Here we have shared class 12 Chemistry Coordination Compounds Notes. The Coordination Compounds notes is a best resources for students who are preparing for their board exam because it compile the entire lesson into short and includes every important topics.
With the help of Coordination Compounds notes students can understand the chapter in a better way. Notes are prepared by very experience teachers in an organised way so students can rely on this notes for their exam preparation.
Class 12 Chemistry Coordination Compounds Handwritten Notes




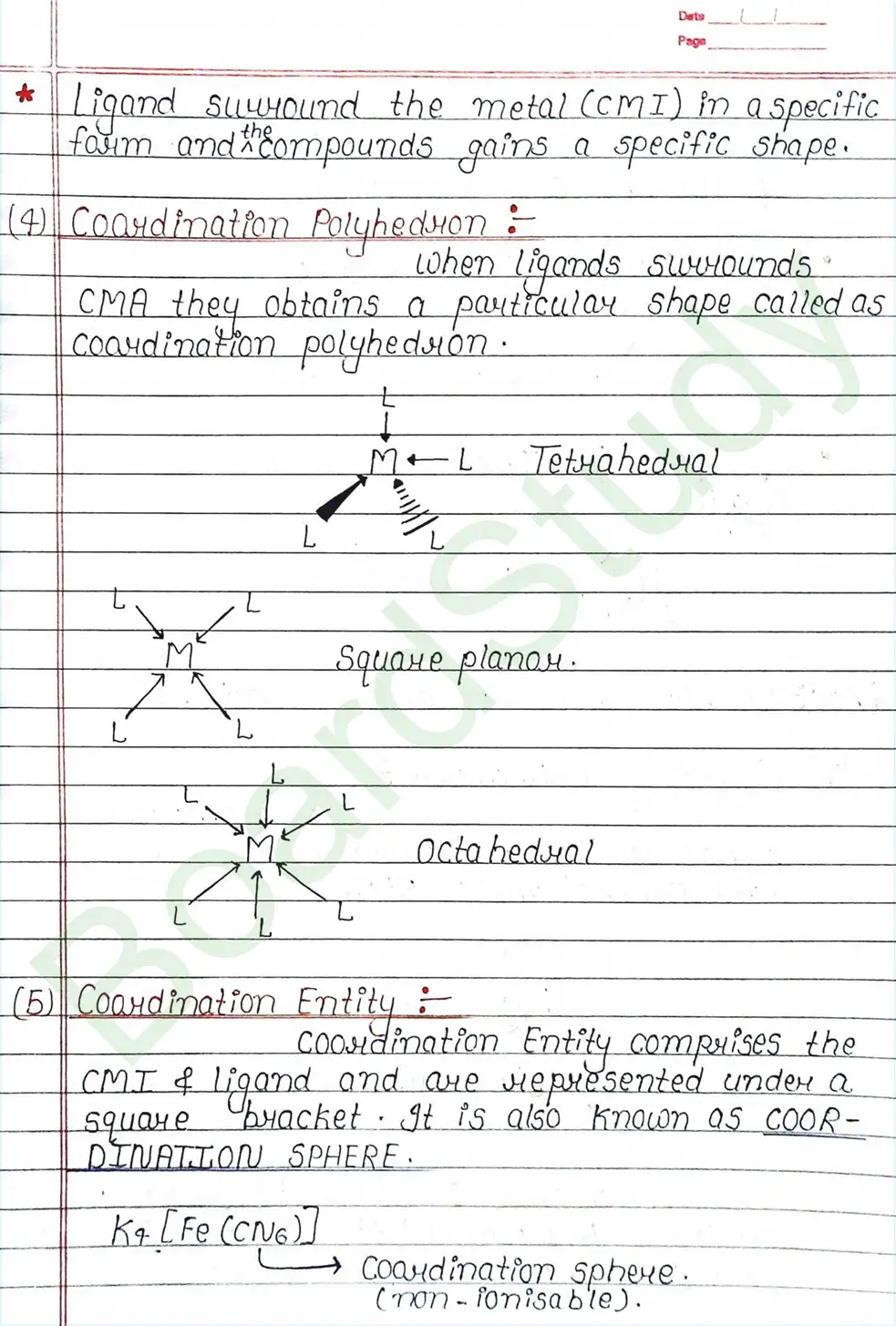




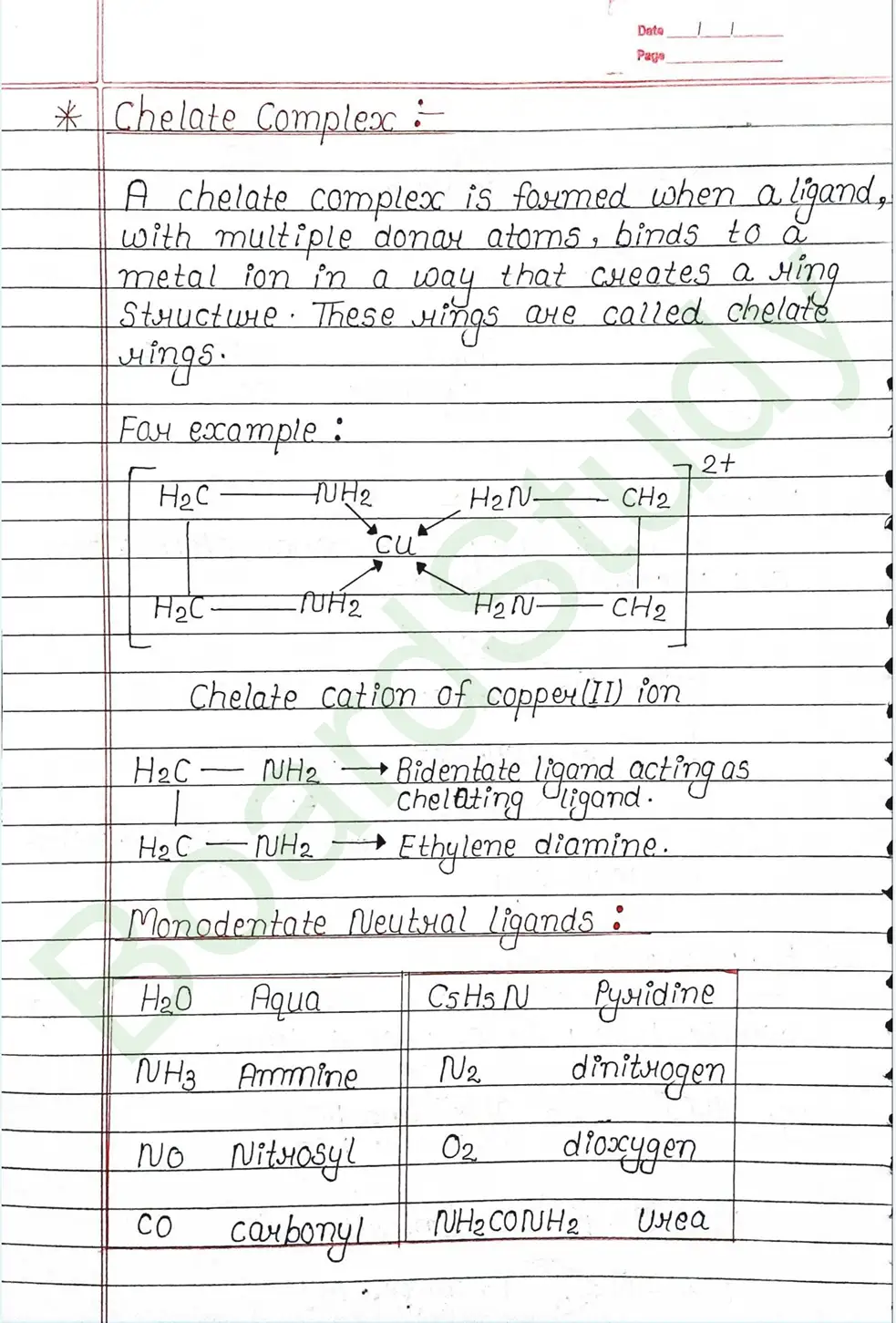
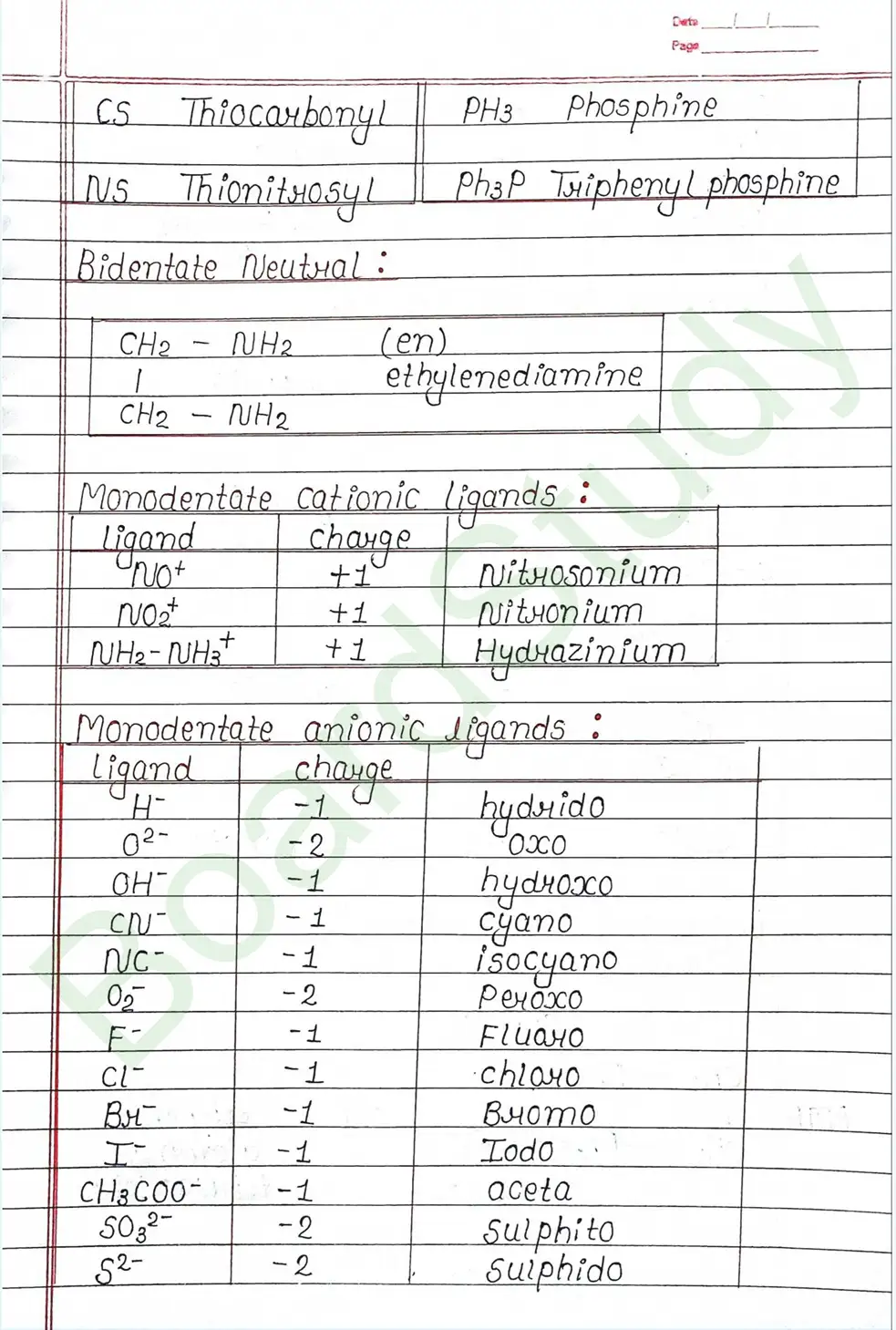
