Here we have shared NCERT Class 12 Biology Human Reproduction Handwritten Notes. The Human Reproduction notes is a best resources for students who are preparing for their board exam because it compile the entire lesson into short and includes every important topics.
With the help of Human Reproduction notes students can understand the chapter in a better way. Notes are prepared by very experience teachers in an organised way so students can rely on this notes for their exam preparation.
NCERT Class 12 Biology Human Reproduction Handwritten Notes


























Next Chapter: Reproductive Health
Previous Chapter: Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
Other Subjects:
Class 12 Physics Notes
Class 12 Chemistry Notes
Students can access this notes anytime on our website for free of cost. If you found notes helpful, you can also help your friends by sharing with them.
Key Points: Human Reproduction Notes PDF
Reproductive Events
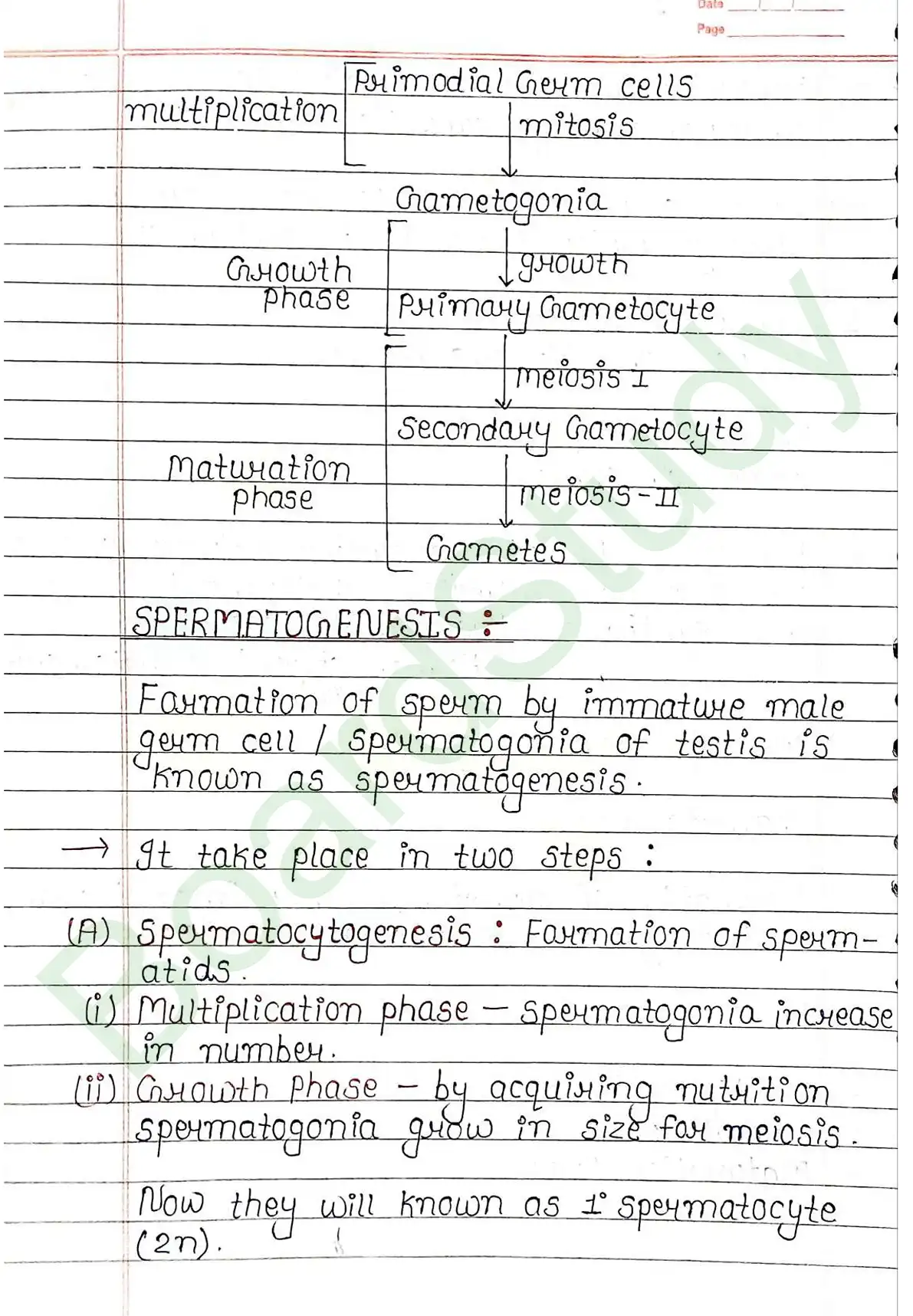
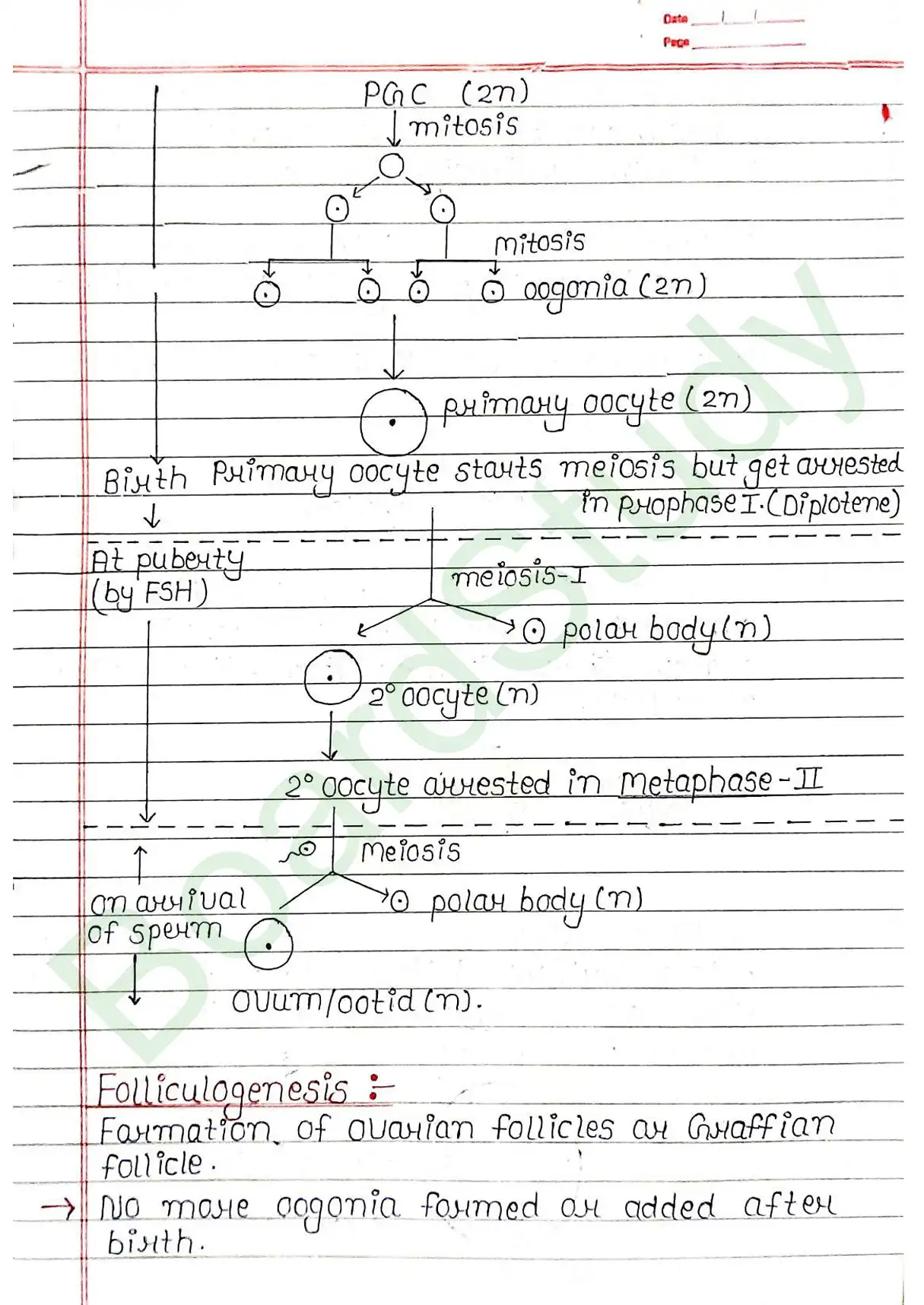
- Gametogenesis: Formation of gametes i.e., Sperm & ovum.
