Some students find Math a very hard subject so here on BoardStudy, we have shared class 12 Math Chapter 11 Three-Dimensional Geometry notes. We have covered every topic in a simple and easy way so anyone can understand the chapter and perform well in exam.
Notes are very clean and colourful written by BoardStudy subject matter experts. Every important concept, formula, diagram and derivation is shared in Three-Dimensional Geometry notes that will help you solve the problem. These notes are designed to make complex topics easier which will definitely boost the students’ confidence during the exam.
Three-Dimensional Geometry Notes PDF



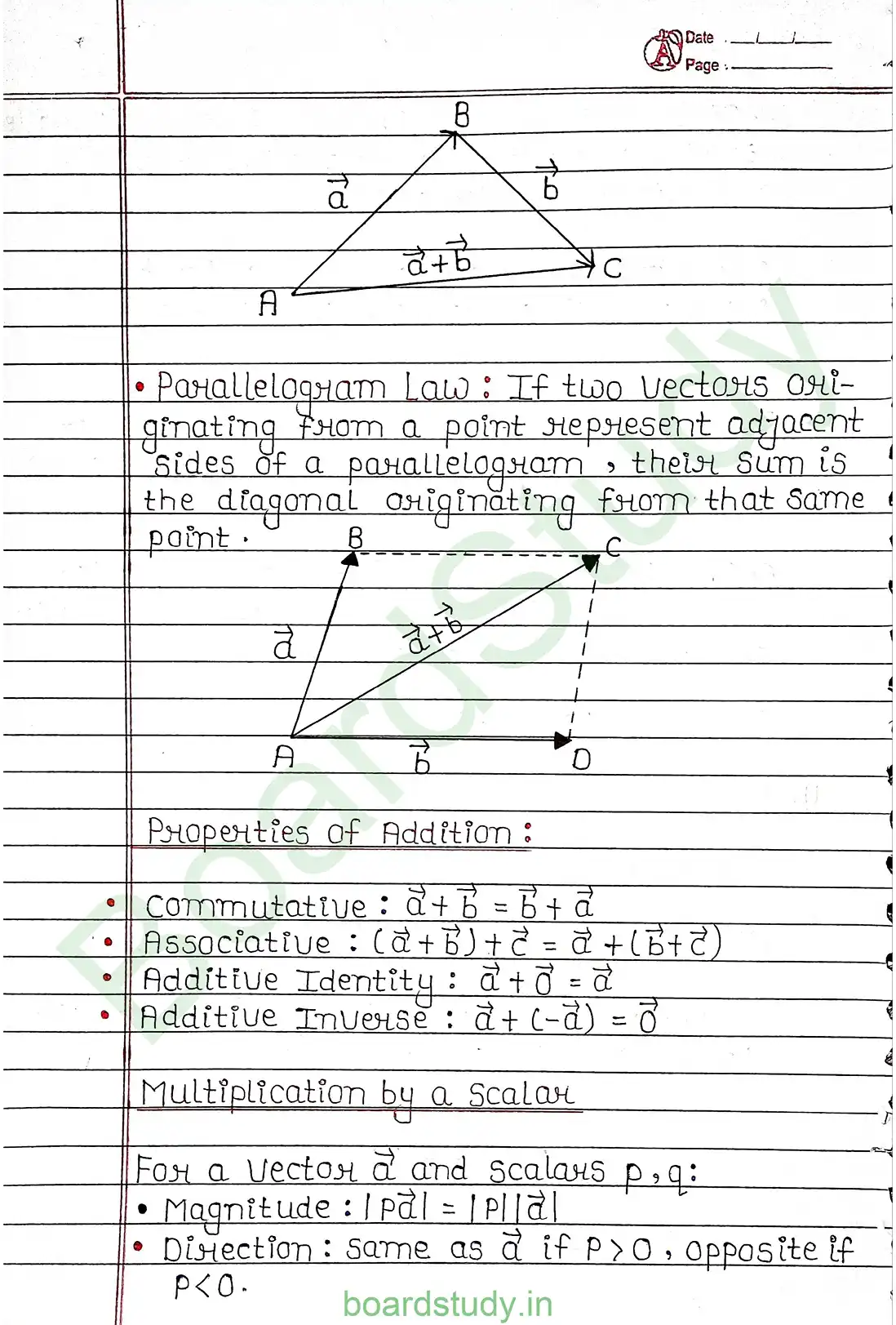

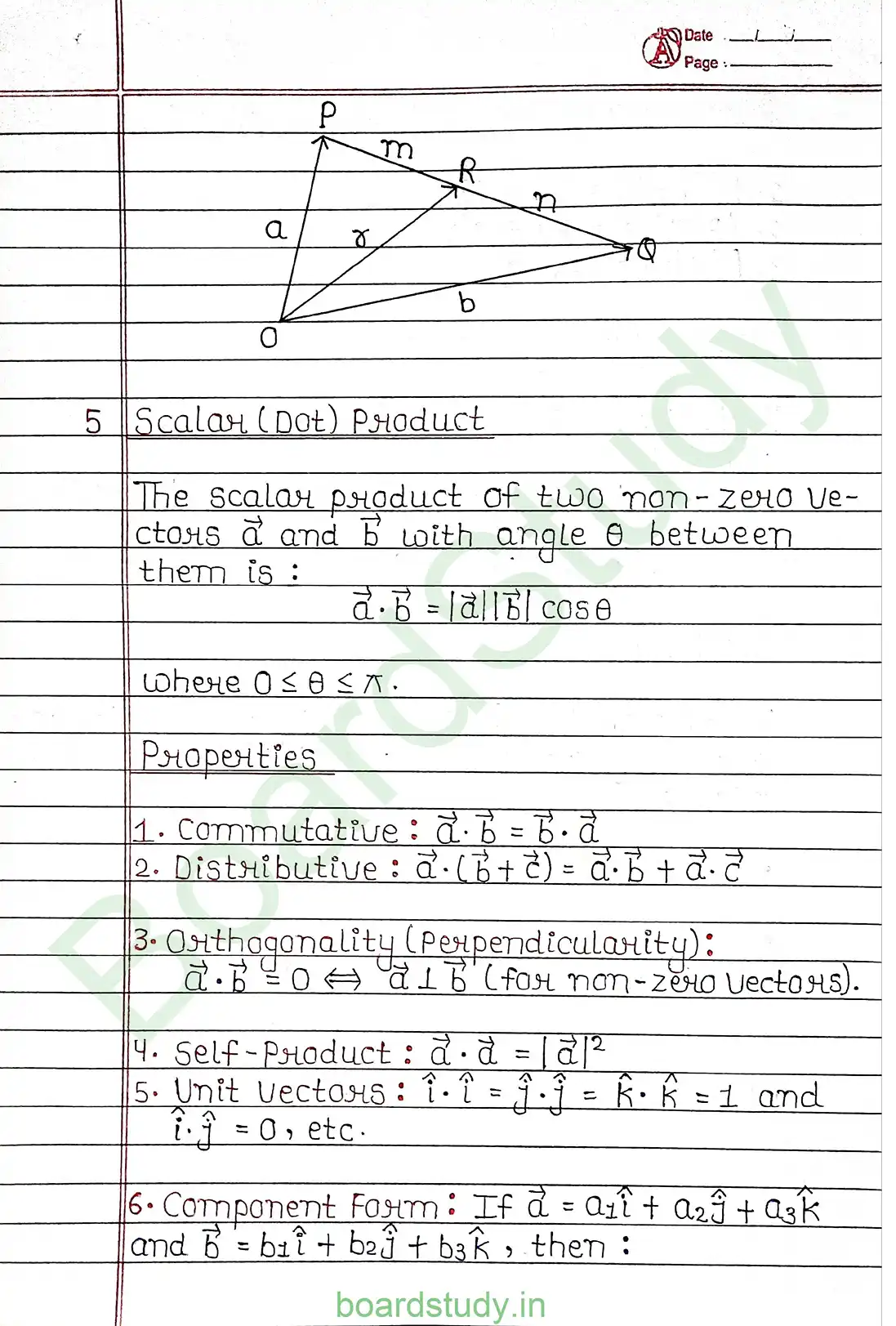



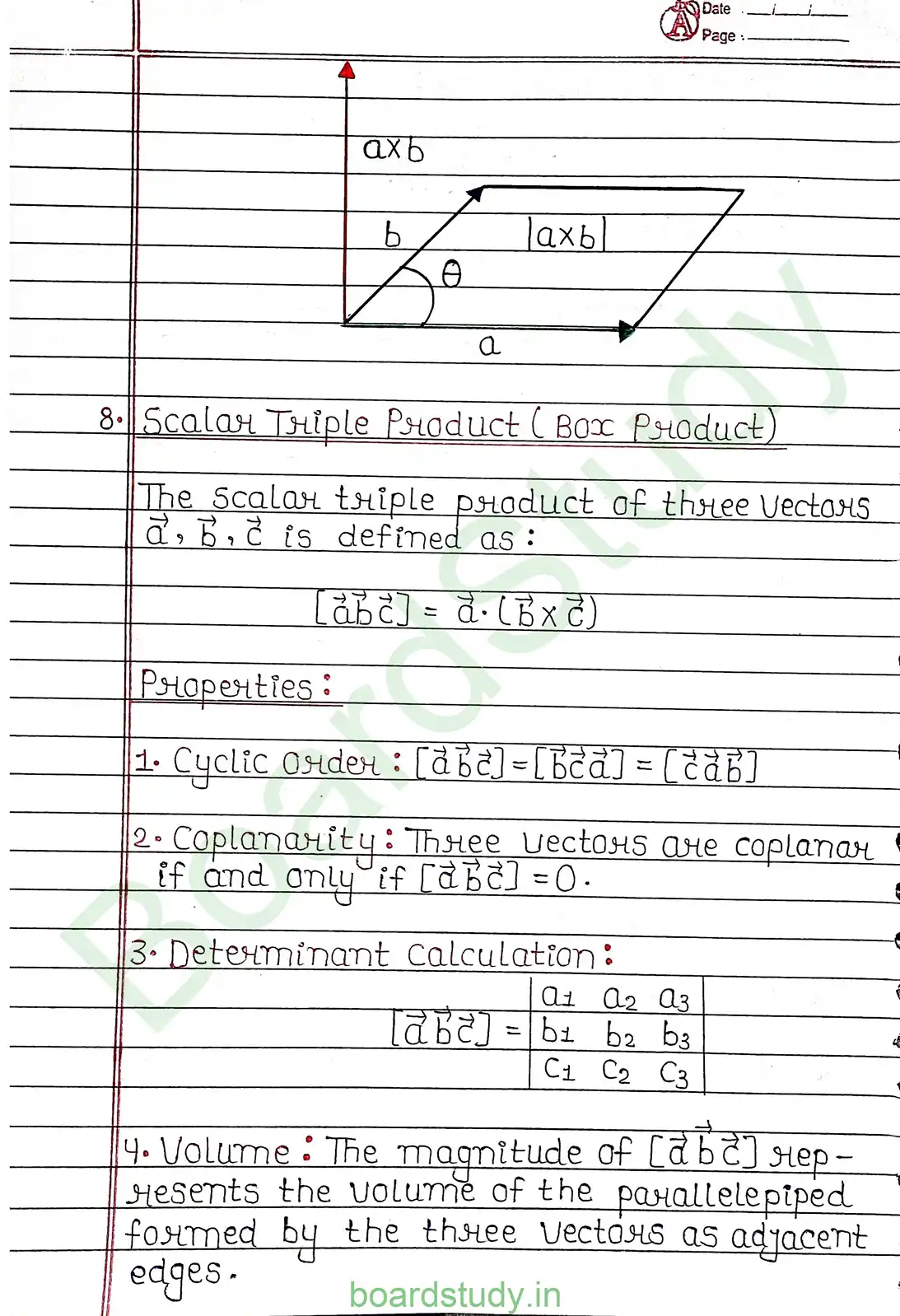

Chapter 10: Vector Algebra
Chapter 12: Linear Programming
Other Subjects:
Class 12 Physics Notes PDF
Class 12 Chemistry Notes PDF
