Here we have shared class 12 Chemistry Solutions Notes. Solutions notes is a best resources for students who are preparing for their board exam because it compile the entire lesson into short and includes every important topics.
With the help of Solutions notes students can understand the chapter in a better way. Notes are prepared by very experience teachers in an organised way so students can rely on this notes for their exam preparation.
Class 12 Chemistry Solutions Handwritten Notes






















Next Chapter: Electrochemistry
Other Subjects:
Class 12 Biology Notes
Class 12 Physics Notes
Students can access this notes anytime on our website for free of cost. If you found notes helpful, you can also help your friends by sharing with them.
Key Points: Solutions Notes PDF
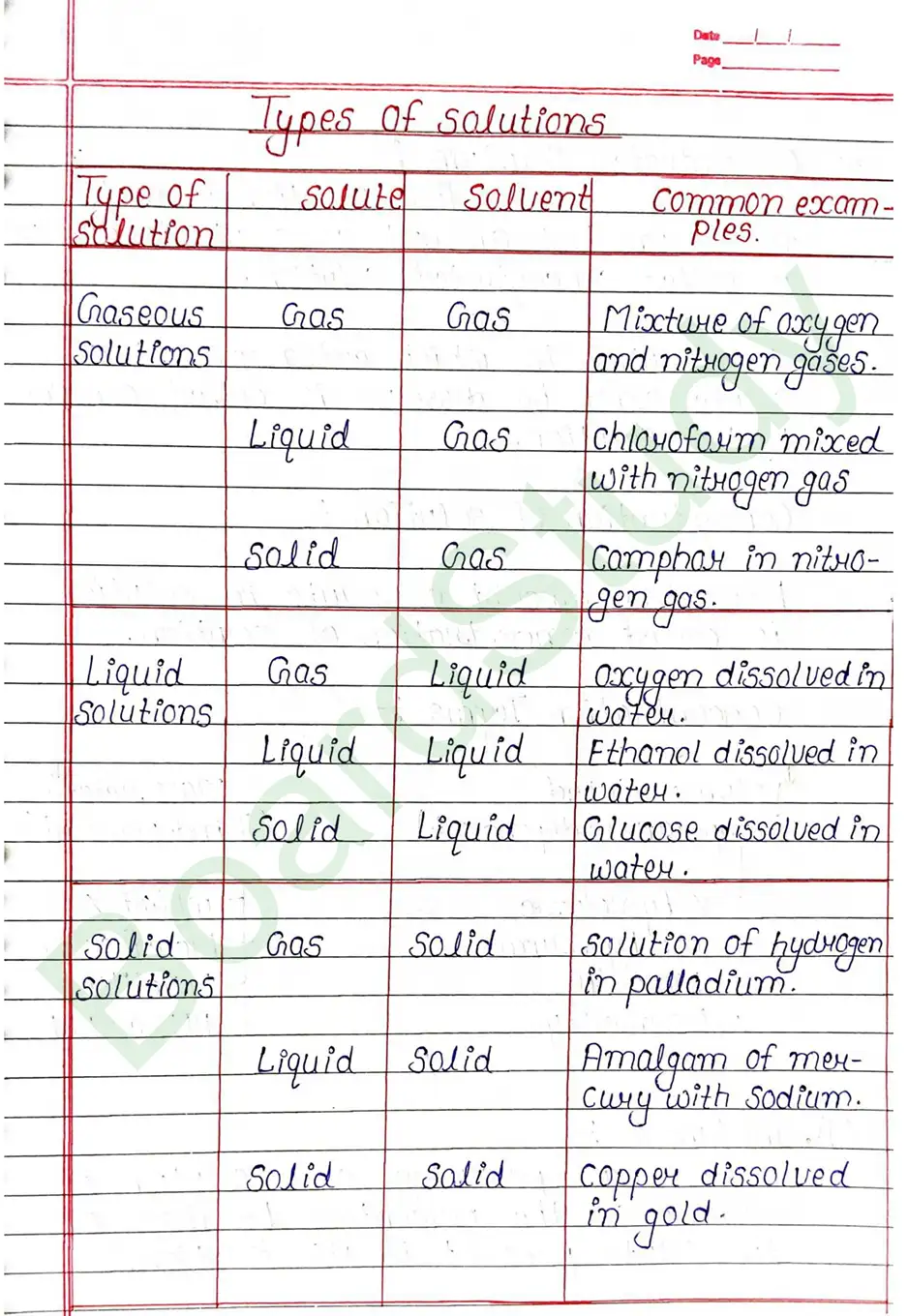
Solution: A solution is a homogeneous mixture of two or more substances, in which the solute is unifarmly dispersed at the molecular or ionic level within the Solvent.
