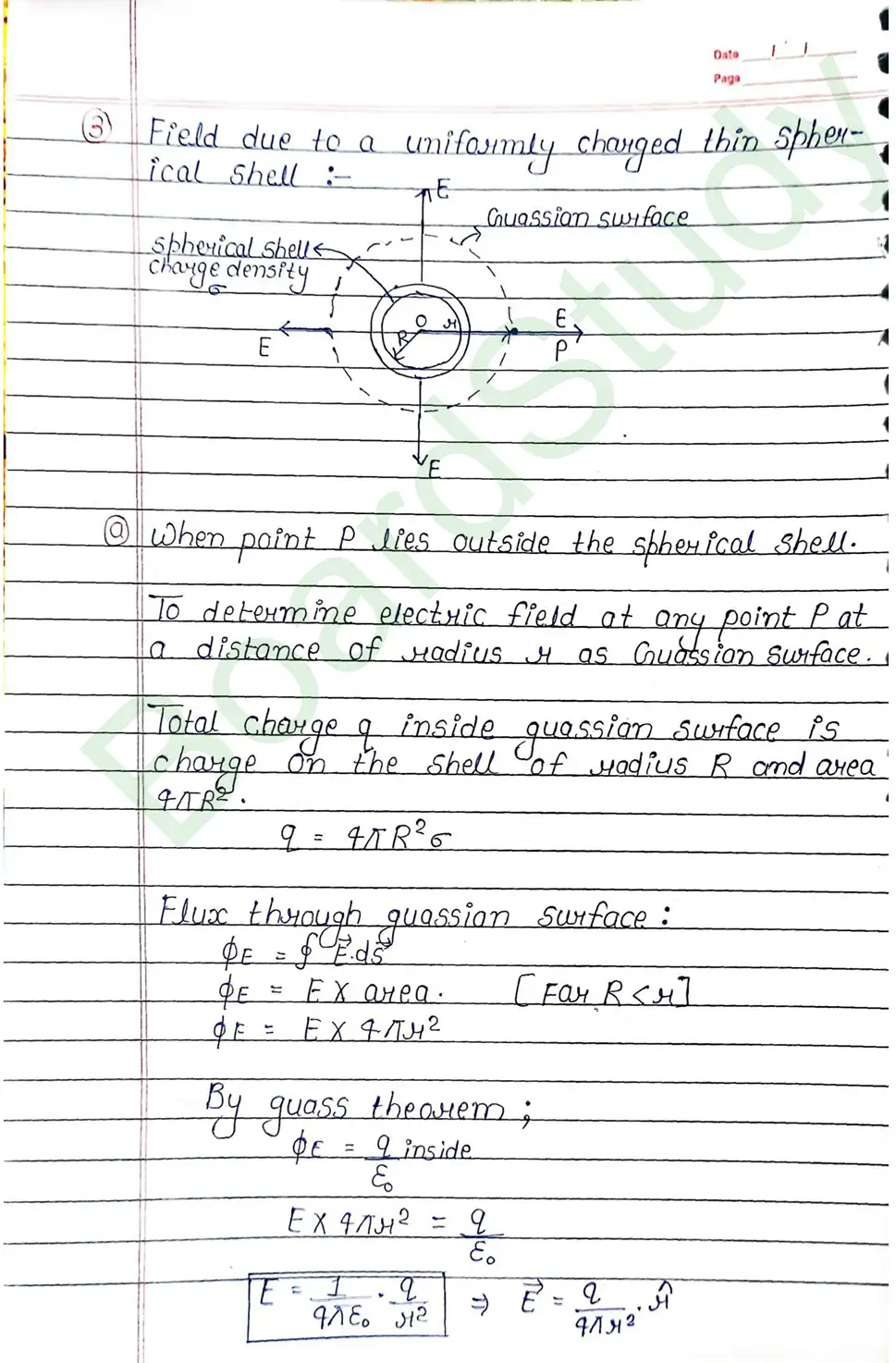
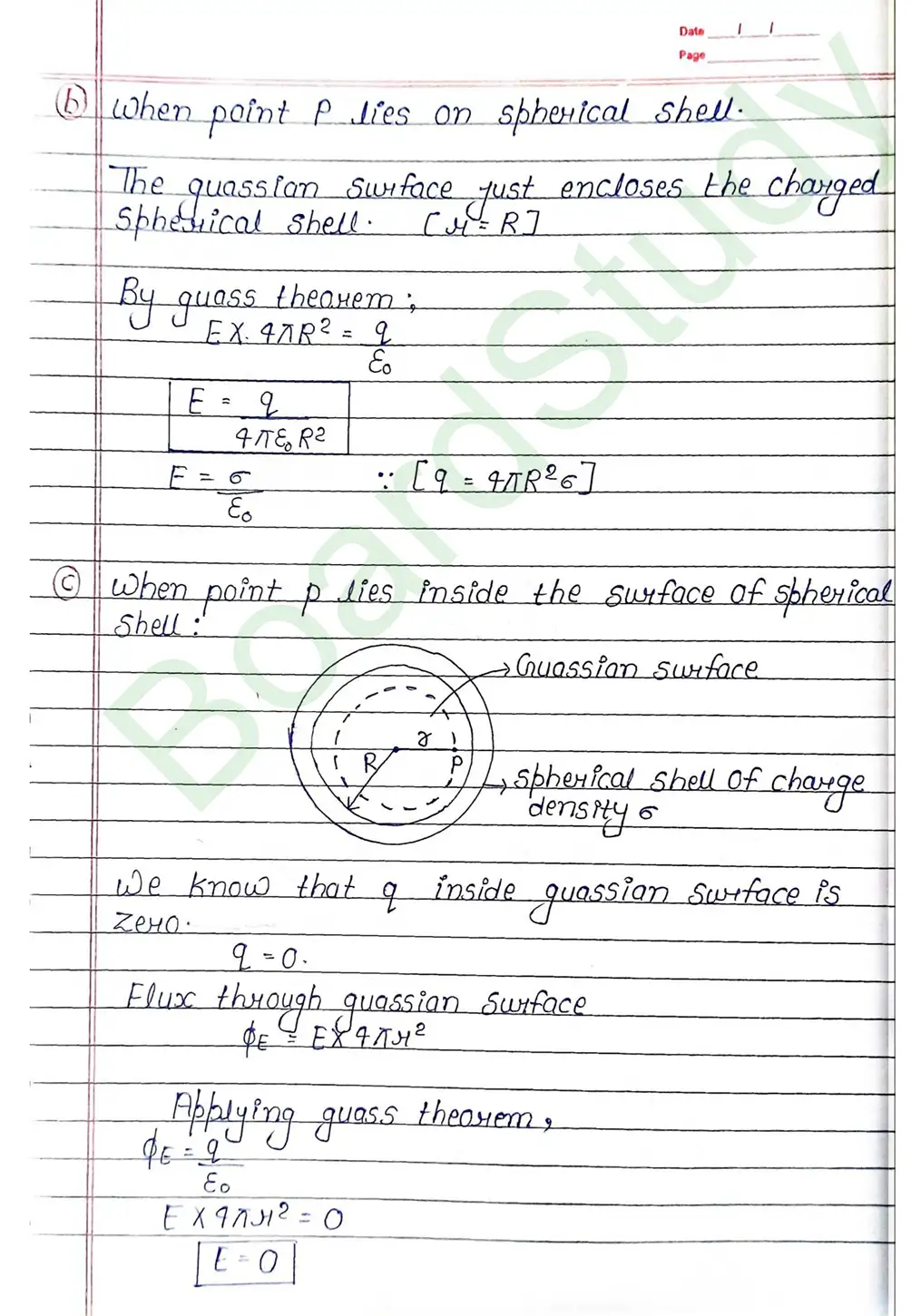
Gauss’s Theorem : It gives a relationship between total flux passing through any closed surface and net charge enclosed by the closed surface. Gauss theorem states that the total flux through a closed surface is times the net charge enclosed by the closed surface.