- Insemination: Transfer of male gamete into female genital tract.
- Fertilisation: Fusion of sperm and ovum.
- Blastulation: Formation and development of the blastula or blastocyst.
- Implantation: Attachment of blastocyst to wall of uterus.
- Gestation: Embryonic development in womb.
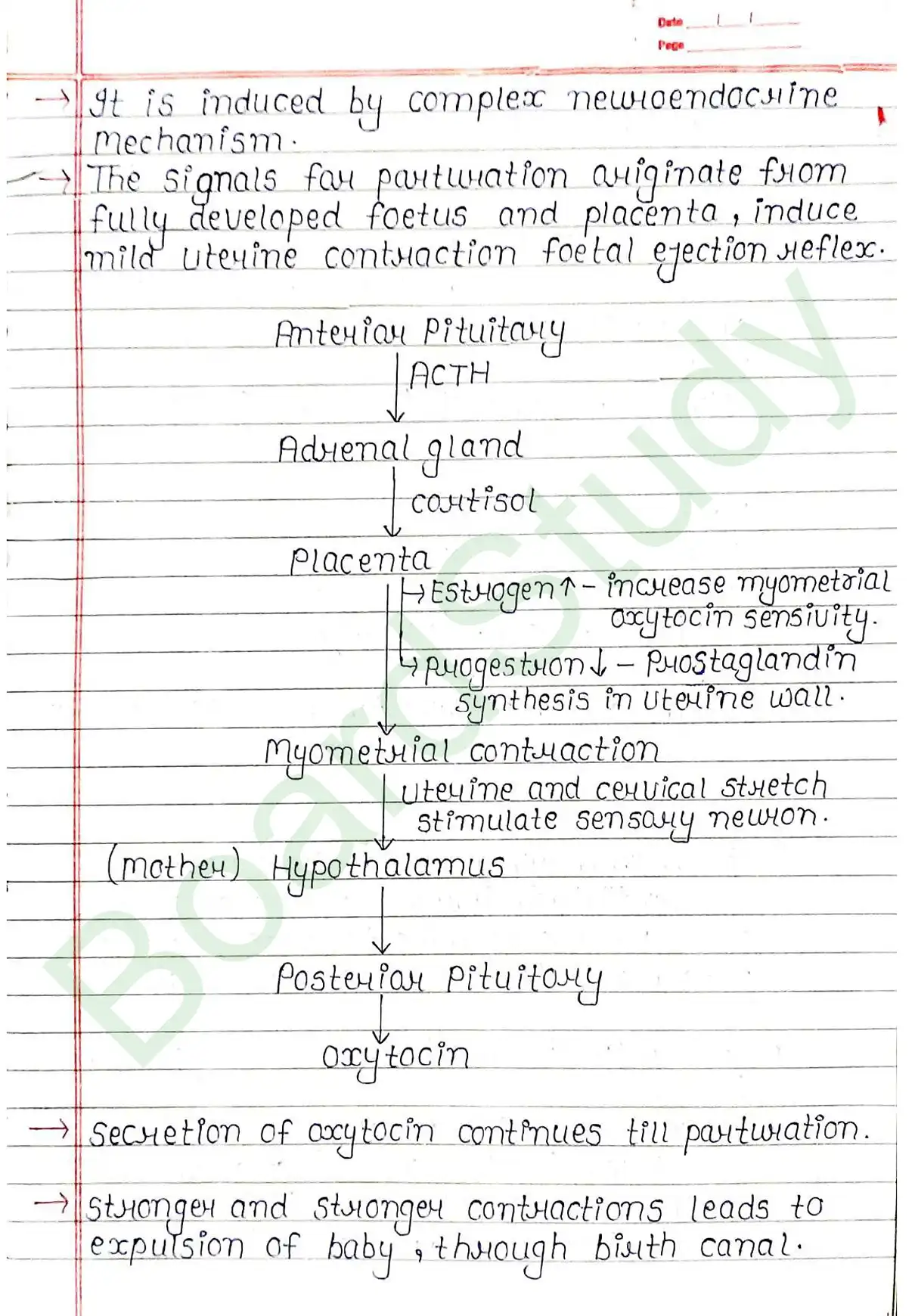
- Parturition: Delivery of baby.