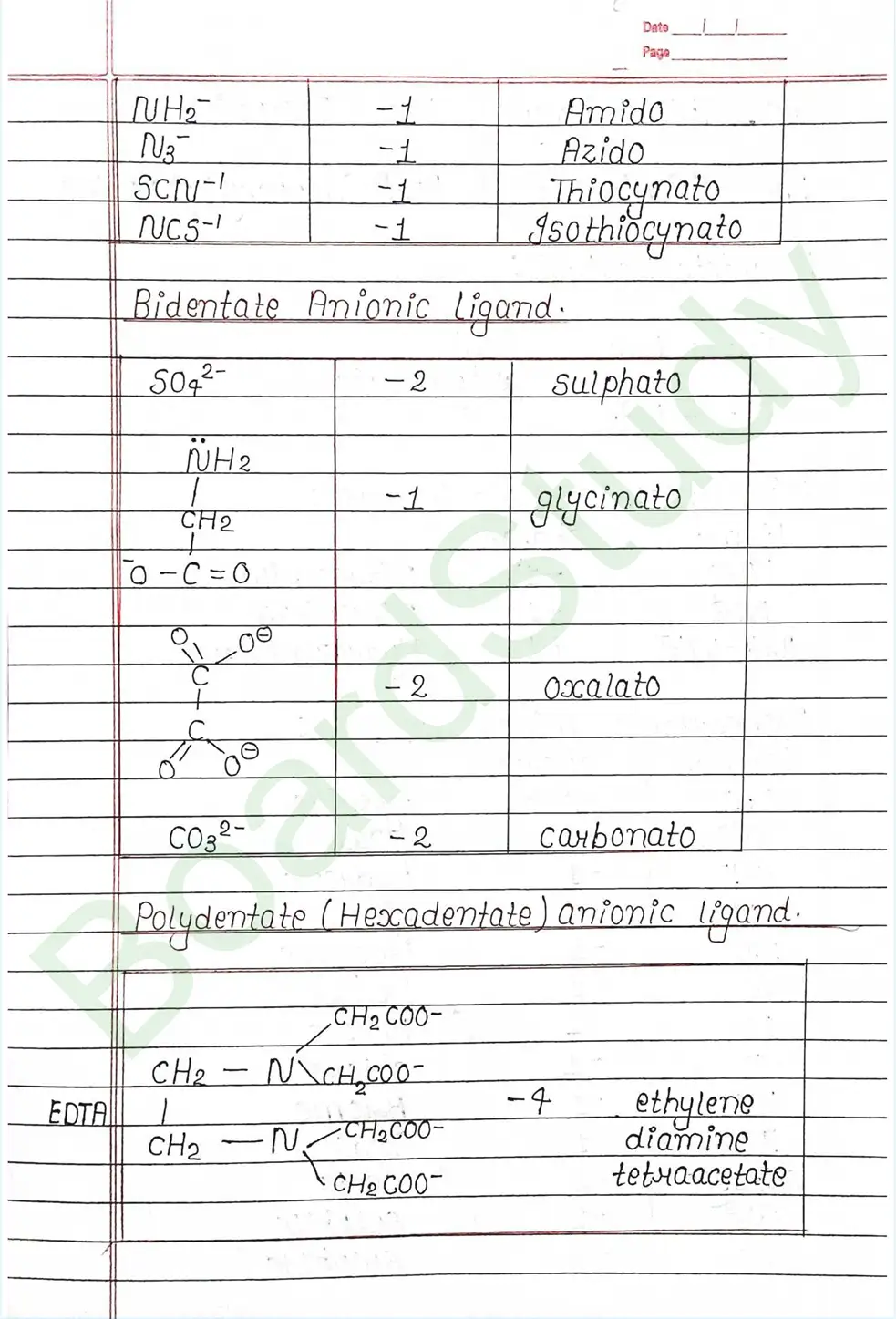








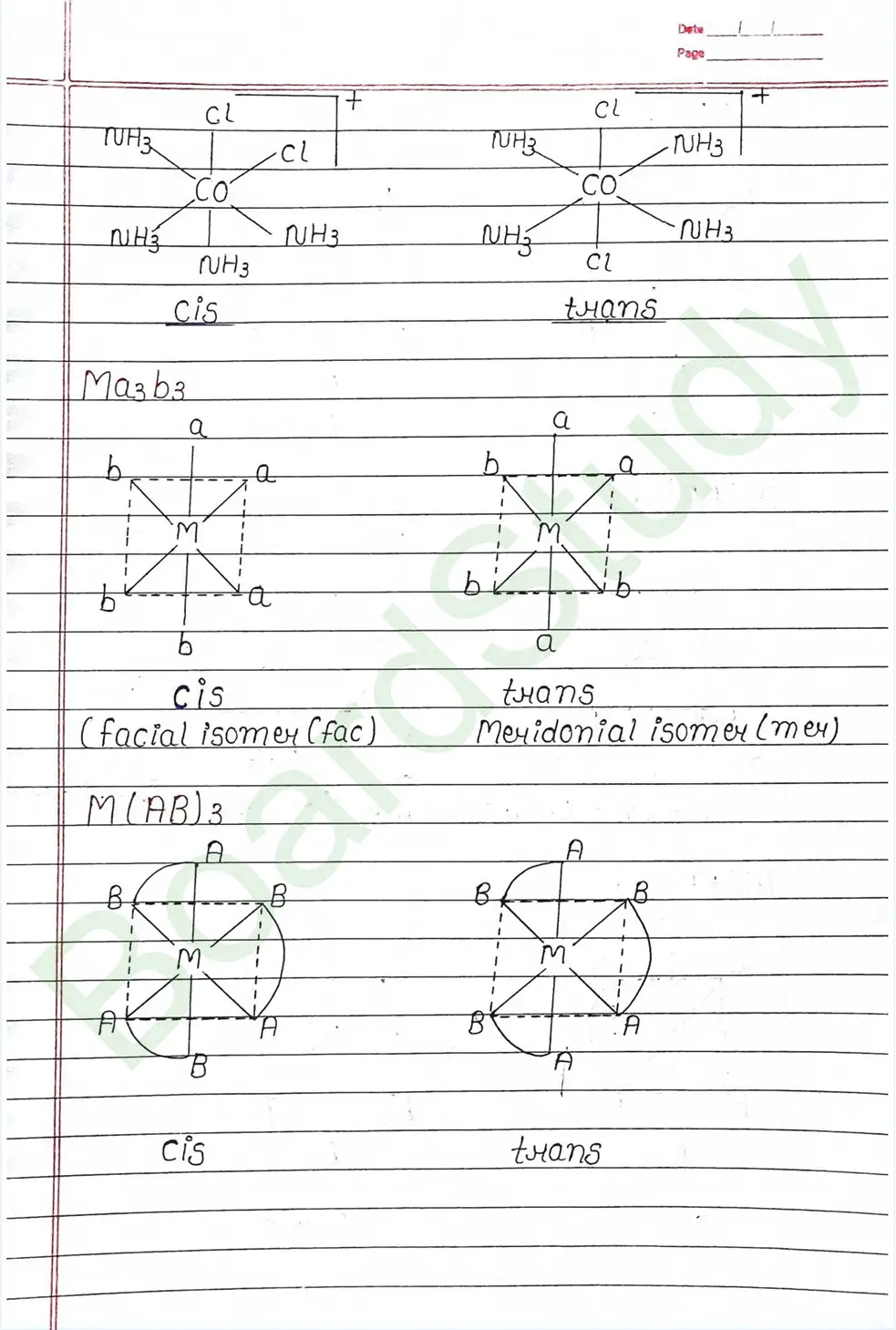
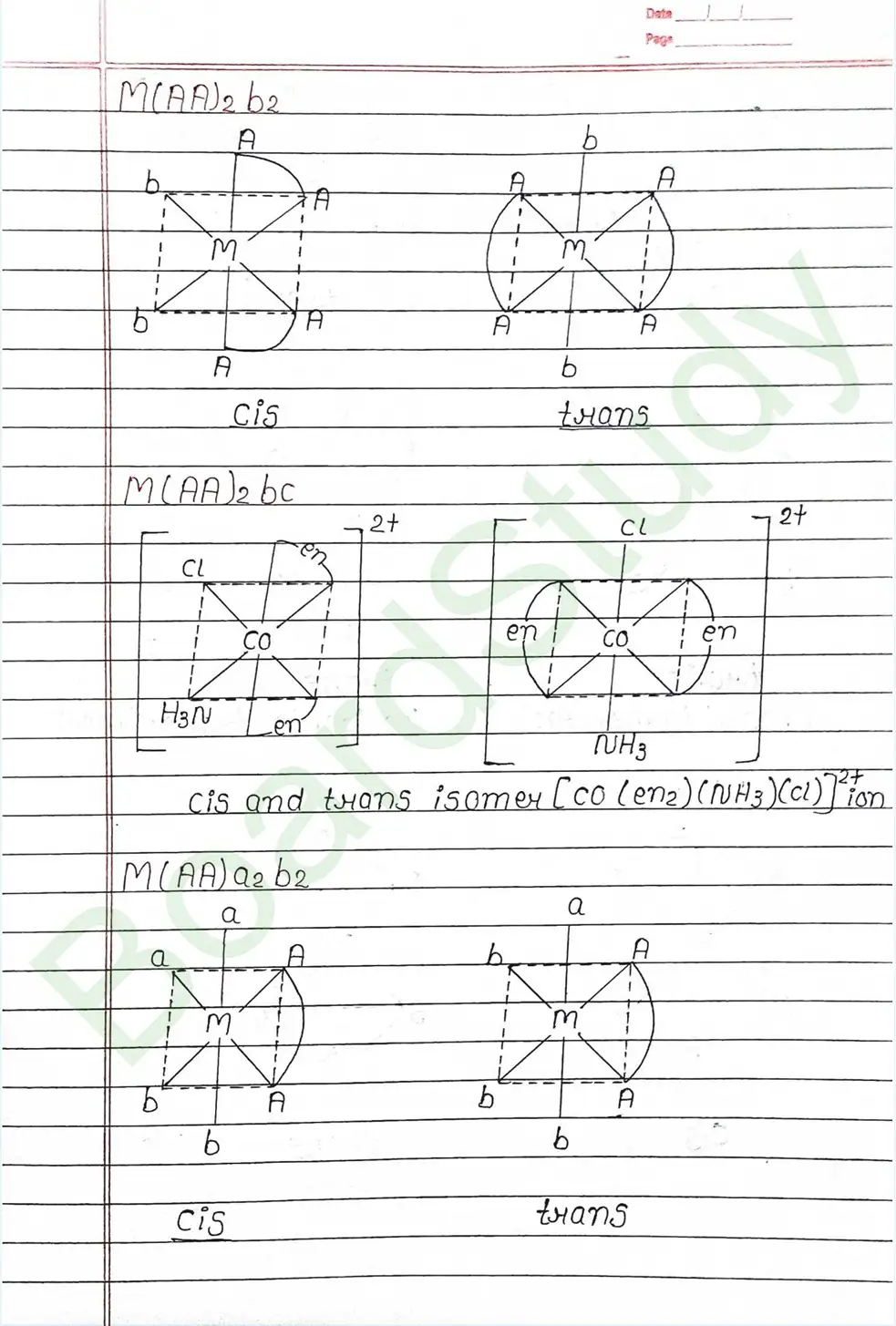
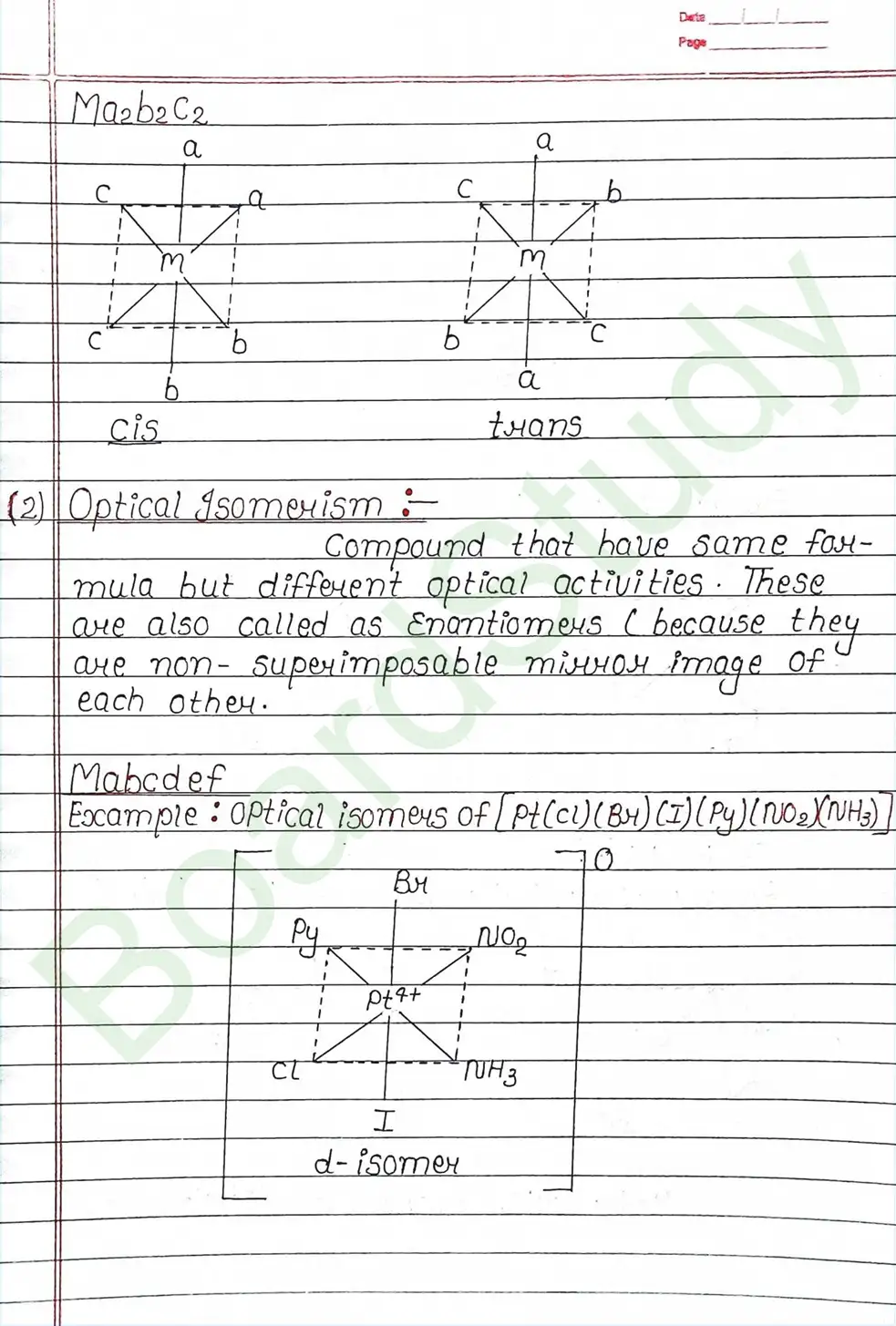
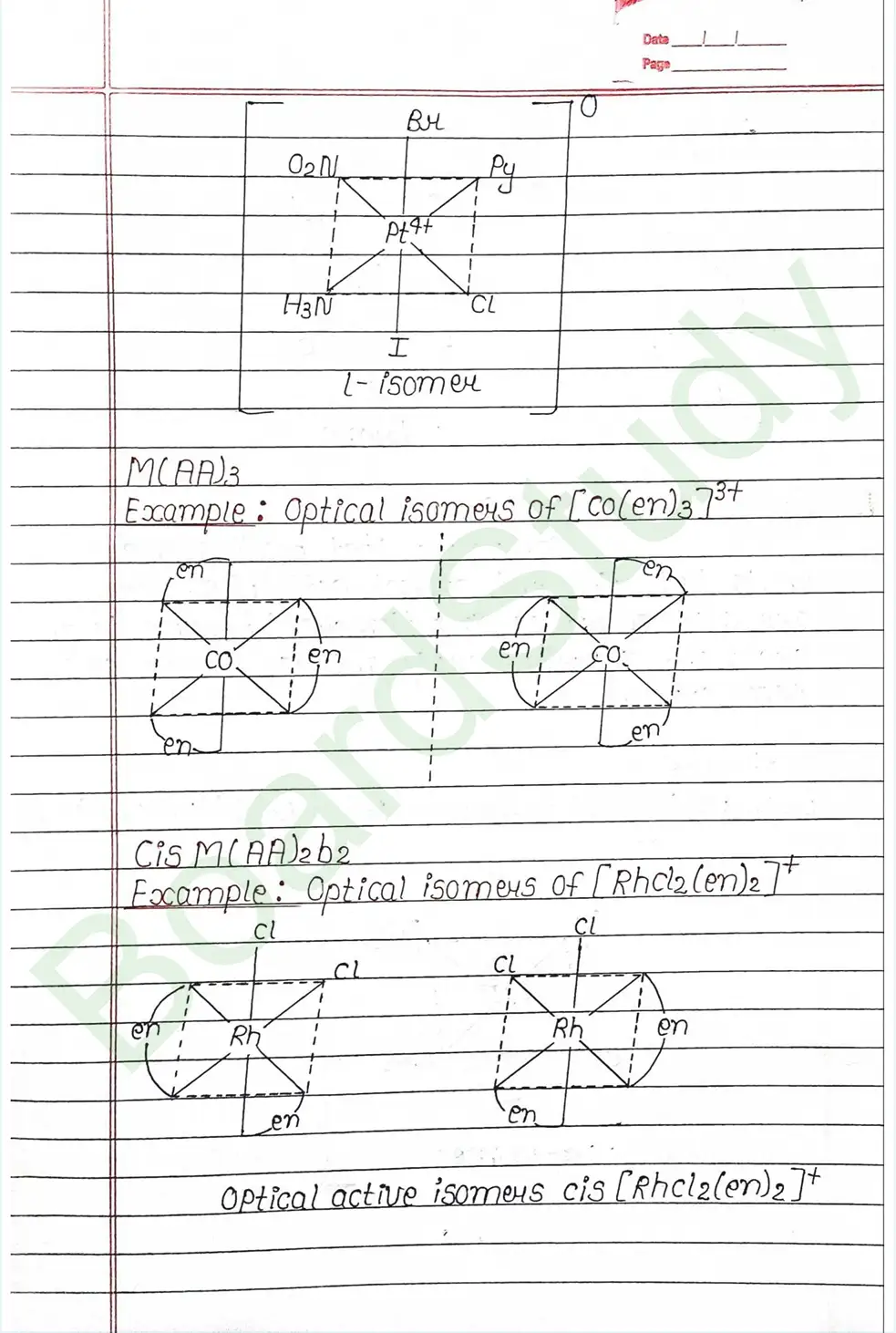








Next Chapter: Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
Previous Chapter: The d & f Block Elements
Other Subjects:
Class 12 Biology Notes
Class 12 Physics Notes
Students can access this notes anytime on our website for free of cost. If you found notes helpful, you can also help your friends by sharing with them.
Key Points: Coordination Compounds Notes PDF
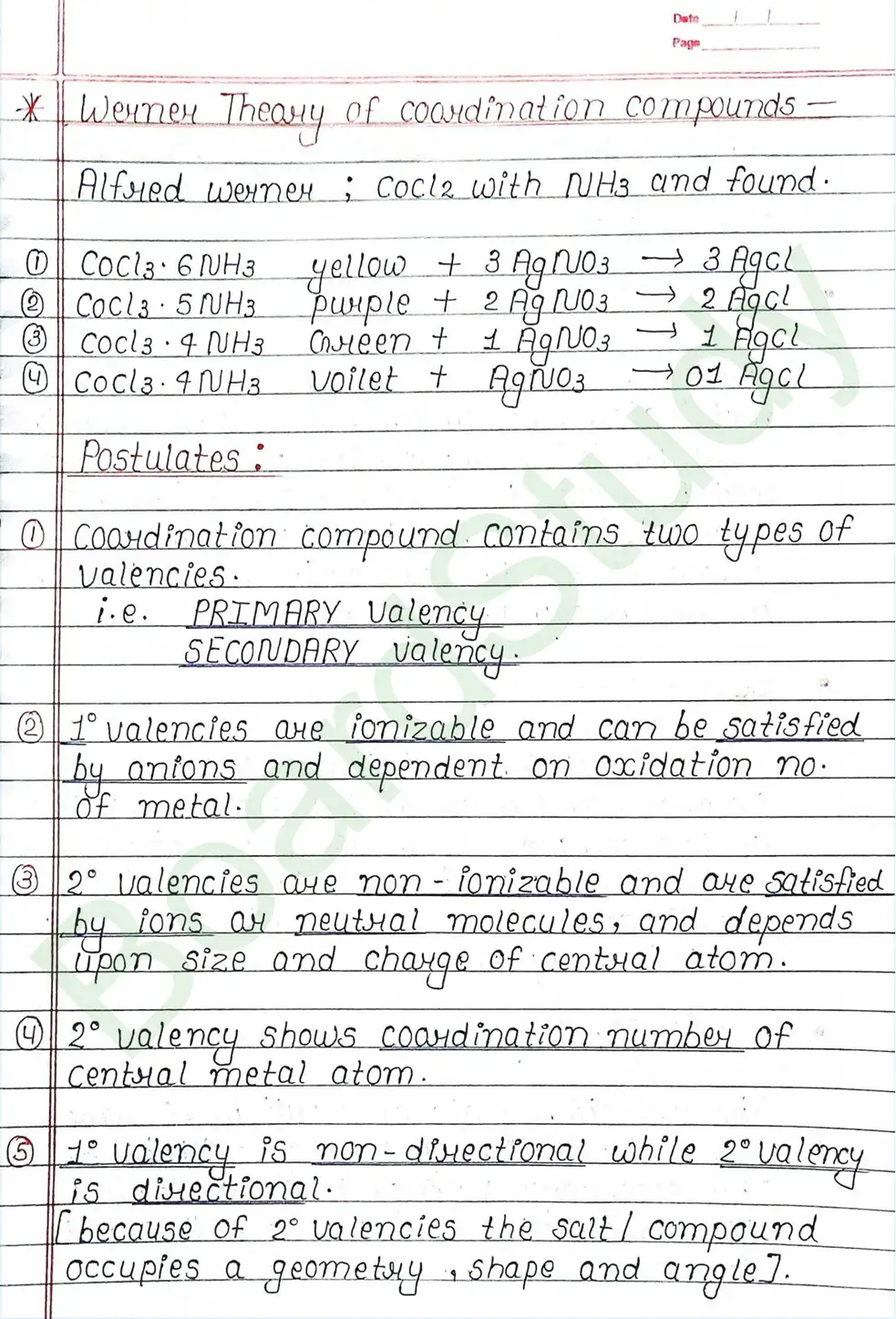
Molecular Addition compounds: When a solution containing two or more simple stable compounds in molecular proportions is allowed to evaporate, it produces crystals of new substances known as molecular or addition compounds.
Types of Molecular Compounds
- Double salt: A double salt is a substance formed by combining two different salts that crystallize as a single substance but ionize as two distinct salts when dissolved in water.
- Coordination compounds: A coordination compound is a molecular compound formed by the combination of two or more simple molecular compounds that retains its identity both solid and dissolved.
Ligands: Are atoms or group of atoms or ions that donates their lone pair of e- to the central metal atom to form coordination bond with it.