Homogeneous mixture :- That mixture which is found as uniform is called homogeneous mixture.
Solute The substance that is dissolved in a solvent to form a solution. It is present in smaller amount.
Solid Solution is a solution in which the Solvent is solid and solid, liquid or gas can be solute.
Concentrated Solution : That solution in which maximum last amount of solute is dissolve is called concentrated solution.
Mole fraction: The ratio of mole of component and mole of solution is called mole fraction.
Molarity: The number of moles of solute dissolved in one liter of solution is called molarity.
Molality or molal concentration: The number of moles of solute dissolved in 1 kilogram of solvent. It is denoted by m.
Mass Fraction: The ratio of the mass of a component to the total mass of the mixture is called mass fraction.
Normality: Number of gram equivalent of solute which are present in 1L solution. It is denoted by N.
Solubility: At constant temperature, the amount of solid solute that dissolves in 100 g of solvent to form a saturated solution is called Solubility.
Crystallization: Crystallization is the process through which a pure solid forms from its solution by cooling or evaporation in the form of crystals.
Factors affecting solubility
- Nature of solute and solvent
- Temperature
Factors affecting solubility
- Nature of gas and solvent
- Effect of temperature
- Effect of pressure
Vapour pressure: Vapour pressure is the pressure exerted by the vapour of a liquid when it is in dynamic equilibrium with its liquid at a given temperature in a closed container.
- Nature of liquid. Weaker the intermolecular forces, greater the amount of Vapour pressure.
- Temperature Higher the temperature, greater the vapour pressure.
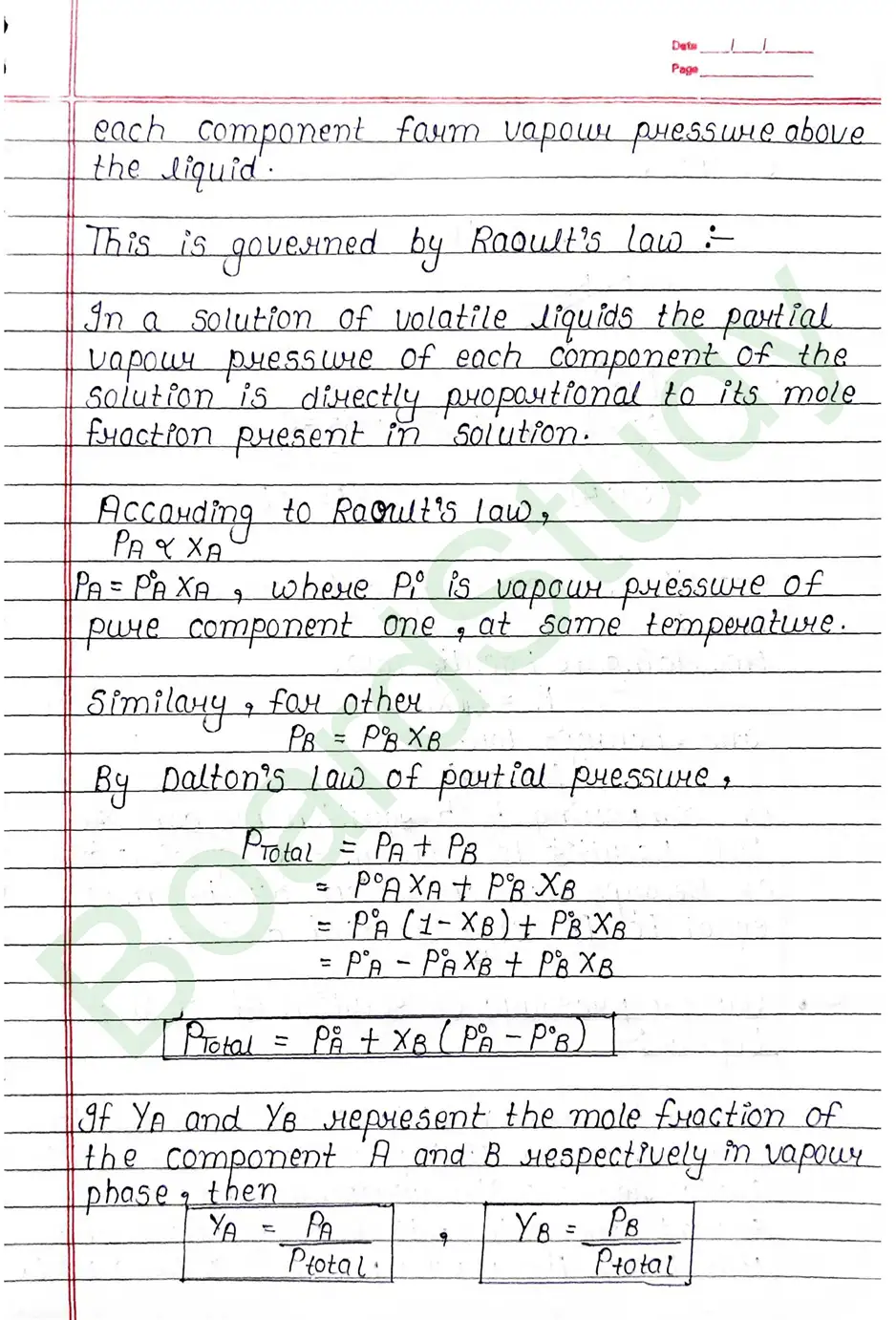
Raoult’s law: In a solution of volatile liquids the partial vapour pressure of each component of the solution is directly proportional to its mole fraction present in solution.
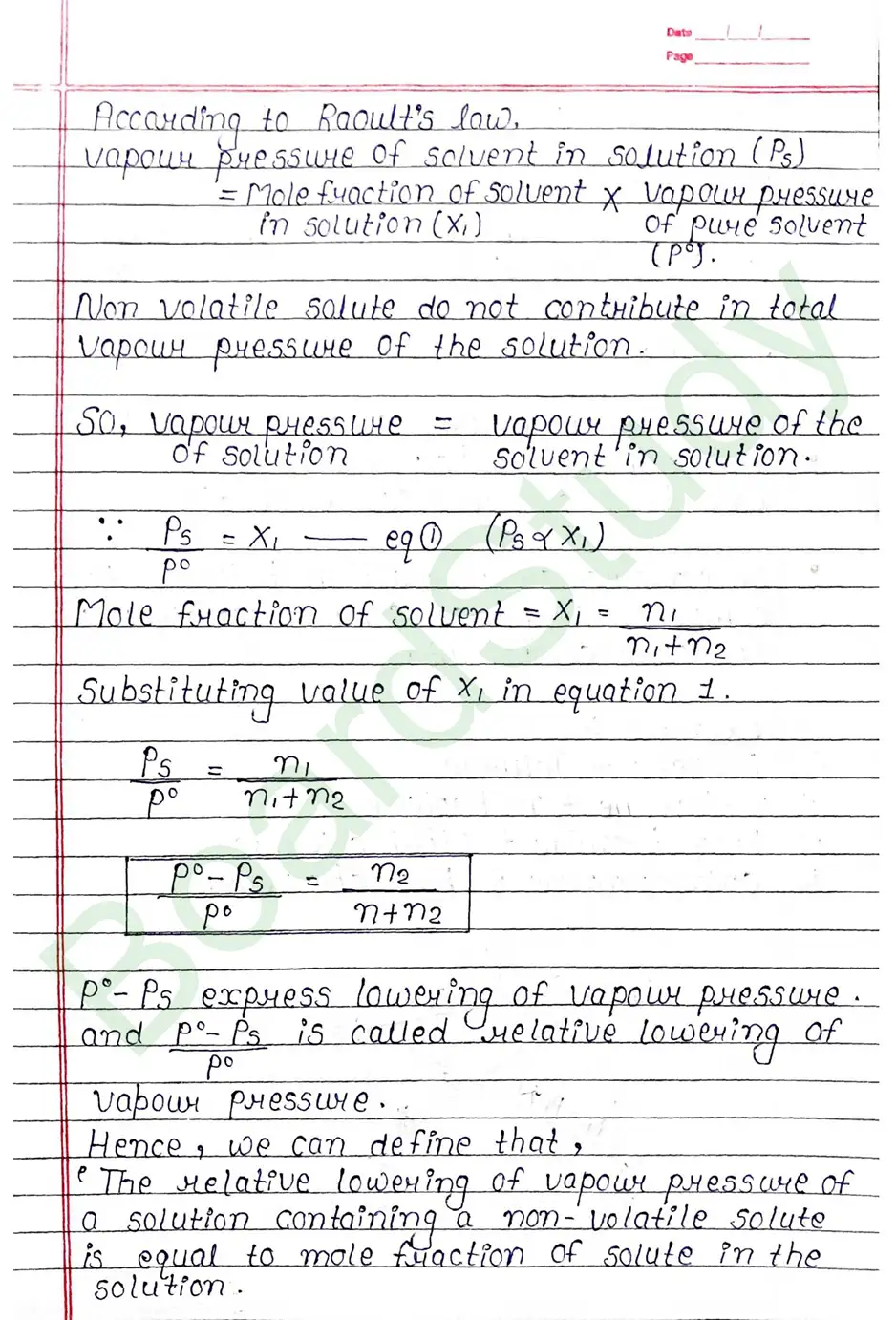
Vapour pressure of solution of solid in Liquid: On adding non-volatile solute in a solution. It is observed that presence of non-volatile solute reduces the escaping tendency of solvent molecule into vapour phase and thus lower the vapour pressure of the solvent.