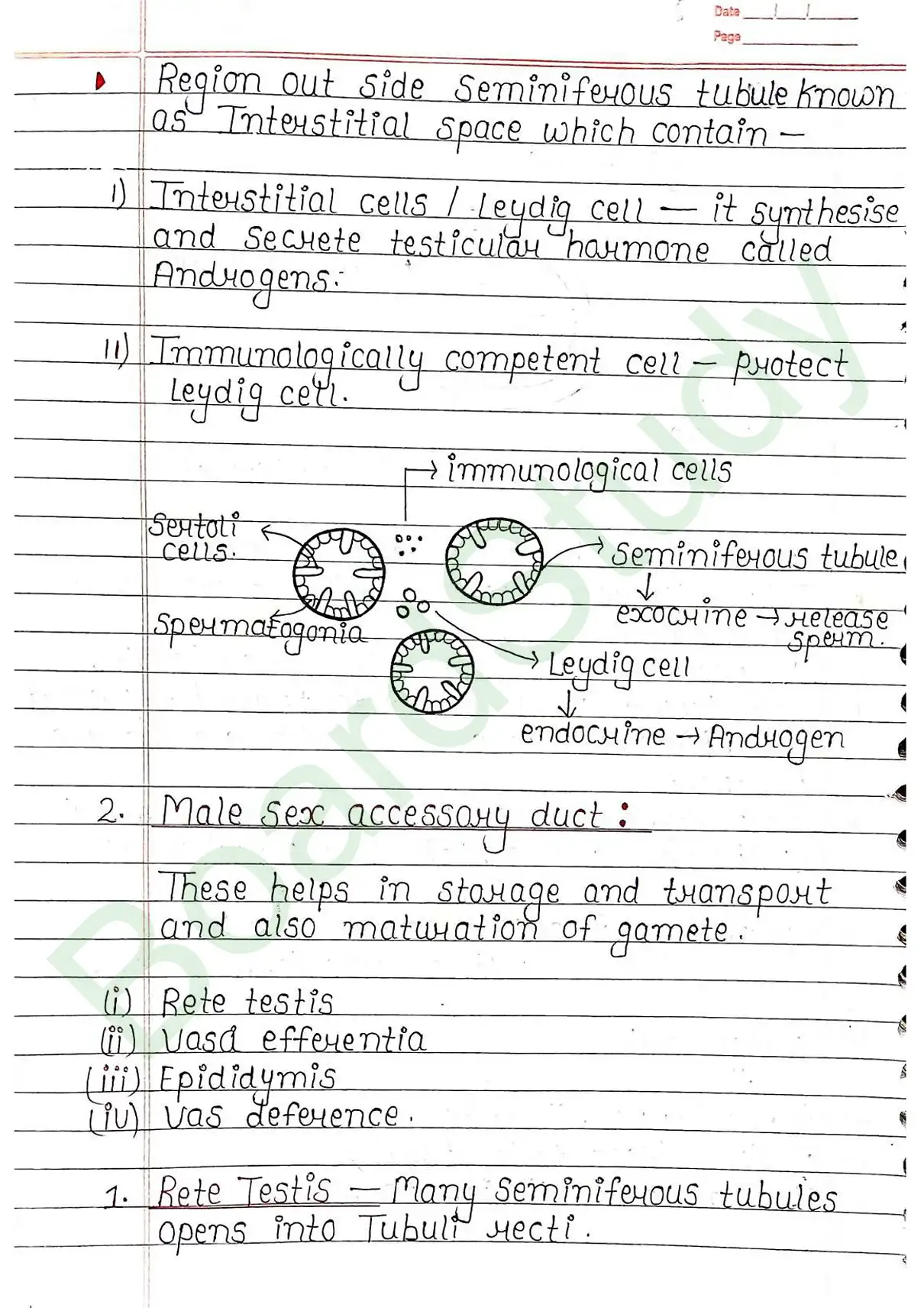
Testis
- Primary sex organ (both endocrine and exocrine).
- Oval shaped.
- Length 4 to 5 cm – width – 2 to 3 cm.
- Testes are situated outside the abdominal cavity within a pouch called scrotum.
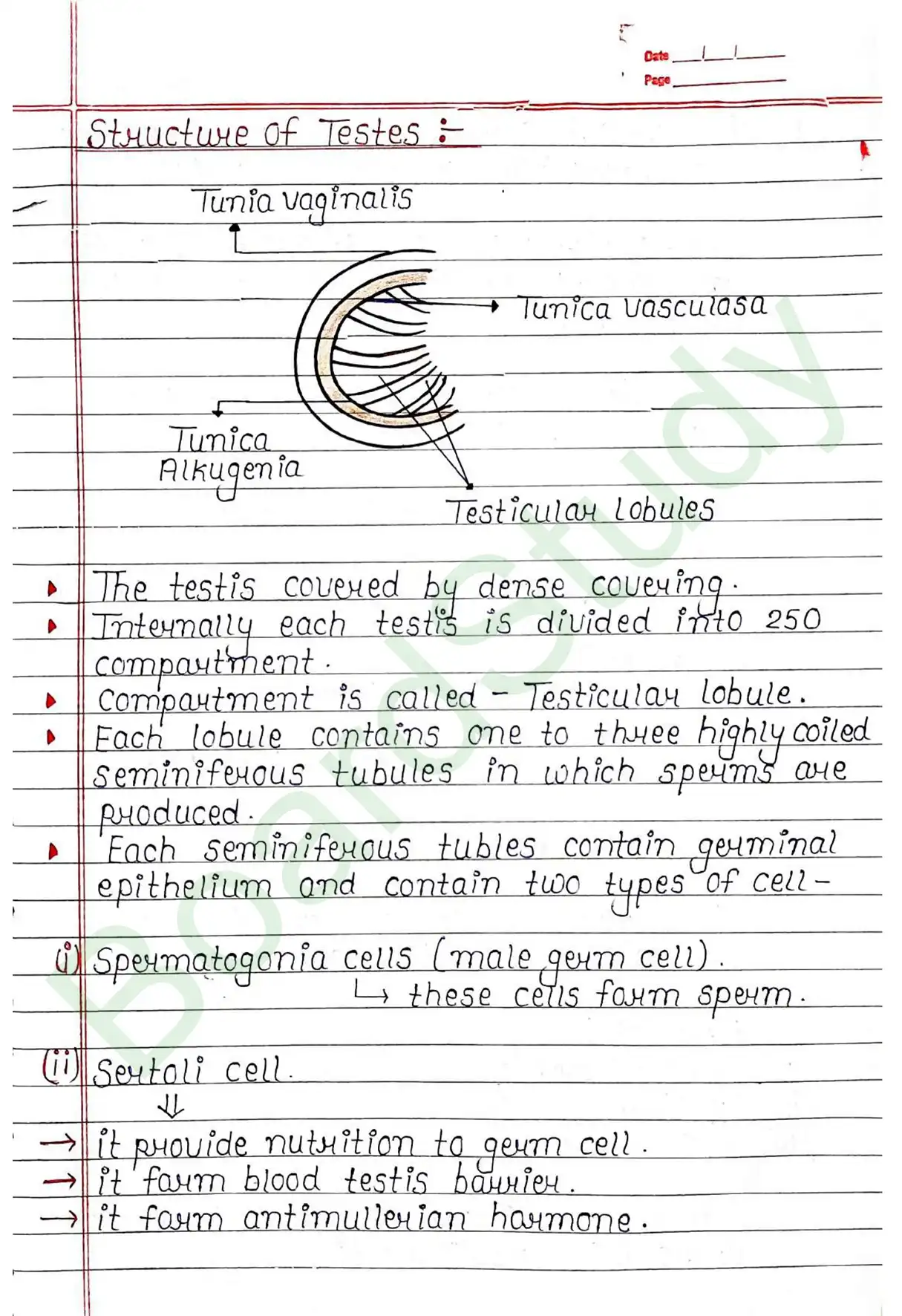
Structure of Testes
- The testis covered by dense covering:
- Internally each testis is divided into 250 compartment.
- Compartment is called – Testicular Lobule.
- Each lobule contains one to three highly coiled Seminiferous tubules in which sperms are produced.
Penis: Male copulatory organ.
- Made up of special type of tissue which help in erection for insemination.
- The end of penis is called ‘Glans Penis’ and covered by skin fold called ‘Foreskin’.
Scrotum: Sac like structure in which testis are placed.