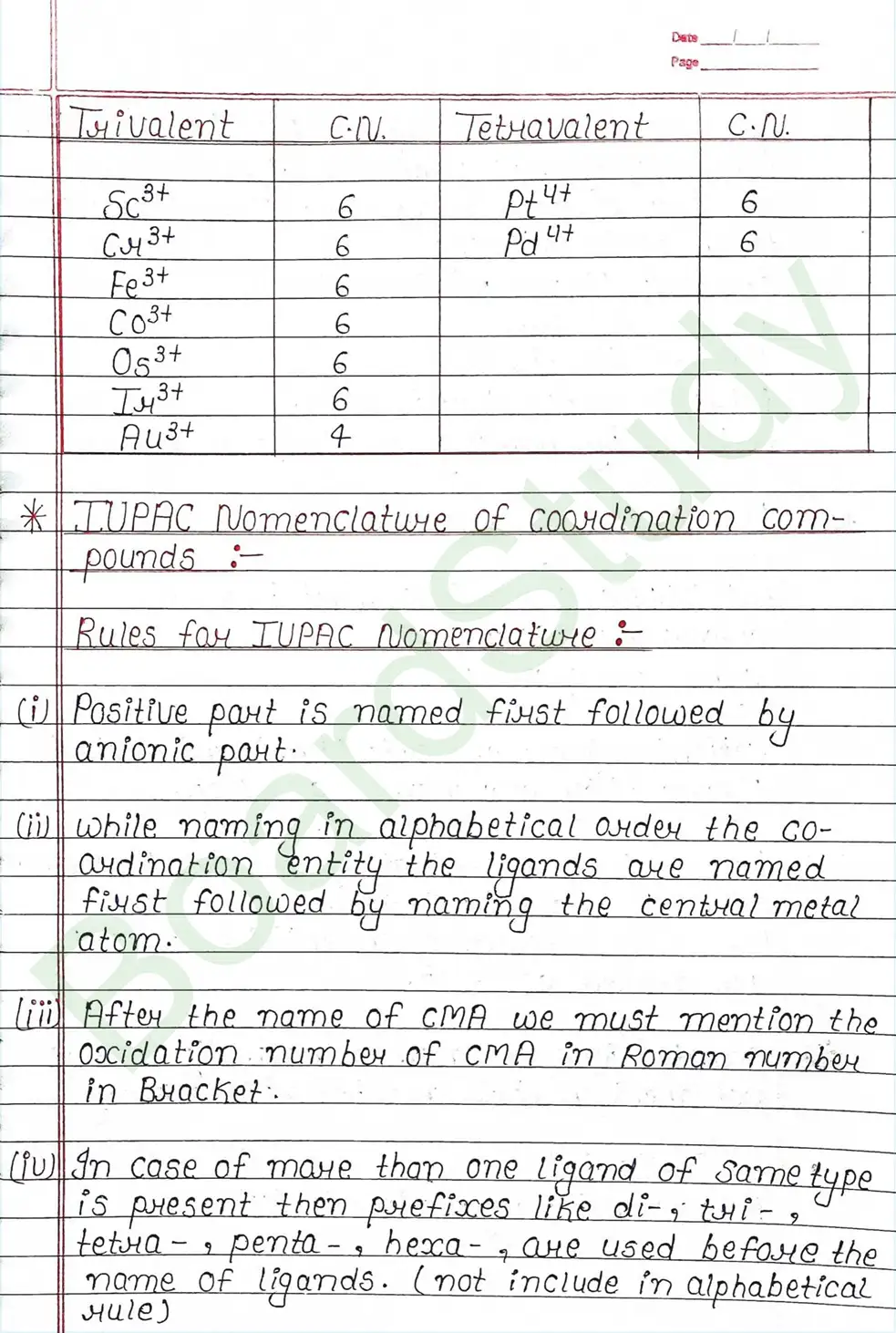
IUPAC Nomenclature of coordination compounds : Rules for IUPAC Nomenclature
- (i) Positive part is named first followed by anionic part.
- (ii) while naming the coordination entity the ligands are named first followed by naming the central metal atom.
- (iii) After the name of CMA we must mention the Oxidation number of CMA in Roman number in Bracket.
- (iv) In case of more than one ligand of same type is present then prefixes like di-, tri-, tetra-, penta-, hexa- , are used.
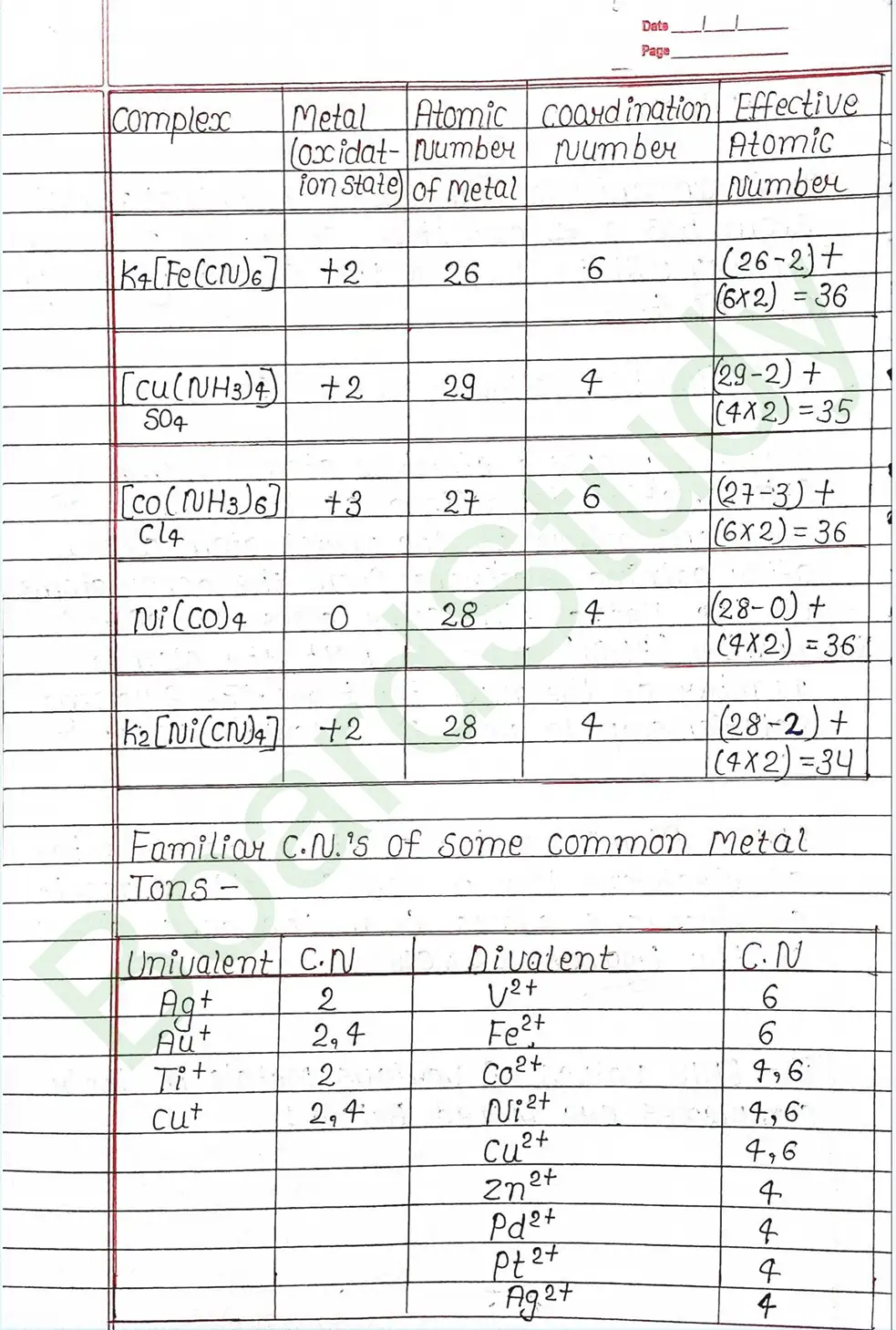
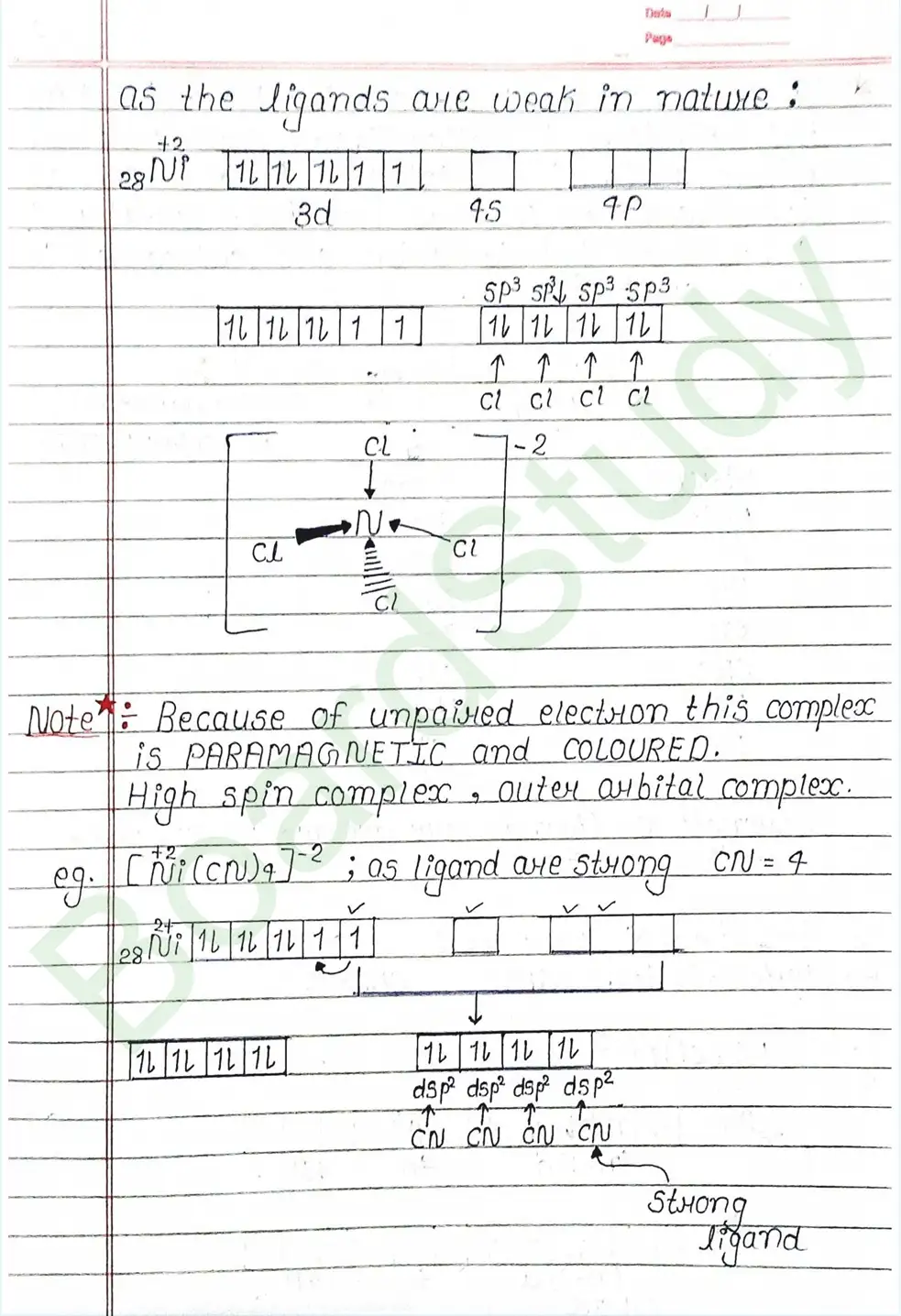
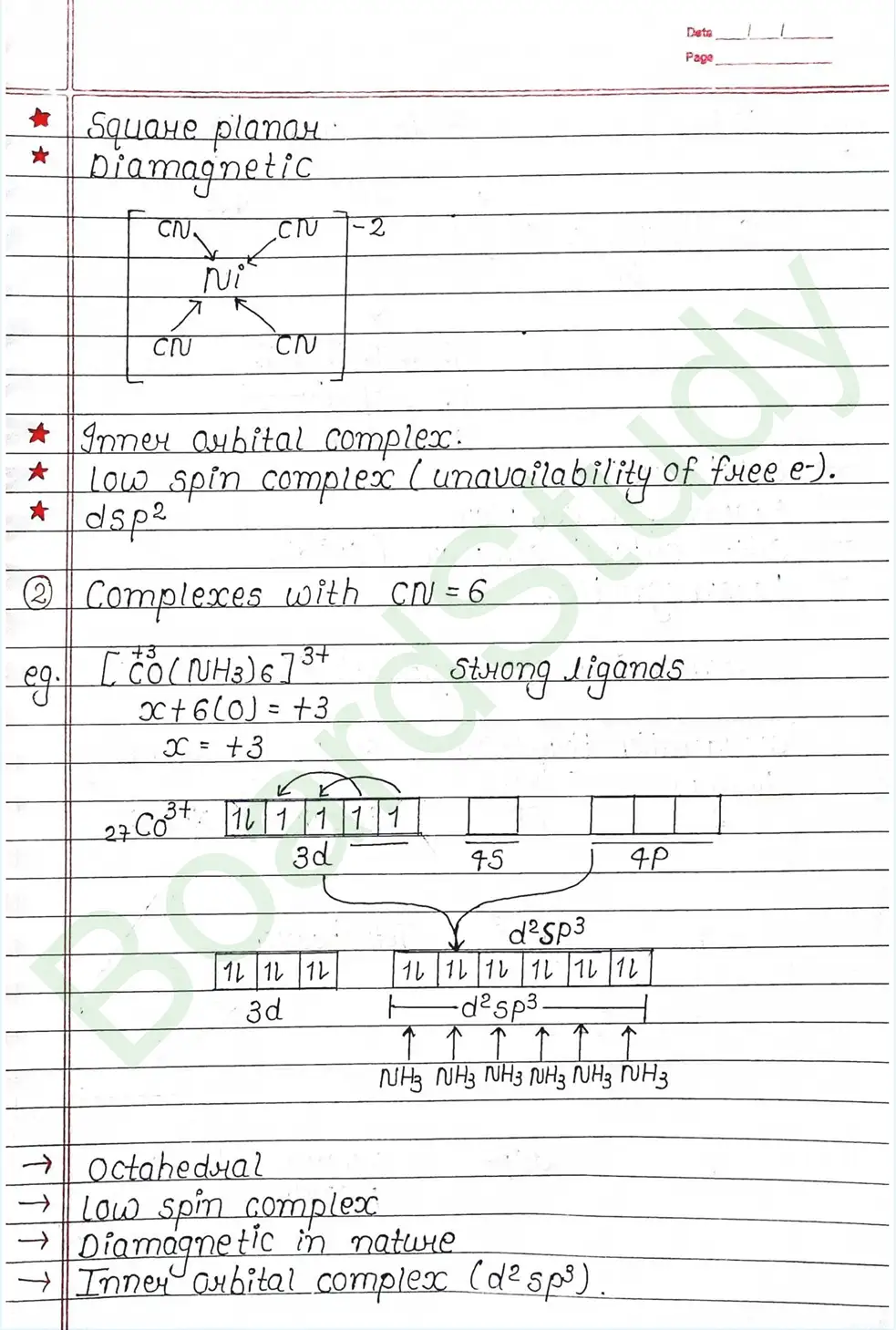
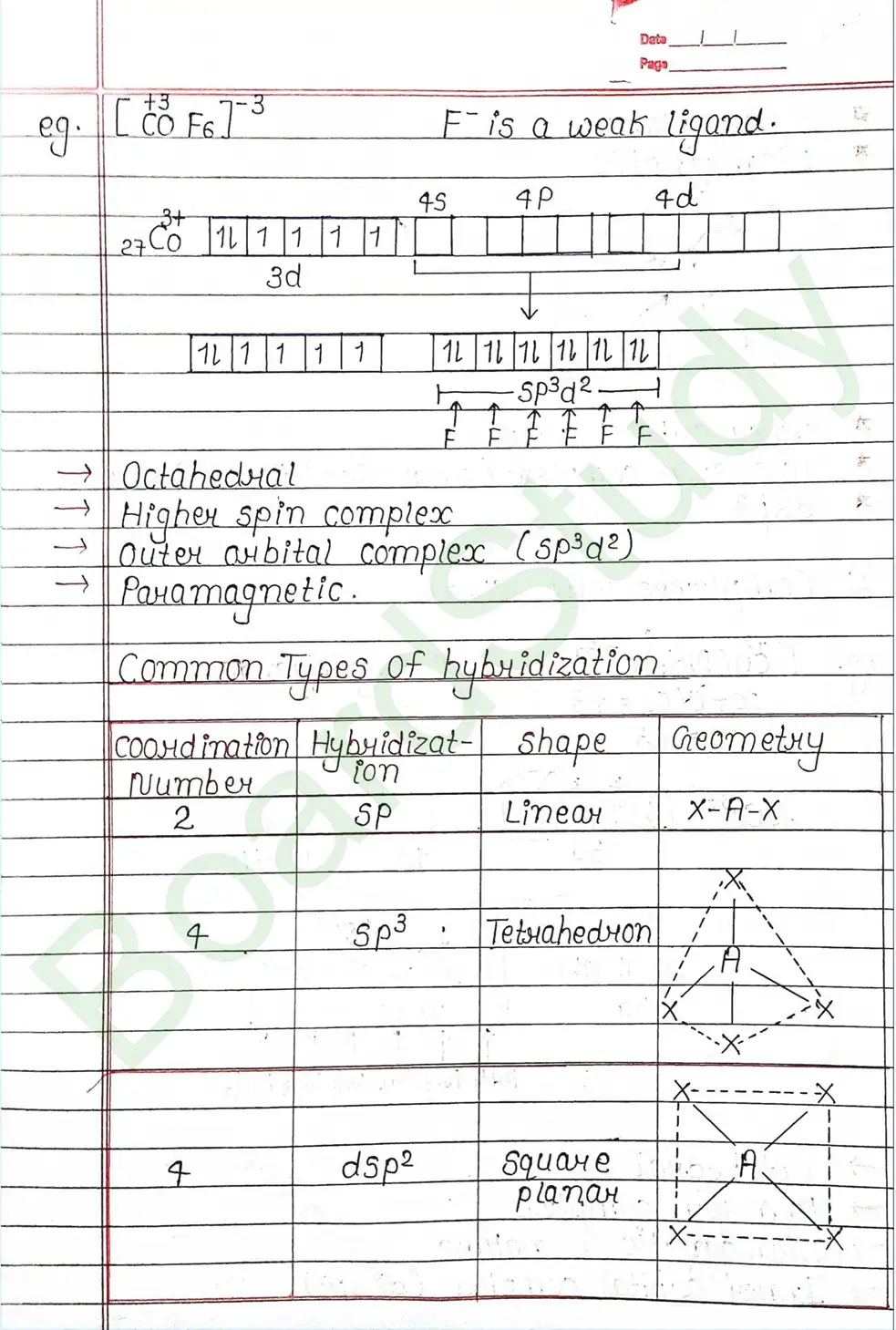