Key Points
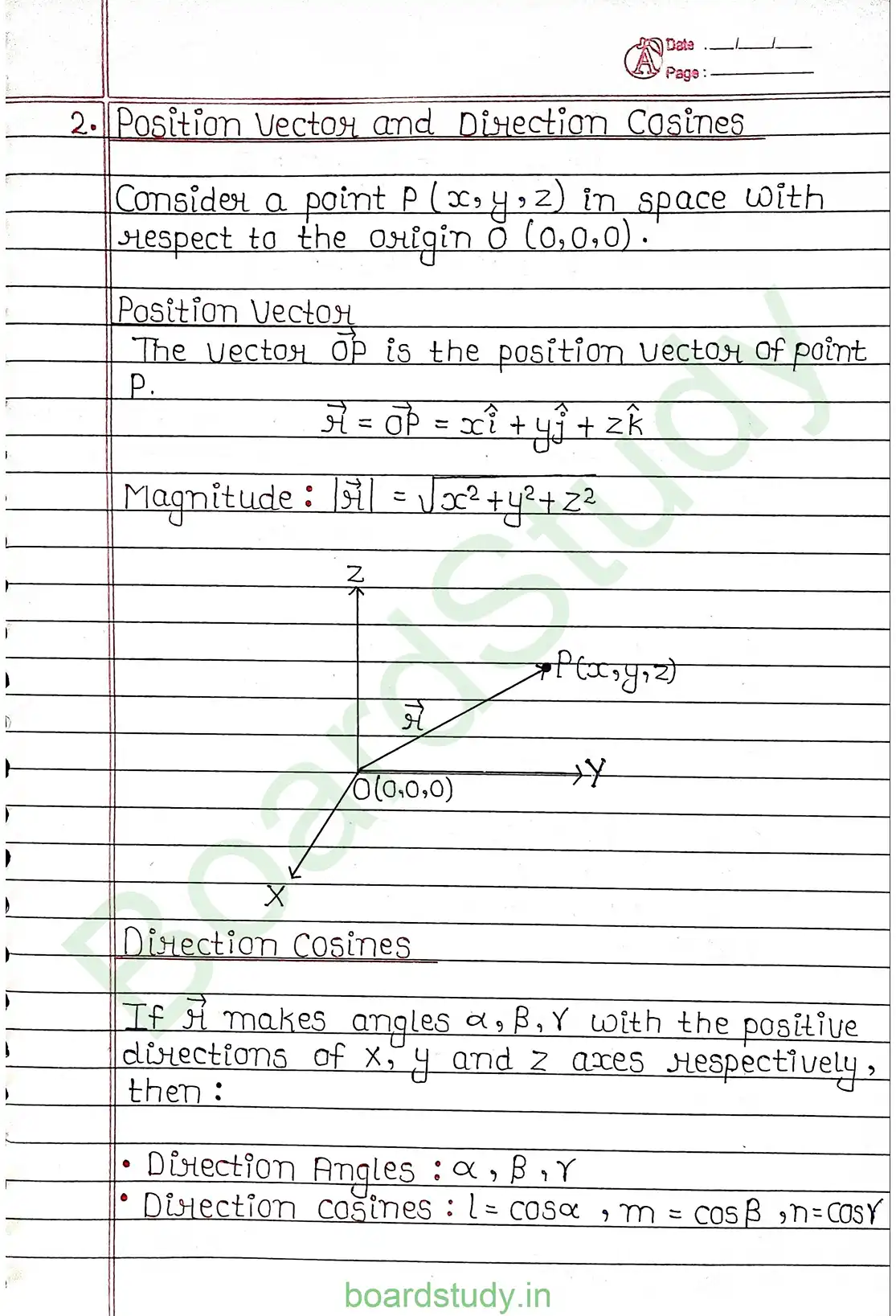
Direction cosines of a line
l = Cos α
m = Cos β
n = Cos γ
NOTE : l² + m² + n² = 1 or Cos²α + Cos²β + Cos²γ = 1
Direction cosines of a directed line are unique.
Direction Ratios of a Line
Numbers proportional to the direction cosines of a line
are called direction ratios of a line.
If a , b and c are direction ratios of a line then
l/a=m/b=n/c
• If a , b , c are direction ratios of a line then its direction cosines are
l = ± a / √(a² + b² + c²)
m = ± b / √(a² + b² + c²)
n = ± c / √(a² + b² + c²)
Shortest distance between two lines
Distance between two skew lines
Two non-parallel and non-intersecting straight lines are called skew lines.
Plane
A plane is a surface such that a line segment joining any two points of it lies wholly on it. A straight line which is perpendicular to every line lying on a plane is called a normal to the plane.