- Temperature regulation by:
- Dartos Muscle
- Cremaster muscle
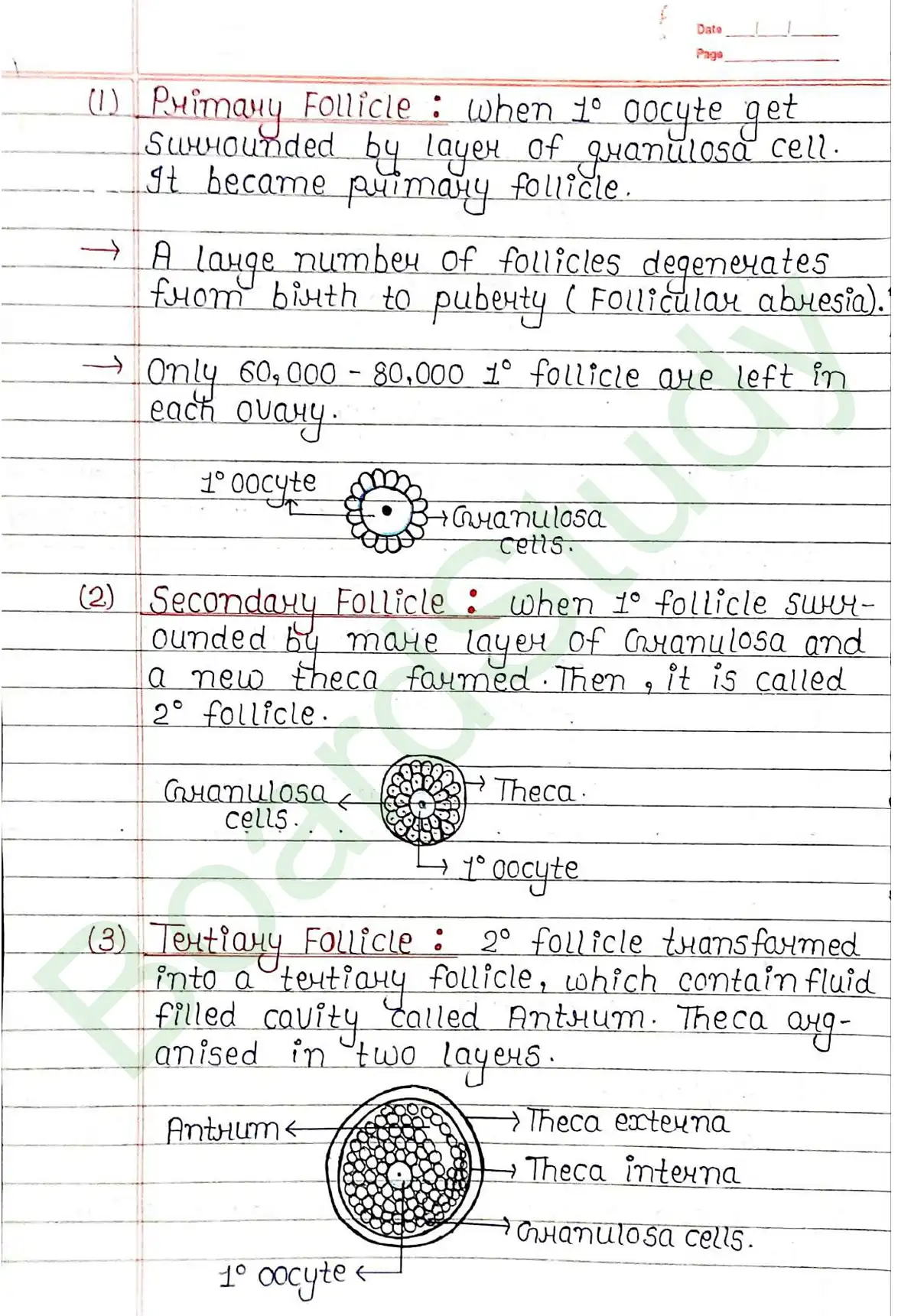
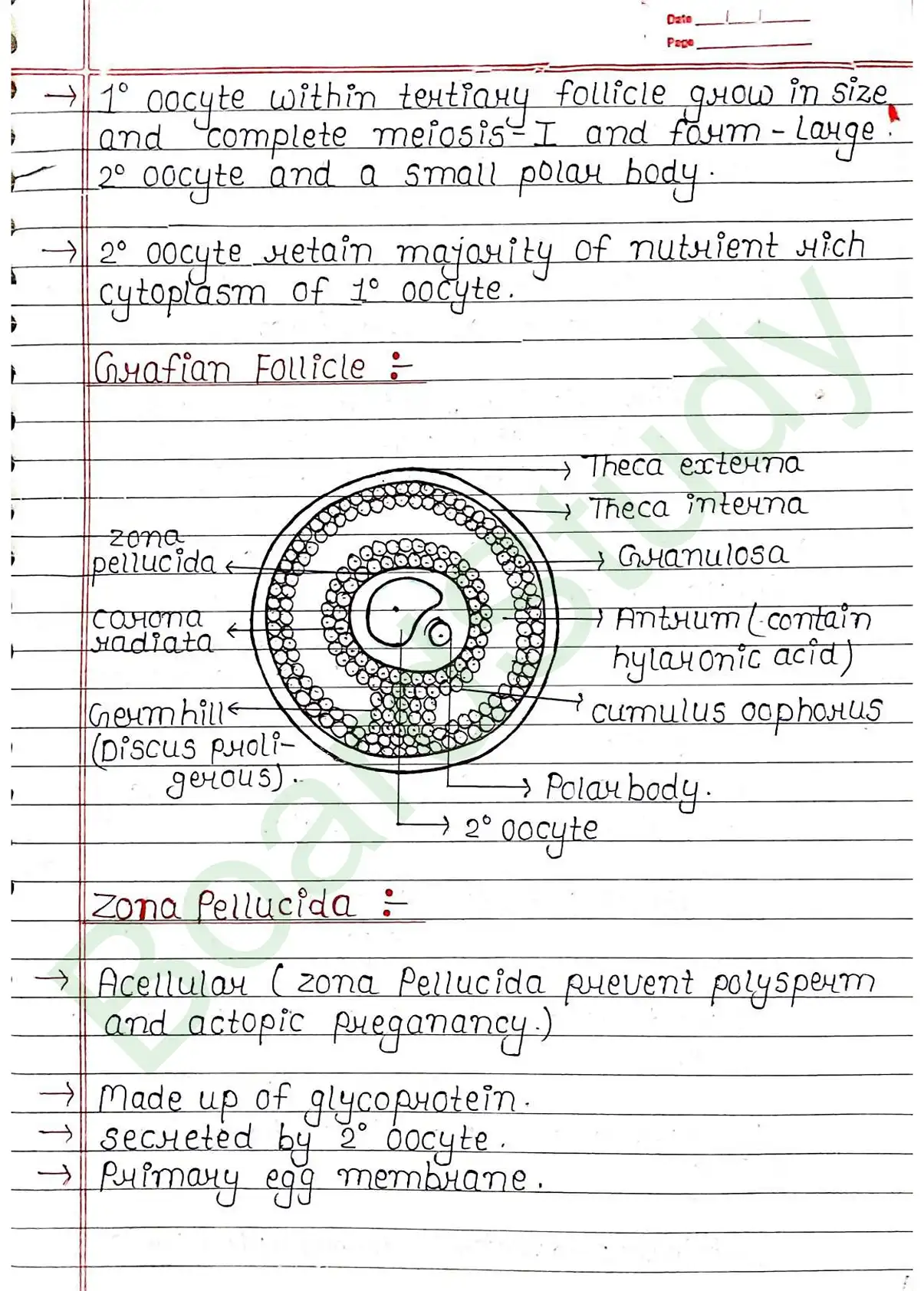
Ovary
- Ovaries are primary female sex organ.