Valence Bond Theory : Valence Bond Theory (VBT) can explain the bonding in coordination compounds because the d orbitals of the majority of transition metal complexes are incomplete.
The following assumption is made by VBT.
- The central metal ion has a number of empty Orbitals that can accept electrons donated by the ligands.
- Strong bonds are formed when the metal orbitals and ligand orbitals overlap.
- Each ligand contributes two electrons to the central metal ion/atom.
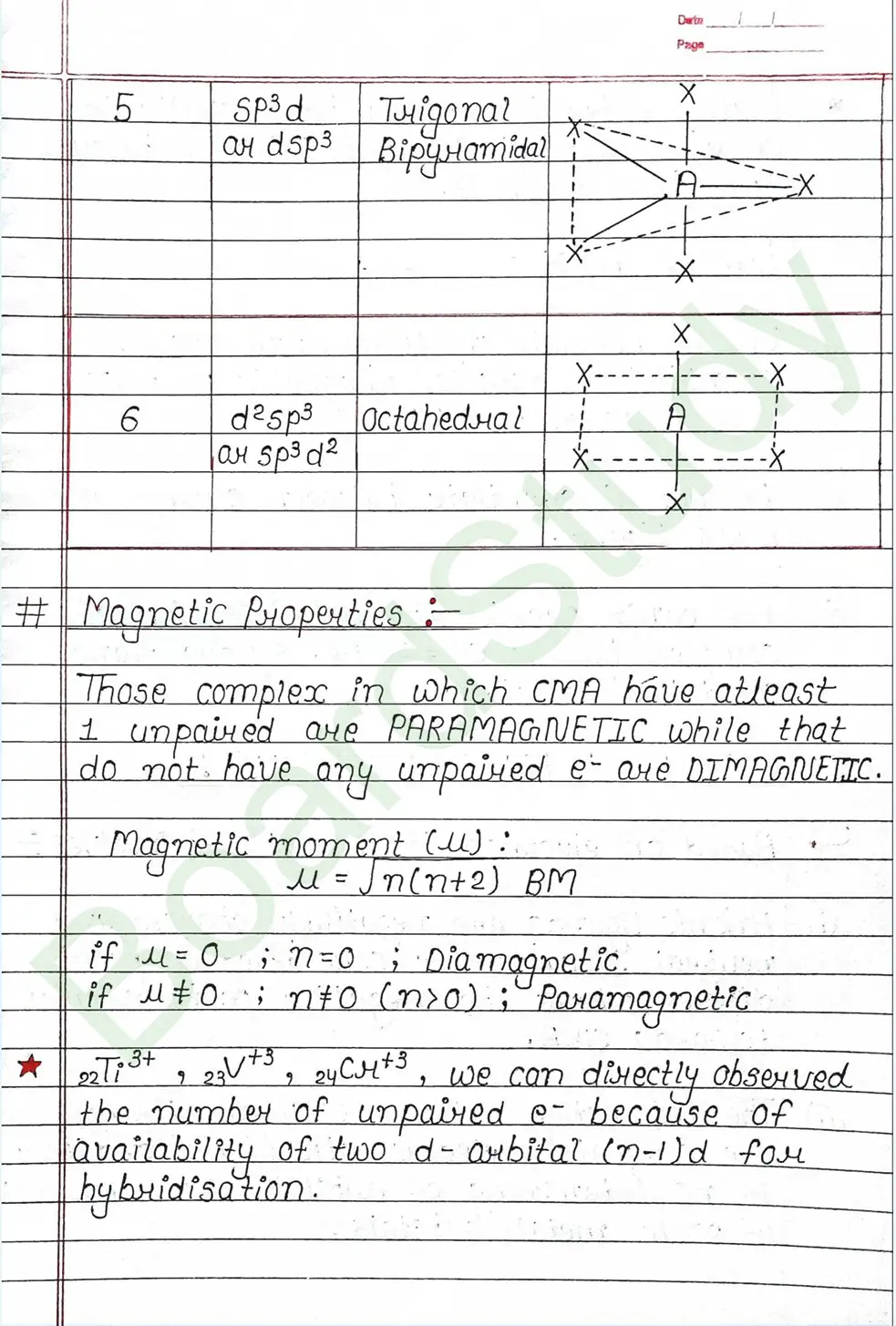
- A complex is paramagnetic if it contains unpaired electrons. The complex is diamagnetic if it does not contain an unpaired electron.
- Under the influence of a strong ligand (CN, CO), electrons can be forced to pair up, thereby violating Hund’s rule of multiplicity.