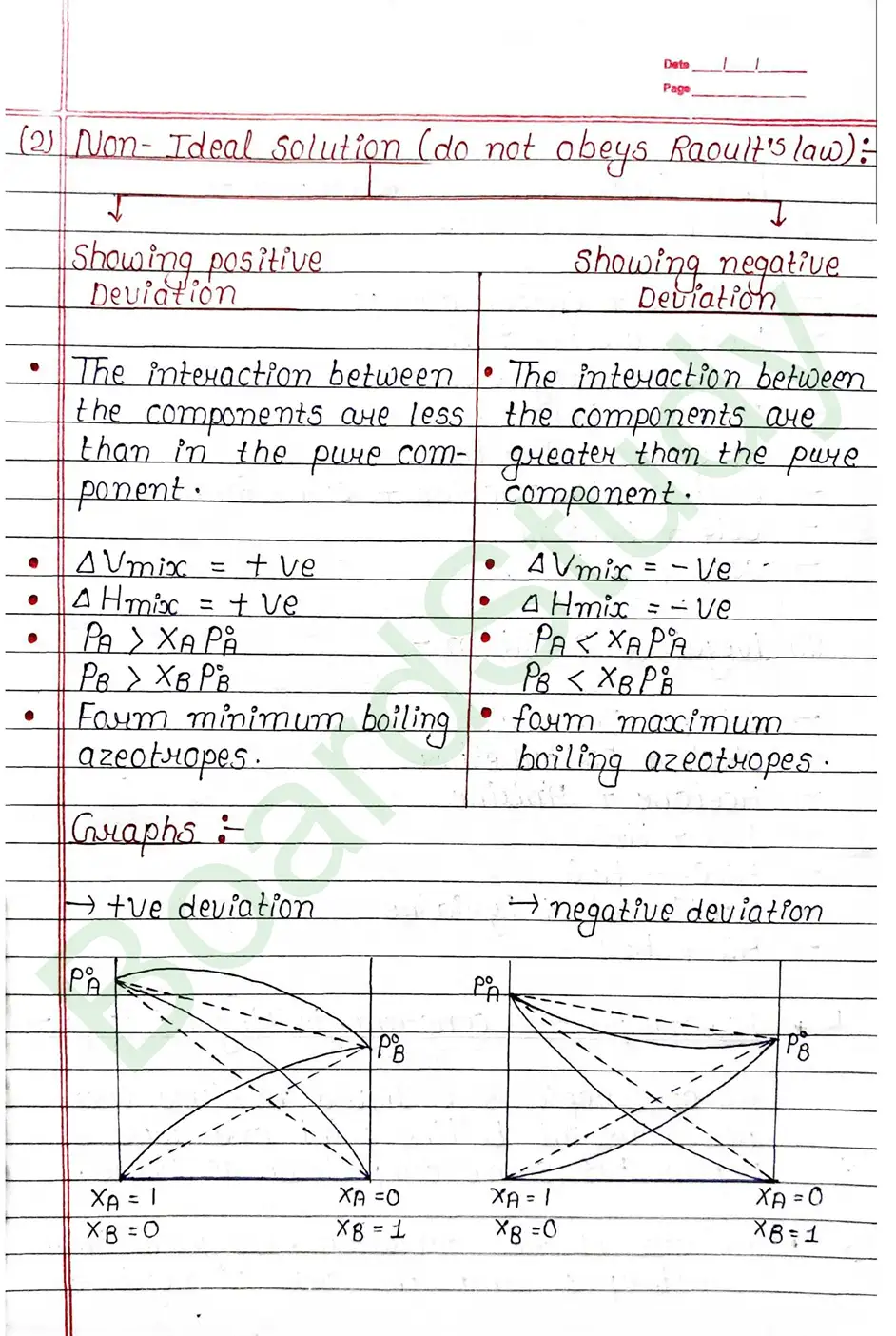
Azeotropic or Constant Boiling Mixture – An azeotrope is a liquid mixture that has constant boiling point and whose vapour has same composition as liquid.