- Produce female gamete (ovum).
- Produce several steroid hormones (Estrogen, Progesterone).
- Locate at lower abdomen.
- Each ovary is about 2-4 cm length.
- It is connected to pelvic wall and uterus by ligaments.
- Each ovary is covered by a thin epithelium, which enclosed the ovarian stroma.
- Stroma is divided into two zones: i) Peripheral cortex, ii) Inner Medulla.
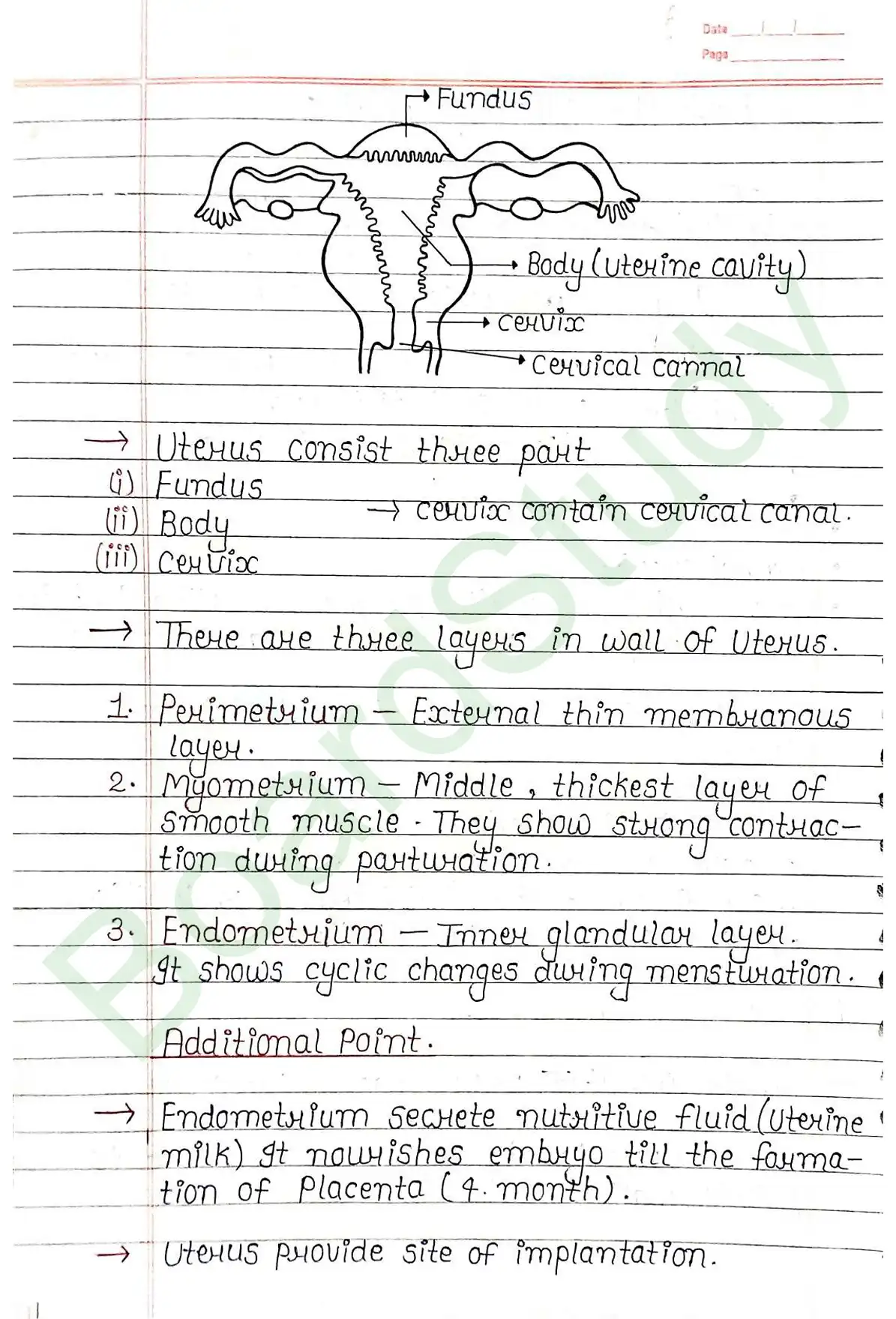
Uterus (womb):
- Single inverted pear-shaped structure.
- It is supported by ligaments attached to pelvic wall.
- Three parts: (i)Fundus , (ii) Body (uterine cavity) , (iii) Cervix.
Vagina : Female copulatory organ.
- 10 cm long tubular structure.
- Fibre muscular canal lined with mucous.
- It opens externally in vestibule by vaginal orifice.
- Function: Receive semen by Penis during sexual intercourse.
- Provide passage for menstrual flow.
- Passage for Child birth.
- Vaginal canal + cervical canal = Birth canal
- Mucosa of vaginal wall store glycogen. Lactobacillus acidophilus decomposes and produce organic acid. It protects from infection and PH.
Bartholin Gland : Also known as greater vestibular gland one on both side of vaginal orifice. Secretes lubricating fluid during sexual intercourse.
Paraurethral Gland : Also known as Lesser vestibular gland or Glands of Skene it Secretes mucous during intercourse.