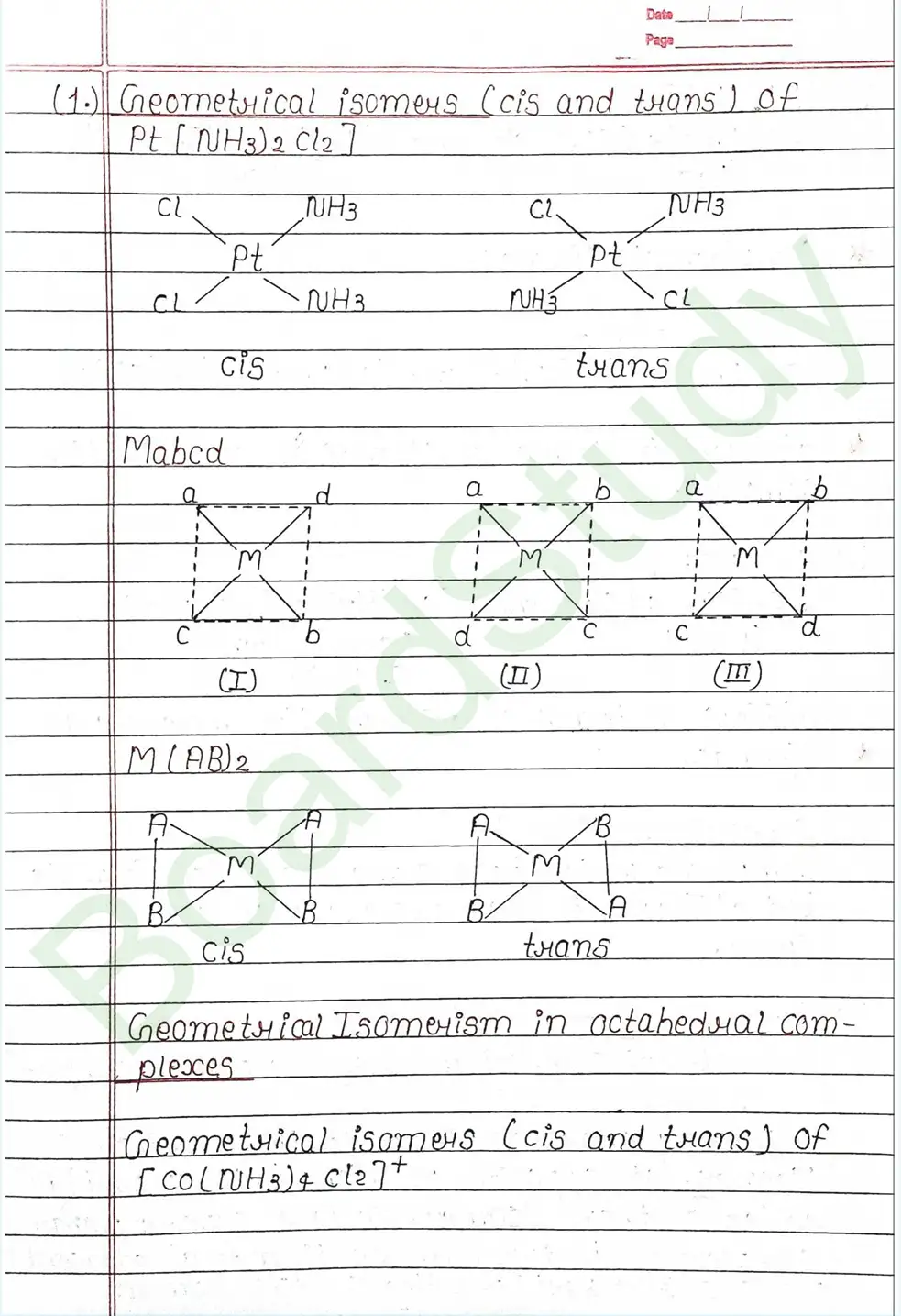
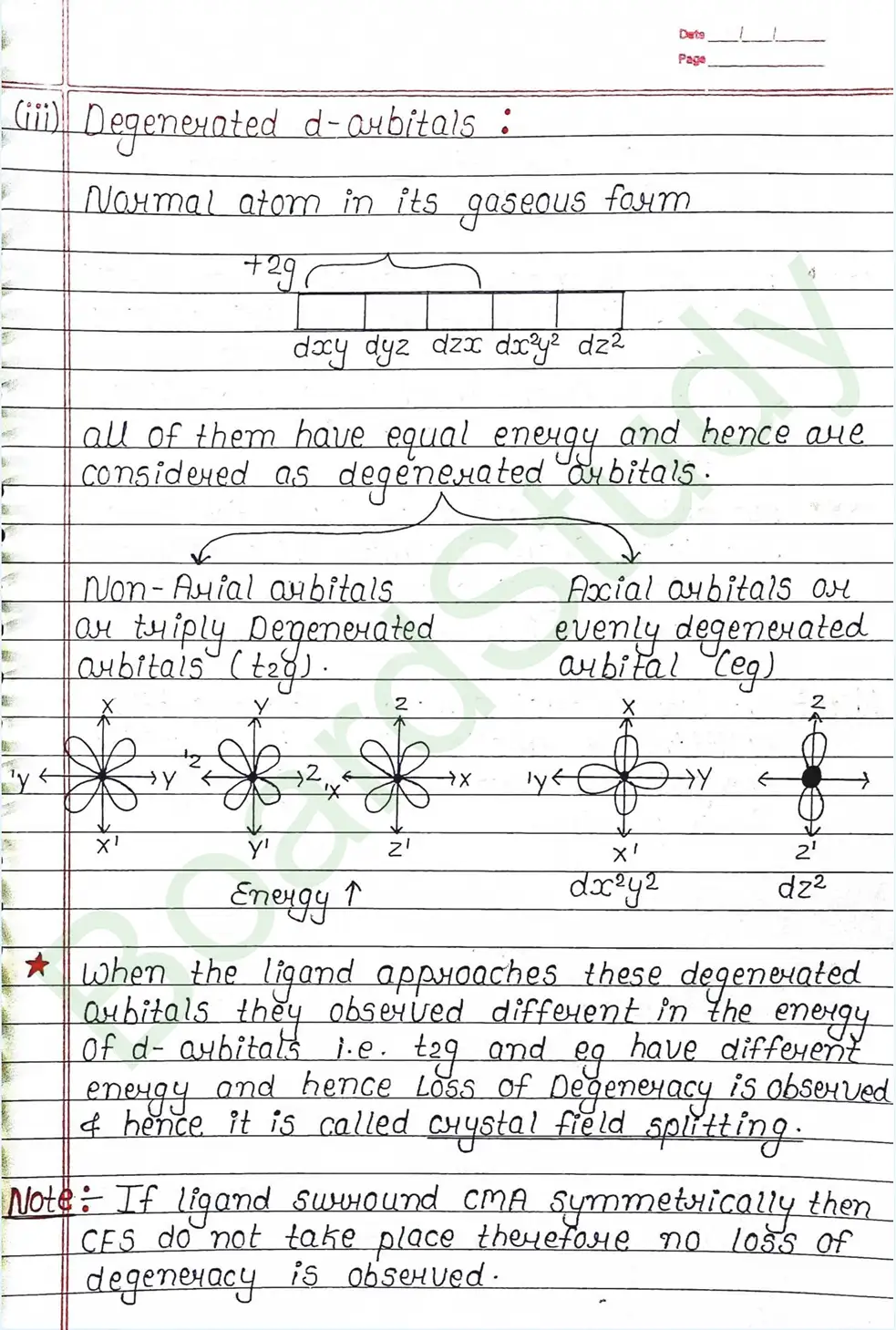
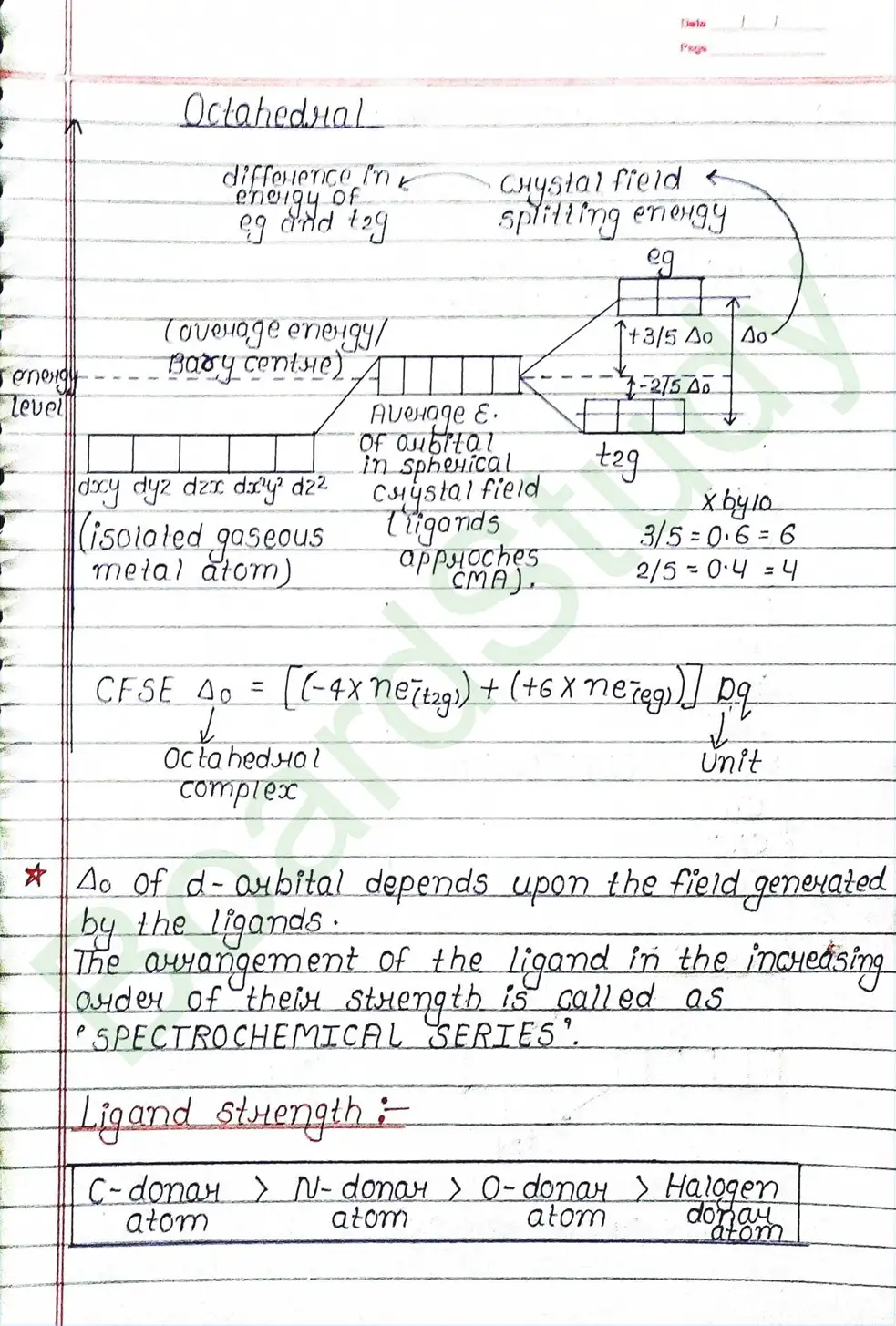
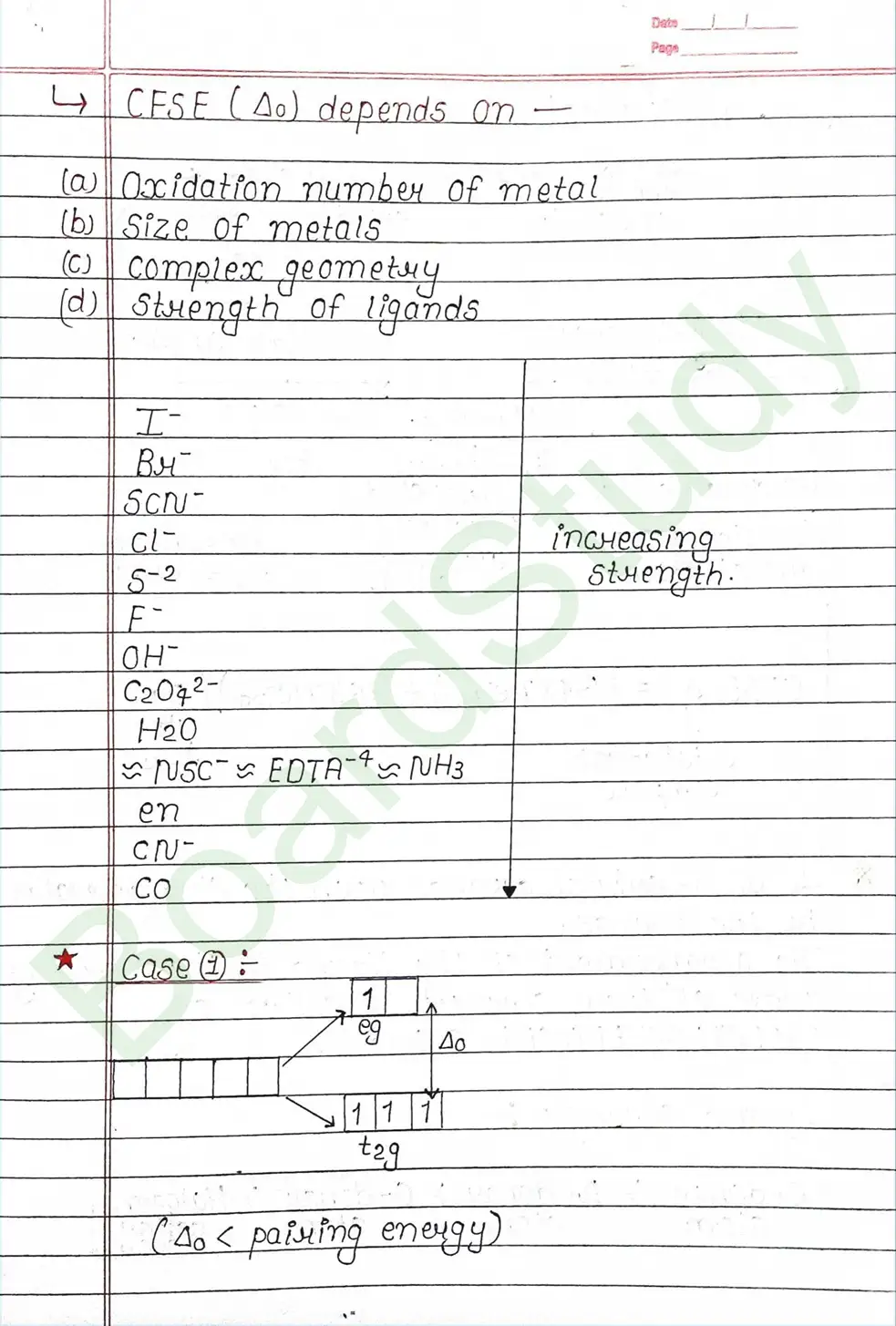
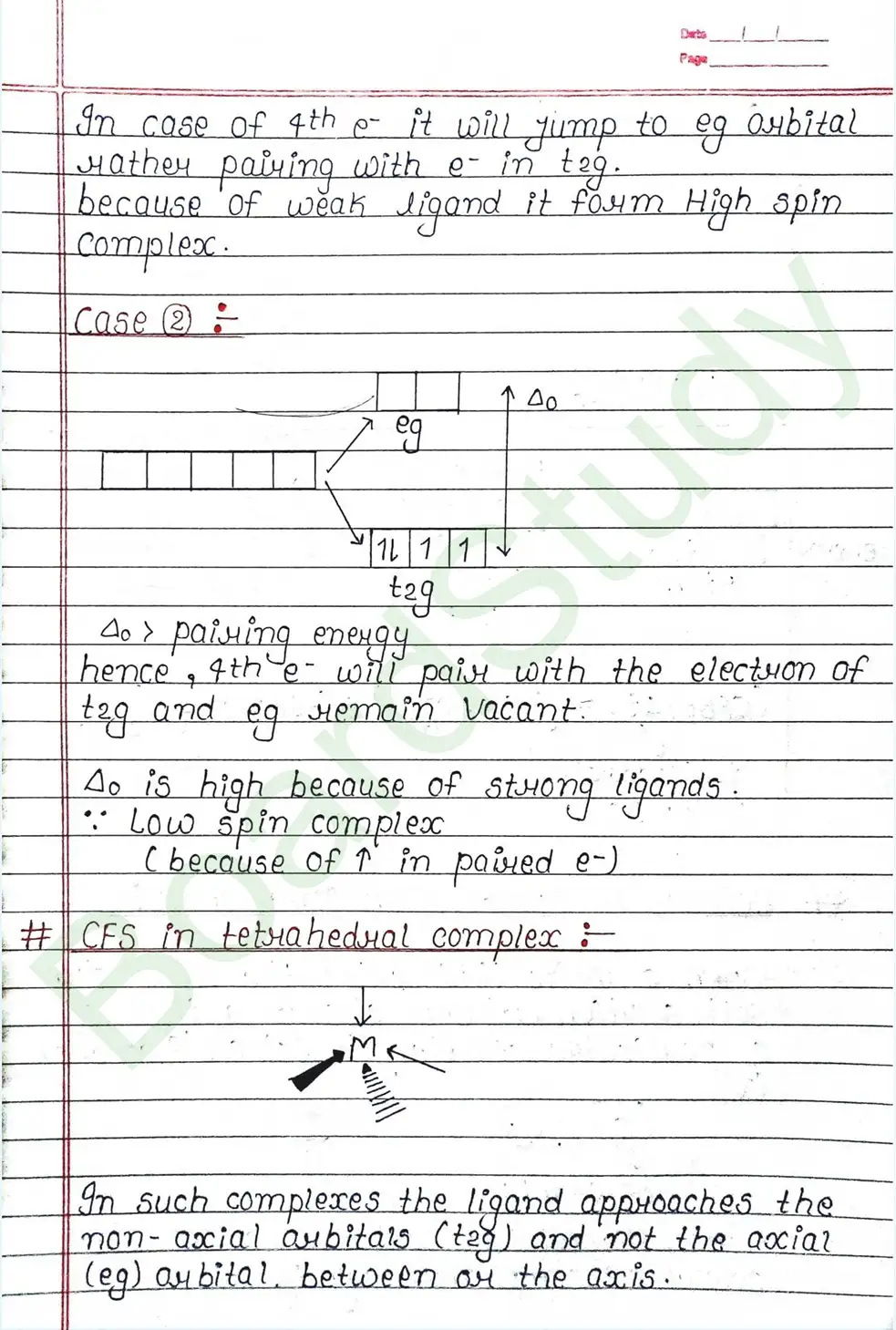
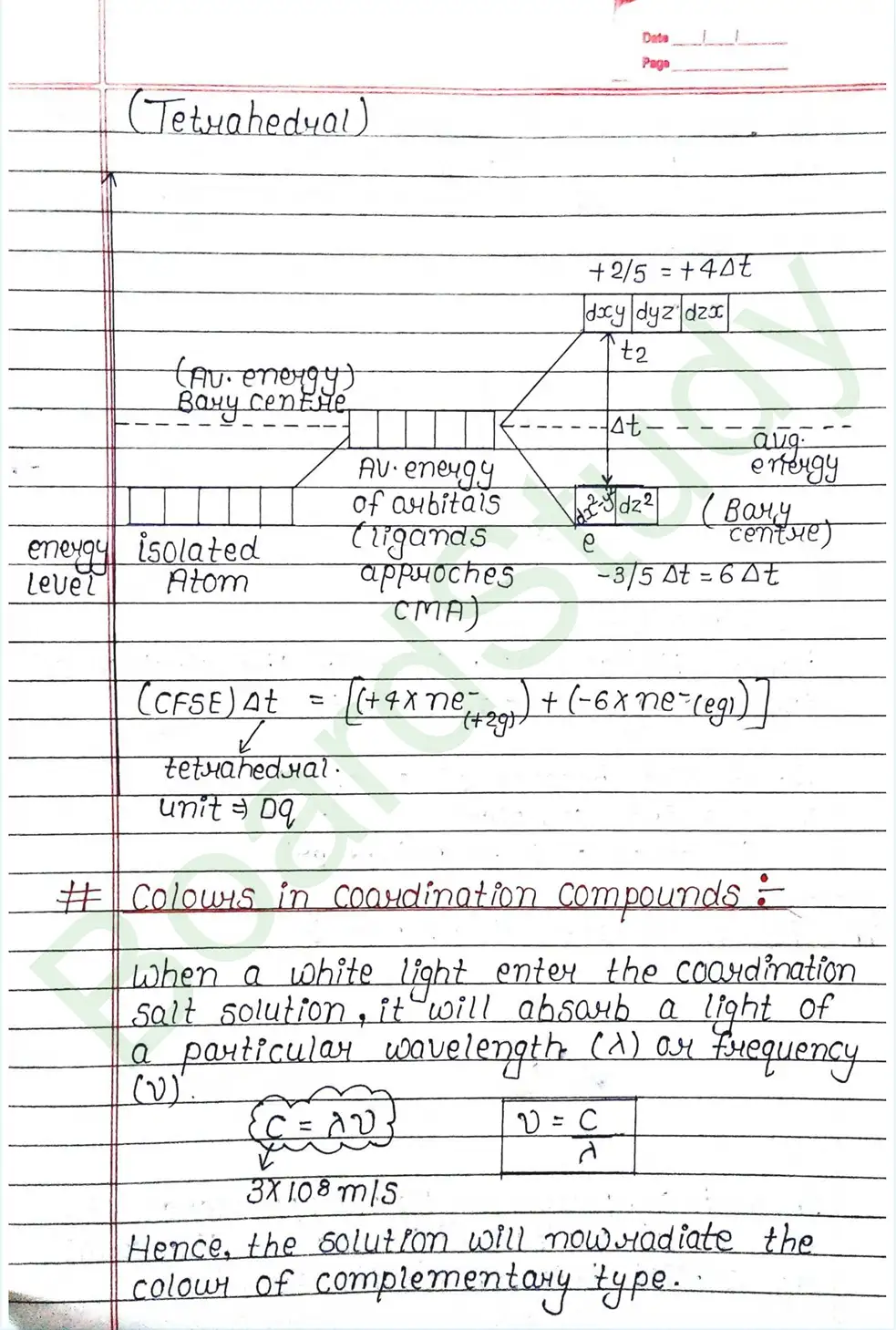
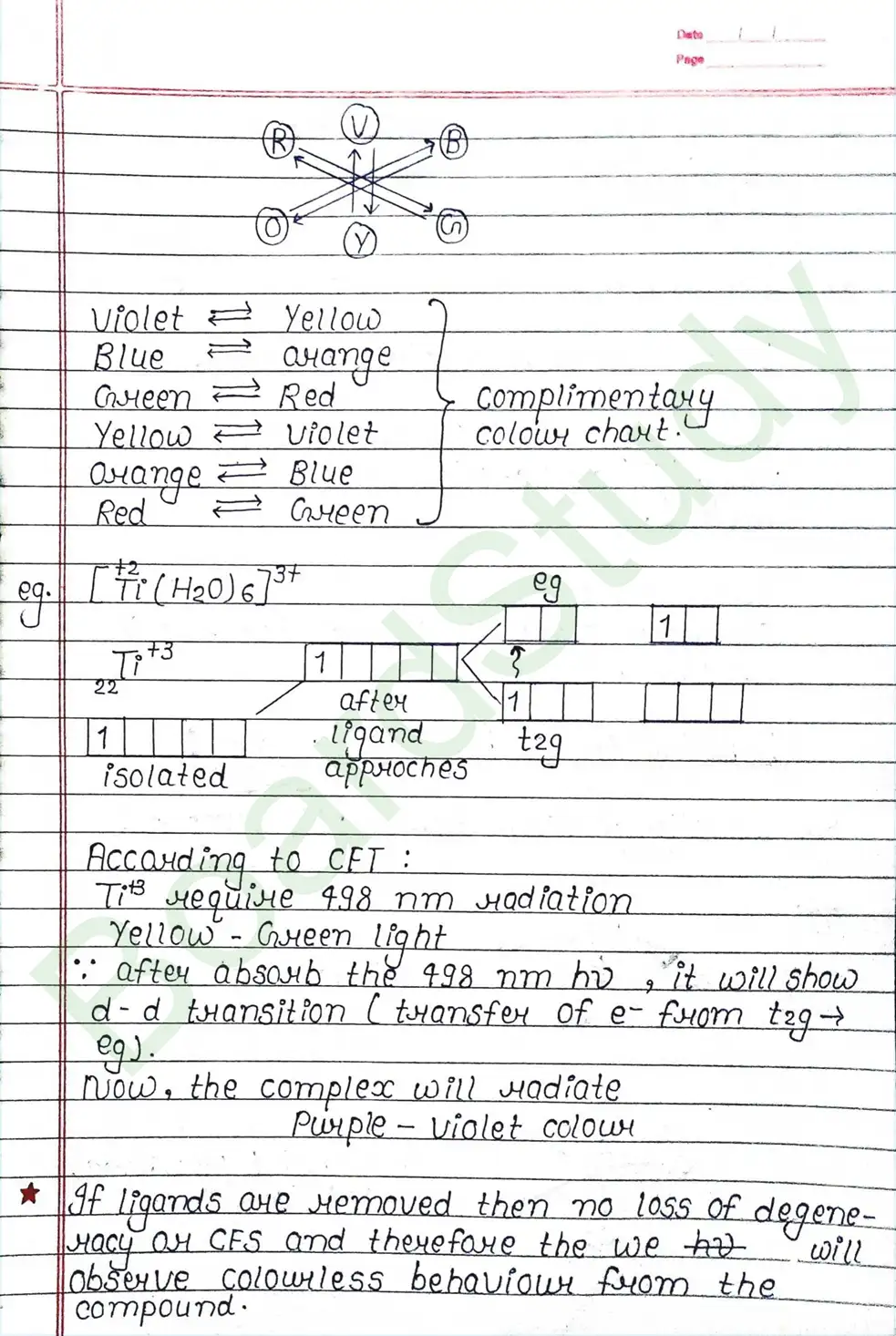
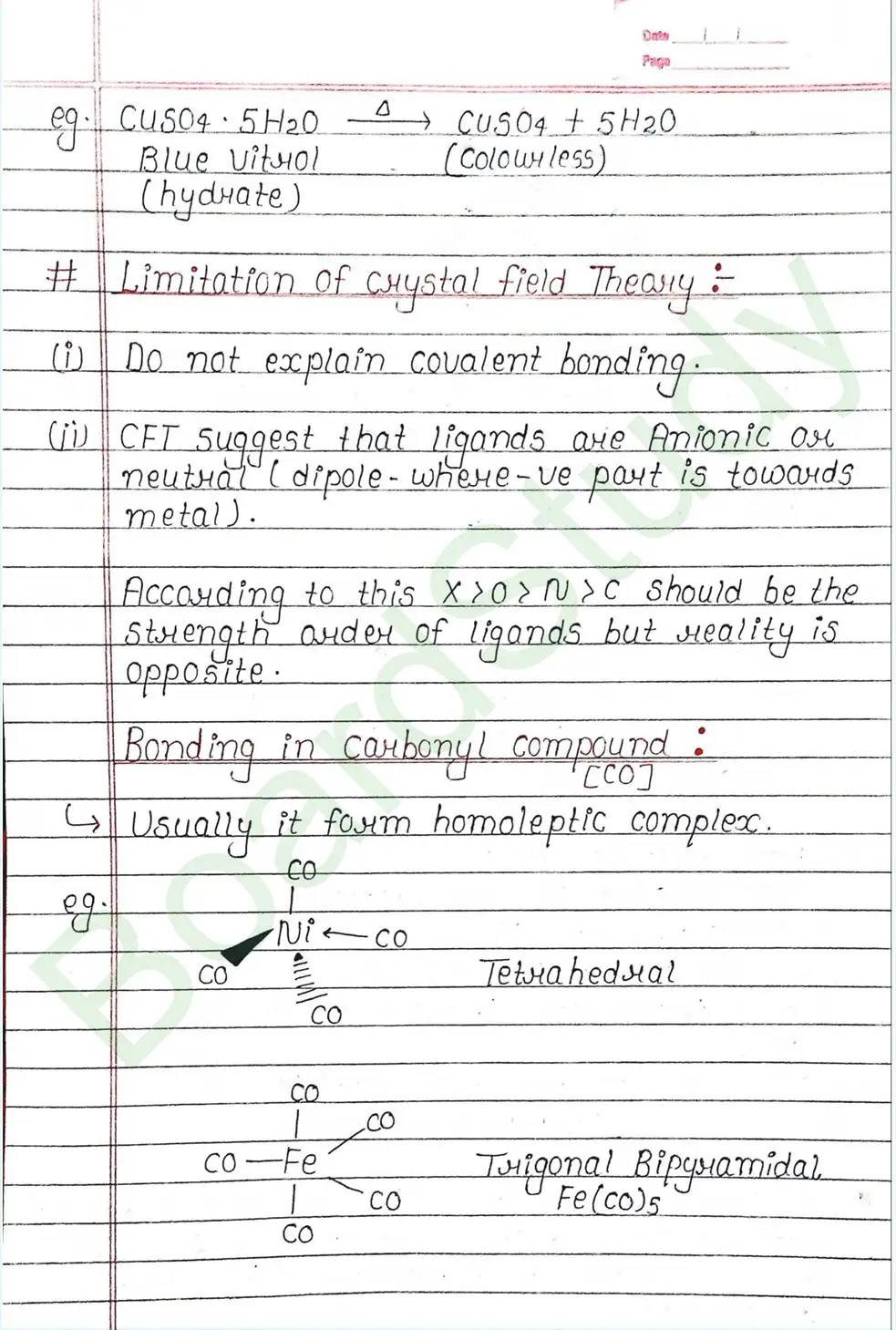
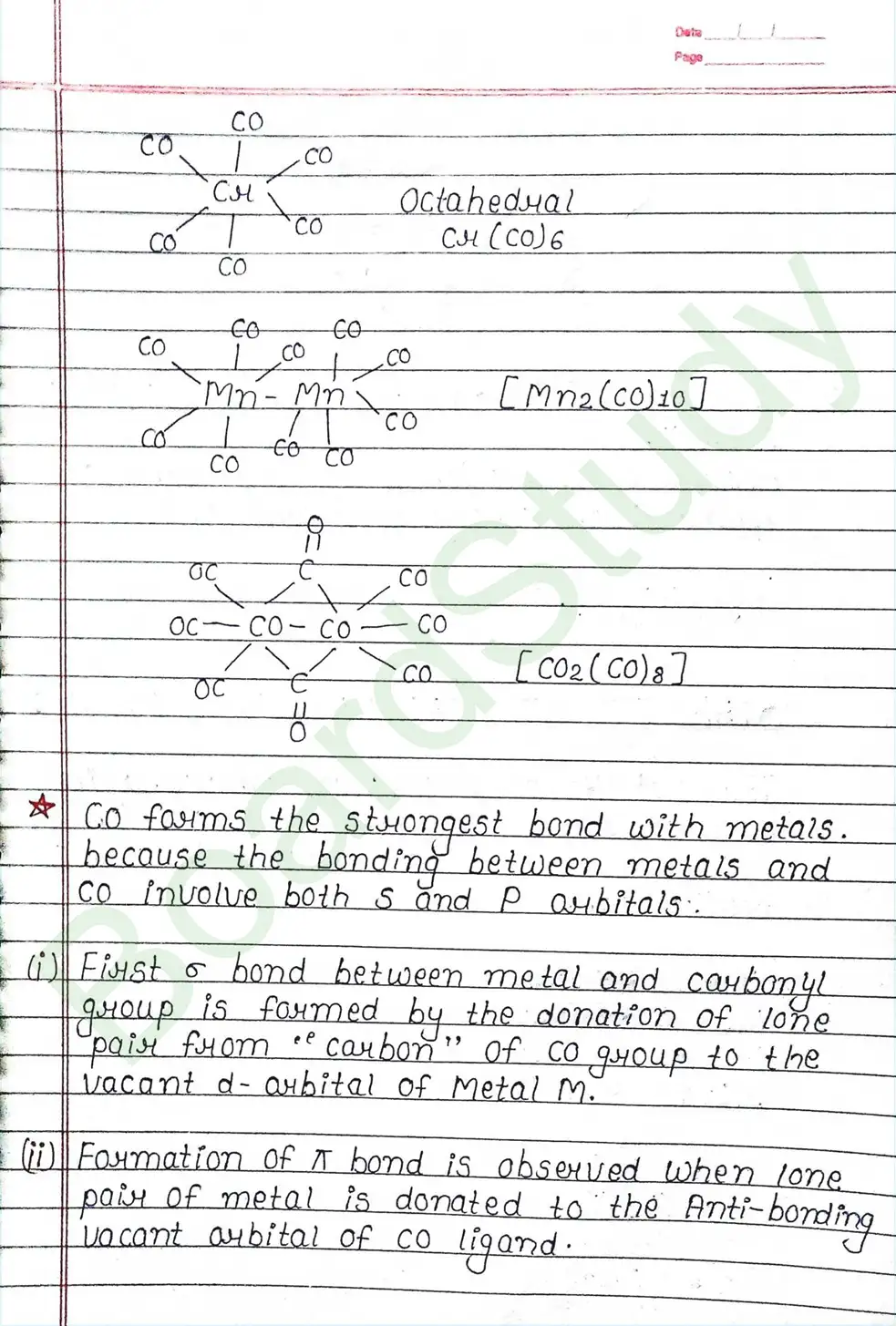
CRYSTAL FIELD THEORY (CFT)
- Based on electrostatic model.
- Anionic ligands are negatively charged and neutral ligands are considered as point dipoles where the negative part is oriented towards CMA.
- The interaction between CMA and Ligands are completely electrostatic (ionic) and there is no intermixing of orbitals & no intersection of e- electron in metal orbital
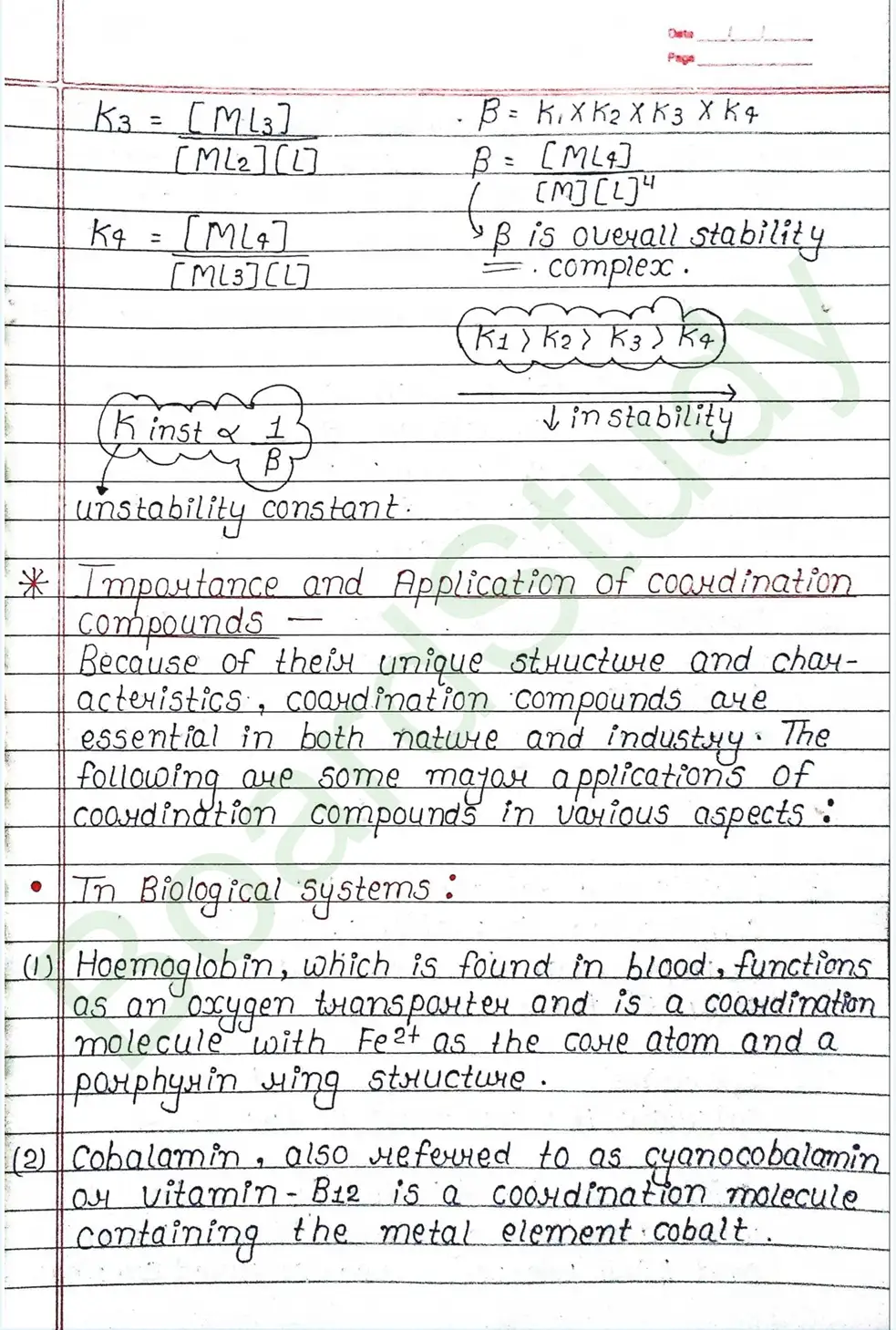
Importance and Application of coordination compounds
Because of their unique structure and characteristics, coordination compounds are essential in both nature and industry. The following are some major applications of coordination compounds in various aspects:
In Biological systems:
- Haemoglobin, which is found in blood, functions as an oxygen transporter and is a coordination molecule with Fe²⁺ as the come atom and a porphyrin ring structure.
- Cobalamin, also referred to as cyanocobalamin vitamin B12 is a coordination molecule containing the metal element cobalt.
- chlorophyll, the pigment responsible for plants’ green colour and photosynthesis, is a coordination molecule containing a Magnesium caré atom.
Features of Notes
- Students can use Coordination Compounds notes for last minute revision.
- In the last few days of exam students feel very stress due to pressure of exam. Notes will be very helpful for managing the stress in the last days of exam.
- All notes are totally free of cost and students can access notes anytime on our for totally free of cost.
- Coordination Compounds Notes PDF are created very carefully so you can rely on this notes.
Summary
| Chapter | Coordination Compounds |
| Chapter Number | 5 |
| Subject | Chemistry |
| Class | 12 |
| Medium | English |
FAQ
what is double salt ?
A double salt is a substance formed by combining two different salts that crystallize as a single substance but ionize as two distinct salts when dissolved in water. These salts lose their identity in solution, which means that when dissolved in water, they test positive for all of the ions present in the salt. eg. Mohr’s salt, potash alum.
What is coordination compound ?
Coordination compounds: A coordination compound is a molecular compound formed by the combination of two or more simple molecular compounds that retains its identity both solid and dissolved.
Are these notes sufficient for board exam?
Coordination Compounds handwritten notes are created by topper’s and expert teacher keeping board exam in mind so you can score maximum in board exam.
Are Coordination Compounds Handwritten notes according to NCERT latest syllabus?
Yes notes are created according to the NCERT latest syllabus.
How can i download Coordination Compounds Notes PDF?
For downloading Coordination Compounds Notes PDF click on Download PDF button.

Thanks 🙏🙏🙏