Application of Gauss theorem
- Field due to an infinitely long straight uniformly
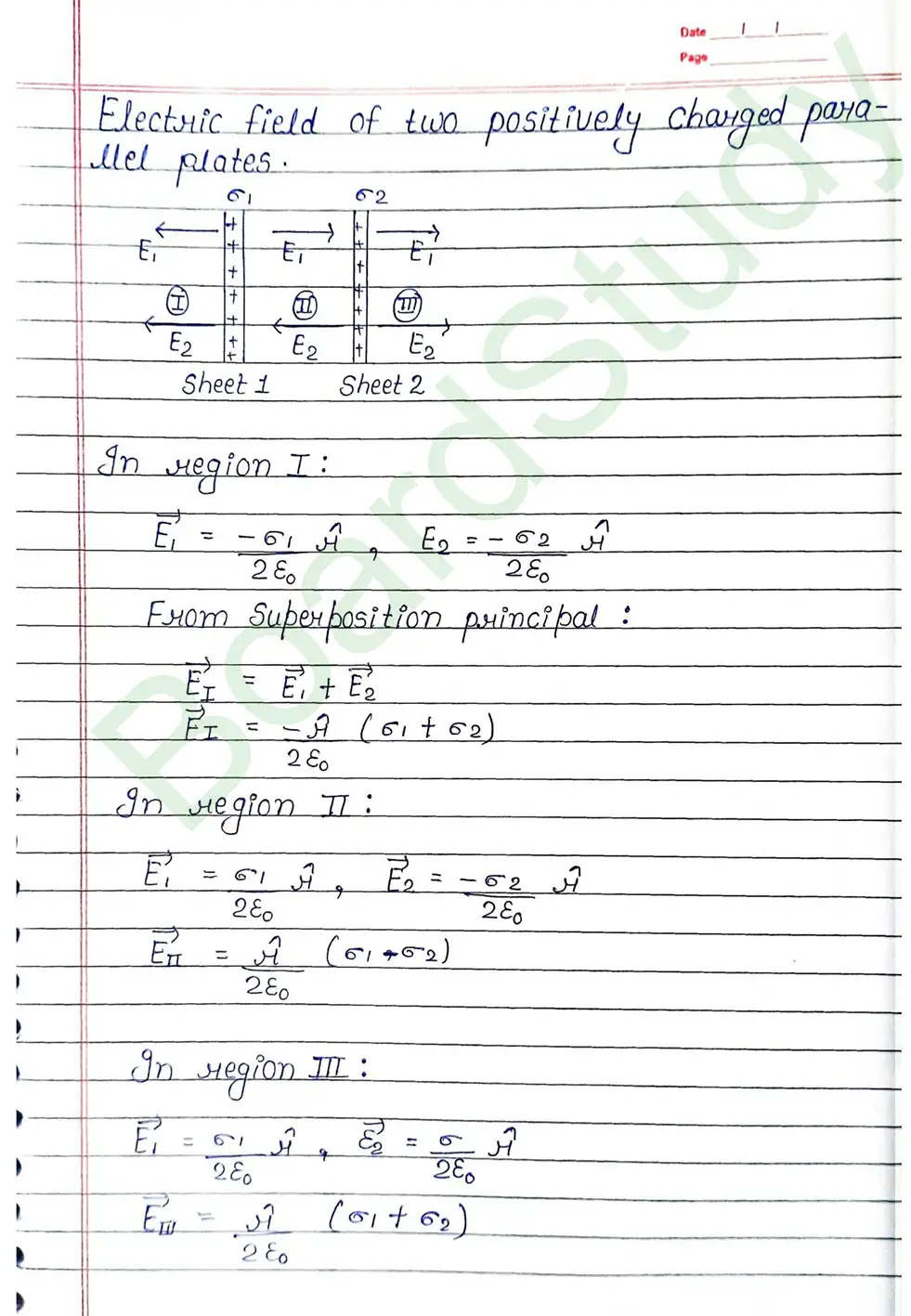
- Electric field due to a uniformly charged infinite plane sheet
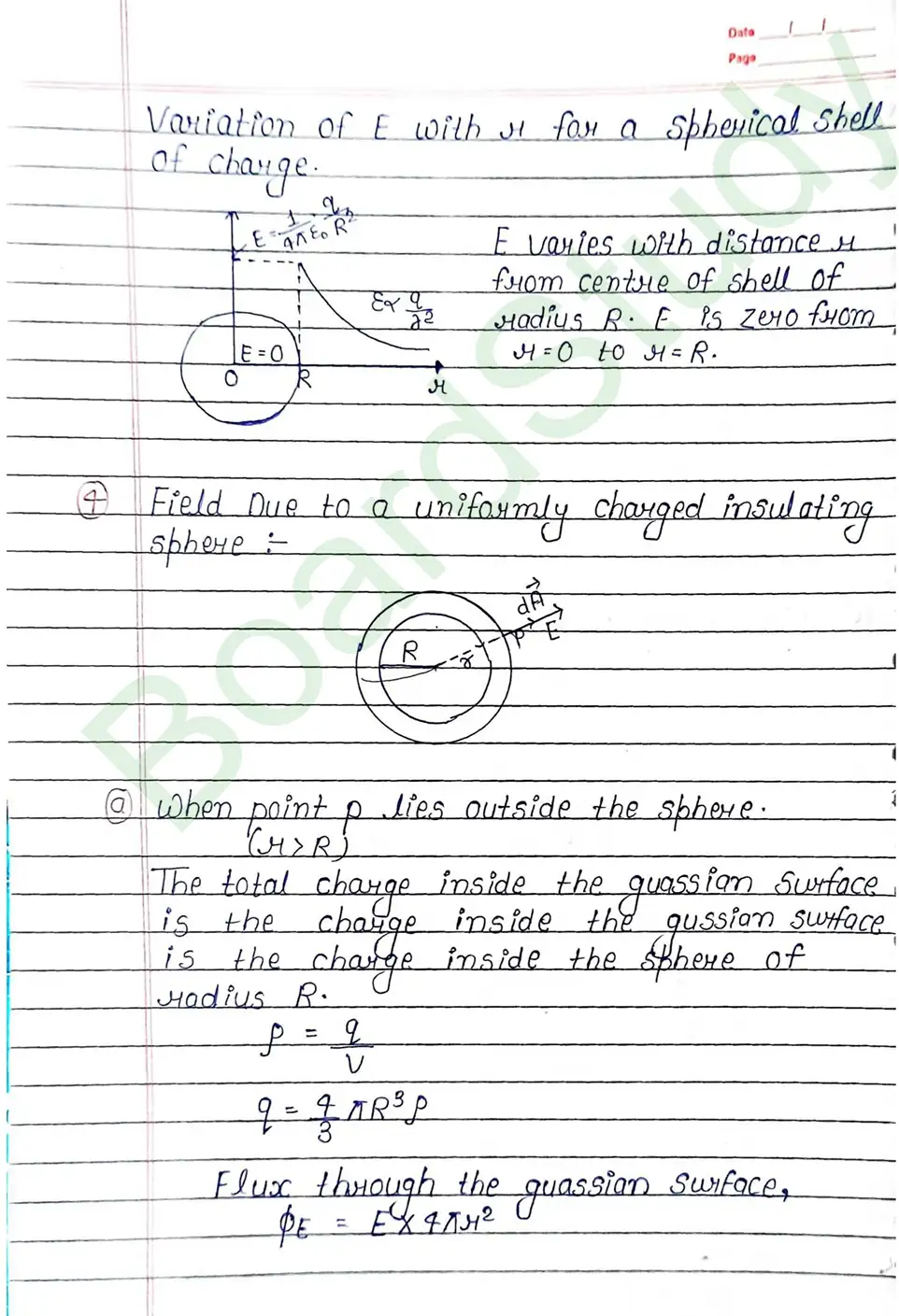
- Field due to a uniformly charged thin spherical shell
- Field Due to a uniformly charged insulating sphere
Features of Notes
- Students can use Electric Charges and Fields notes for last minute revision.
- In the last few days of the exam, students feel very stressed due to the pressure of the exam. Notes will be very helpful for managing the stress in the last days of the exam.
- All notes are totally free of cost and students can access notes anytime on our for totally free of cost..
- Electric Charges and Fields Notes PDF are created very carefully so you can rely on this notes.
Summary
| Chapter | Electric Charges and Fields |
| Chapter Number | 1 |
| Subject | Physics |
| Class | 12 |
| Medium | English |
FAQ
Are these notes sufficient for board exam?
Electric Charges and Fields handwritten notes are created by topper’s and expert teacher keeping board exam in mind so you can score maximum in board exam.
Are Electric Charges and Fields Handwritten notes according to NCERT latest syllabus?
Yes notes are created according to the NCERT latest syllabus.
How can i download Electric Charges and Fields Notes PDF?
For downloading Electric Charges and Fields Notes PDF click on Download PDF button.
What is Semi-conductor ?
It behaves like an insulator at low temperatures, but as the temperature increases, it starts conducting electricity and act like a conductor. eg : silicon, Germanium etc.
What is Test charge ?
A test charge is a charge with a so small magnitude that placing it at a point has negligible affect on field around. It does not create any field of its own

very helpful thank youu
thanks it helps me a lot 🙂