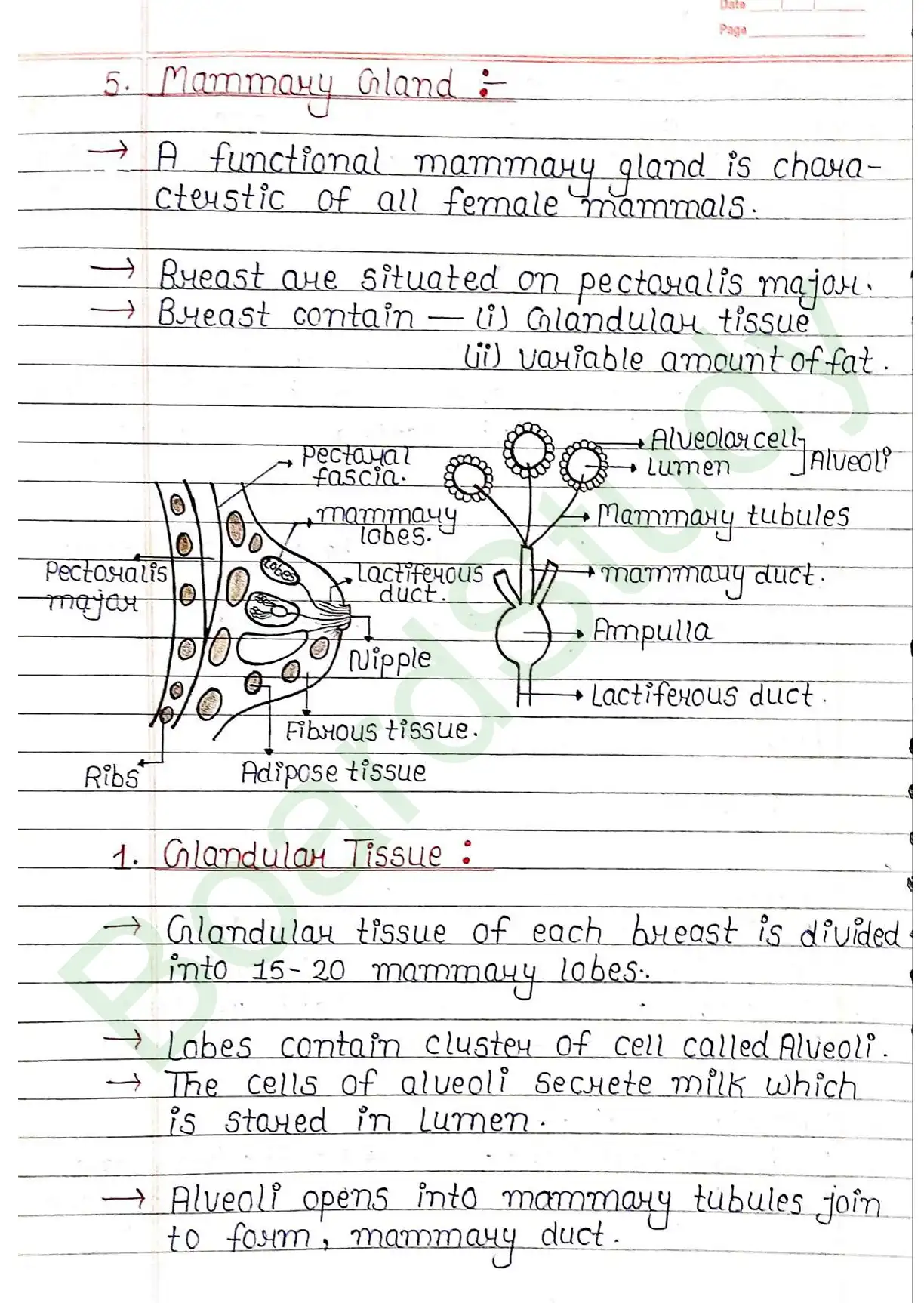
Glandular Tissue:
- Glandular tissue of each breast divided into 15-20 mammary lobes.
- Lobes contain cluster of cell called Alveoli.
- The Cells of alveoli Secrete milk which is stored in Lumen.
- Alveoli opens into mammary tubules join to form, mammary duct.
- Several mammary duct joins to form a wider mammary ampulla.
- Ampulla is connected to Lactiferous duct, through which the milk is sucked out.
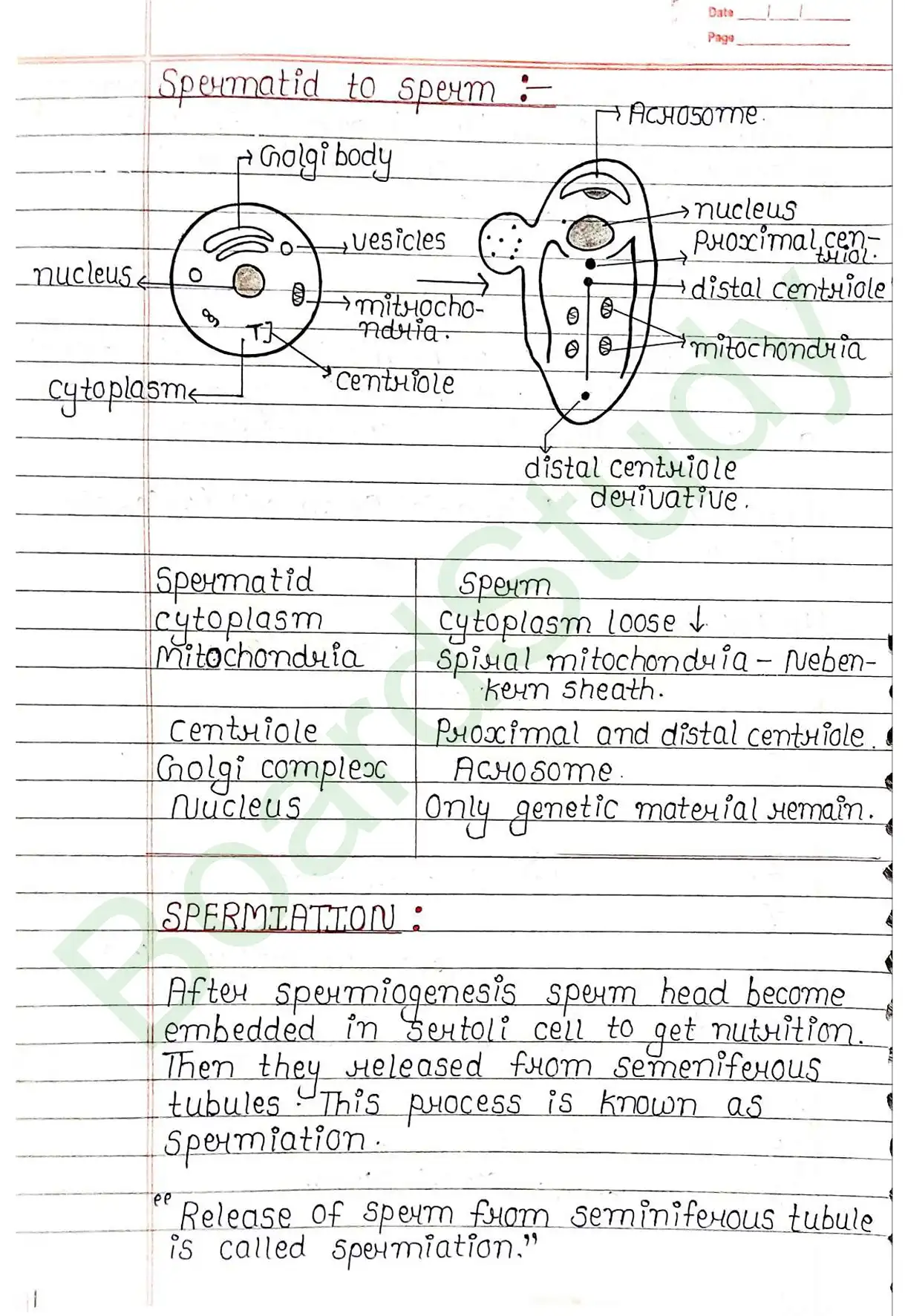
SPERMIATION: After spermiogenesis, sperm head become embedded in sertoli cell to get nutrition. Then they released from seminiferous tubules. This process is known as spermiation.
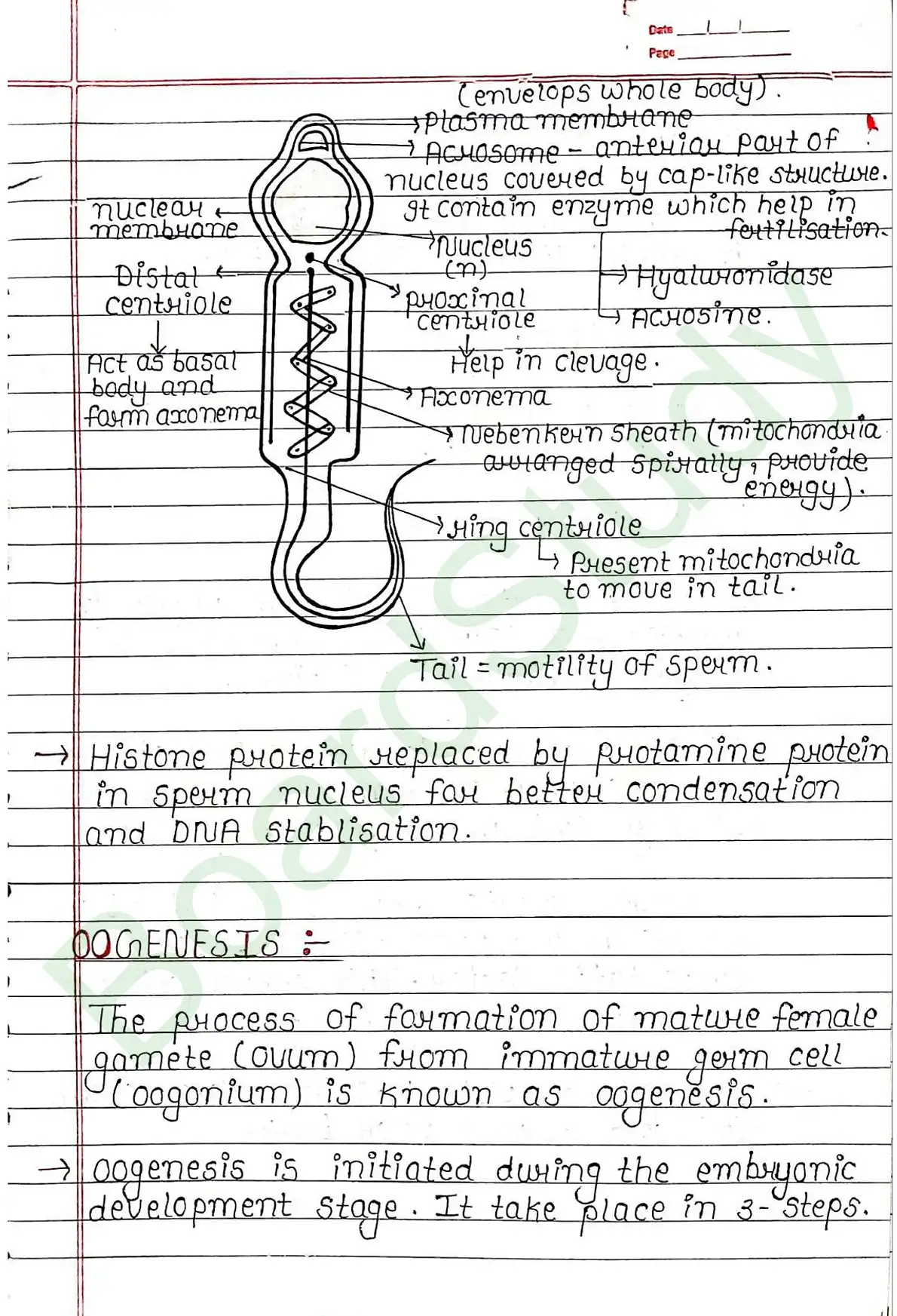
Structure of sperm
- Sperm consist of 4 Parts:
- Head , Neck , Middle Piece , Tail.
Menstrual Cycle
- Monthly reproductive cycle occurs in female primates which involves changes in reproductive tract after Puberty under the influence of pituitary and ovarian hormone is known as Menstrual cycle.
- First Menstruation begins at puberty, called Menarche.
- Last Menstruation cycle around 50 year – Menopause.
- Average interval is 28 days.
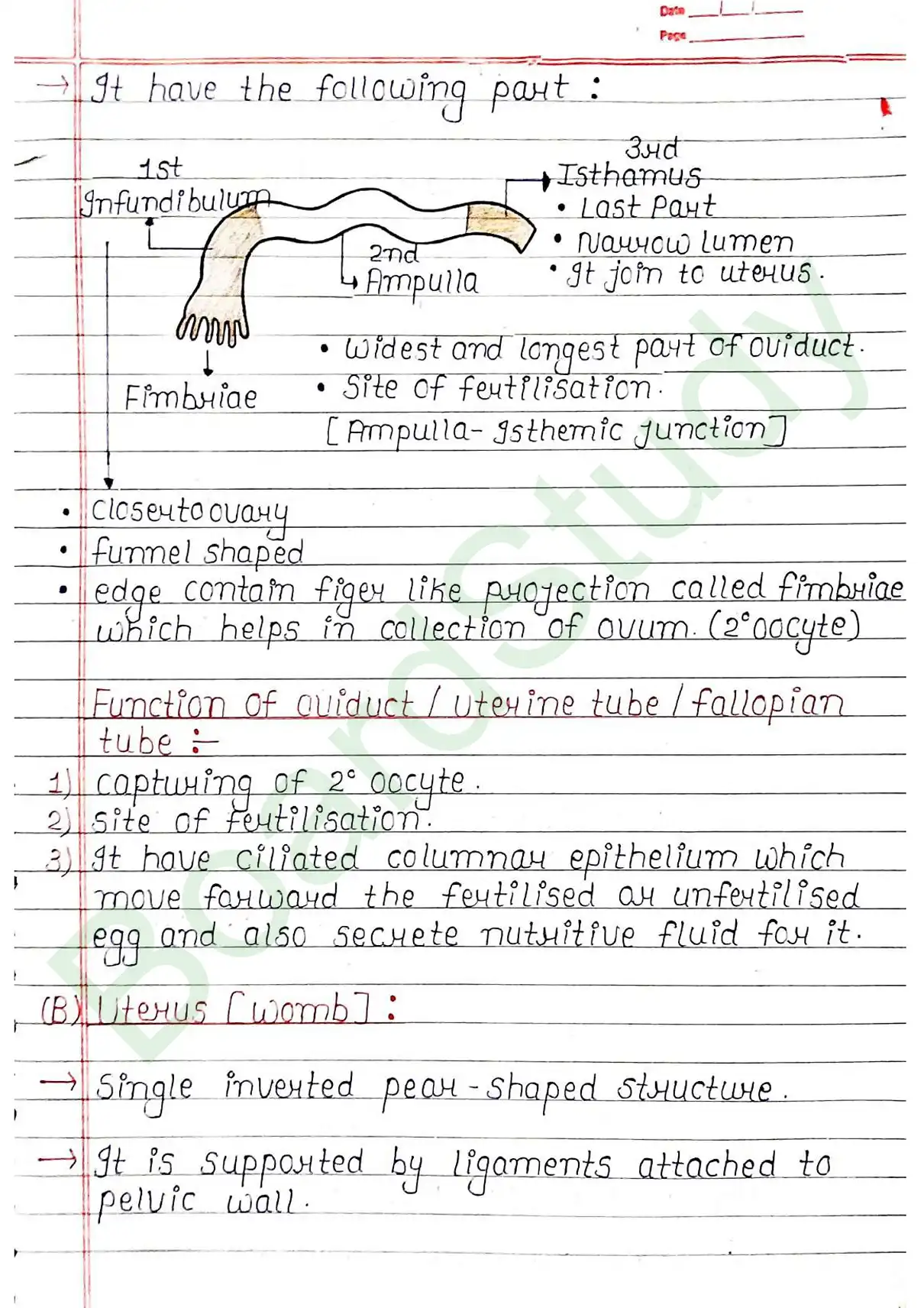
Fertilisation
Fusion of sperm and ovum which results in formation of single celled diploid zygote is termed as Fertilization.
- Fertilization takes place in Ampulla of fallopian tube.
- It Occurs when the ovum and sperm are transported simultaneously to ampullary region.
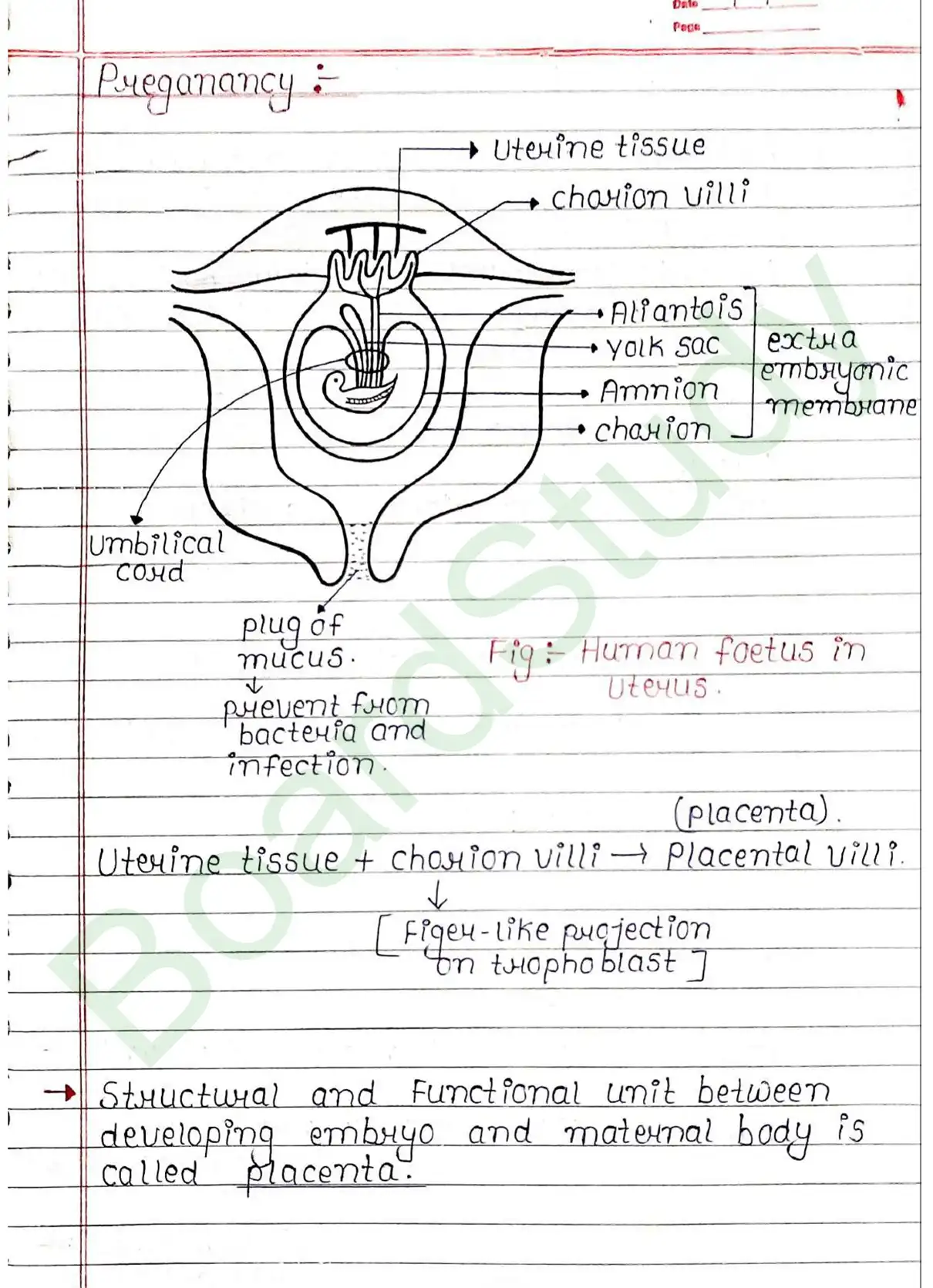
Pregnancy
- Structural and Functional unit between developing embryo and maternal body is called placenta.
Lactation
- Mammary gland of female undergoes differentiation during pregnancy and start producing milk towards the end of pregnancy by process called Lactation.
- This helps the mother in feeding the new born.
- First time milk produced is called colostrum (yellow colour) and if contain IgA antibody and essential nutrients which helps in development of baby.
Benefits of Human Reproduction Notes PDF
- Notes are created by topper’s students and expert teachers so you can rely on our notes for your board exam.
- Human Reproduction handwritten notes are organized in clear and structured way so you can revise whole chapter in very less time.
- By using our notes you can get rid off from making your own notes so you can focus on your study more.
- During exam time students feel very high pressure. Human Reproduction Notes are best for last-minute revision. It covered complex topics in very easy and understandable language very helpful for managing the stress in the last days of exam.
- All notes are totally free of cost and students can access notes anytime on our for totally free of cost.
Summary
| Chapter | Human Reproduction |
| Chapter Number | 2 |
| Subject | Biology |
| Class | 12 |
| Medium | English |
FAQ
What is Fertilisation ?
Fusion of sperm and ovum.
What is Blastulation ?
Blastulation: Formation and development of the blastula or blastocyst.
Are these notes sufficient for board exam?
Yes, notes are created by topper’s and expert teacher keeping board exam in mind so you can score maximum in board exam.
Are Human Reproduction Handwritten notes according to NCERT latest syllabus?
yes notes are created according to the NCERT latest syllabus.
How can i download Human Reproduction Notes PDF?
For downloading Human Reproduction Notes PDF click on Download PDF button.
the notes was useful for my boards and neet exam tooo
I want to pdf note