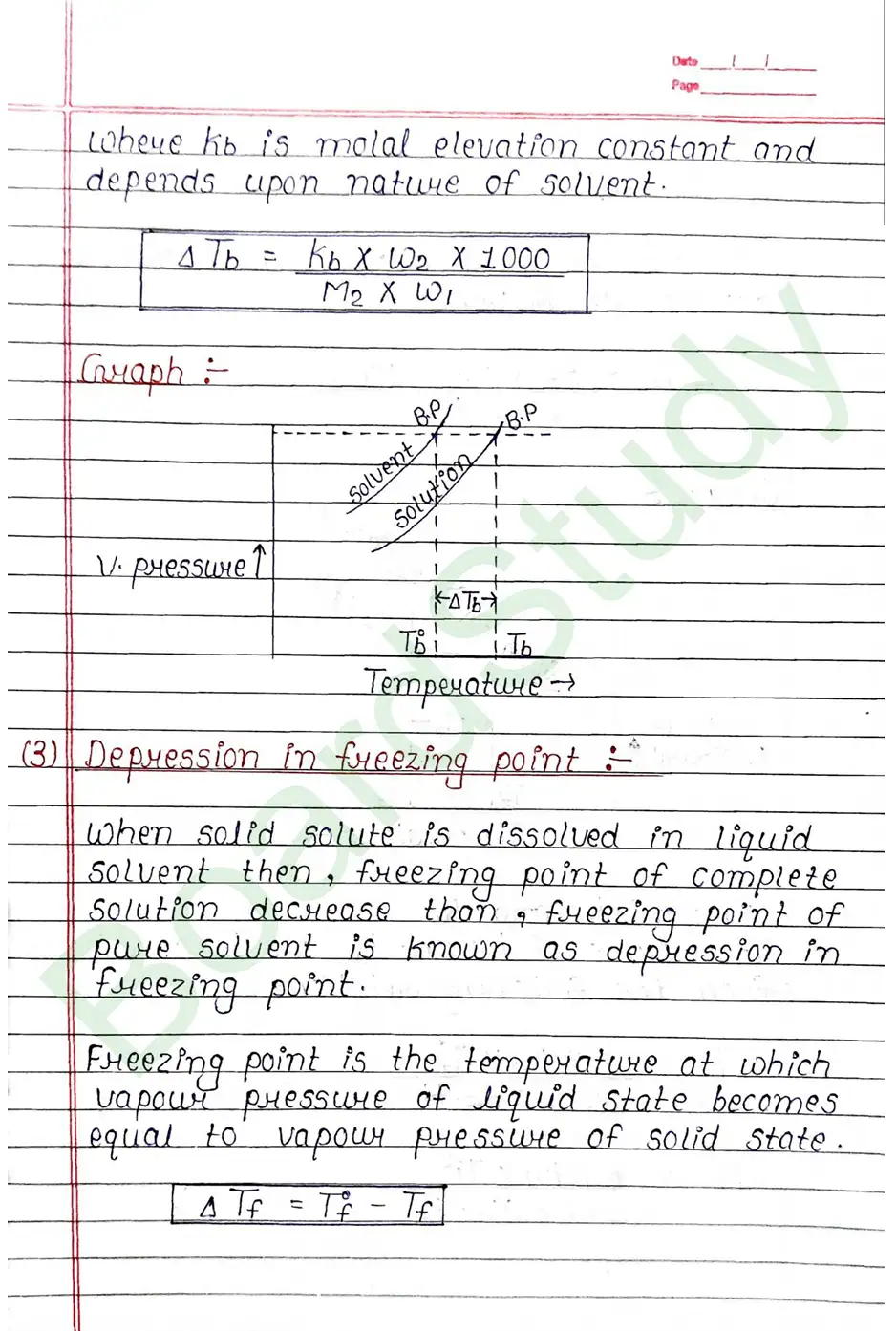
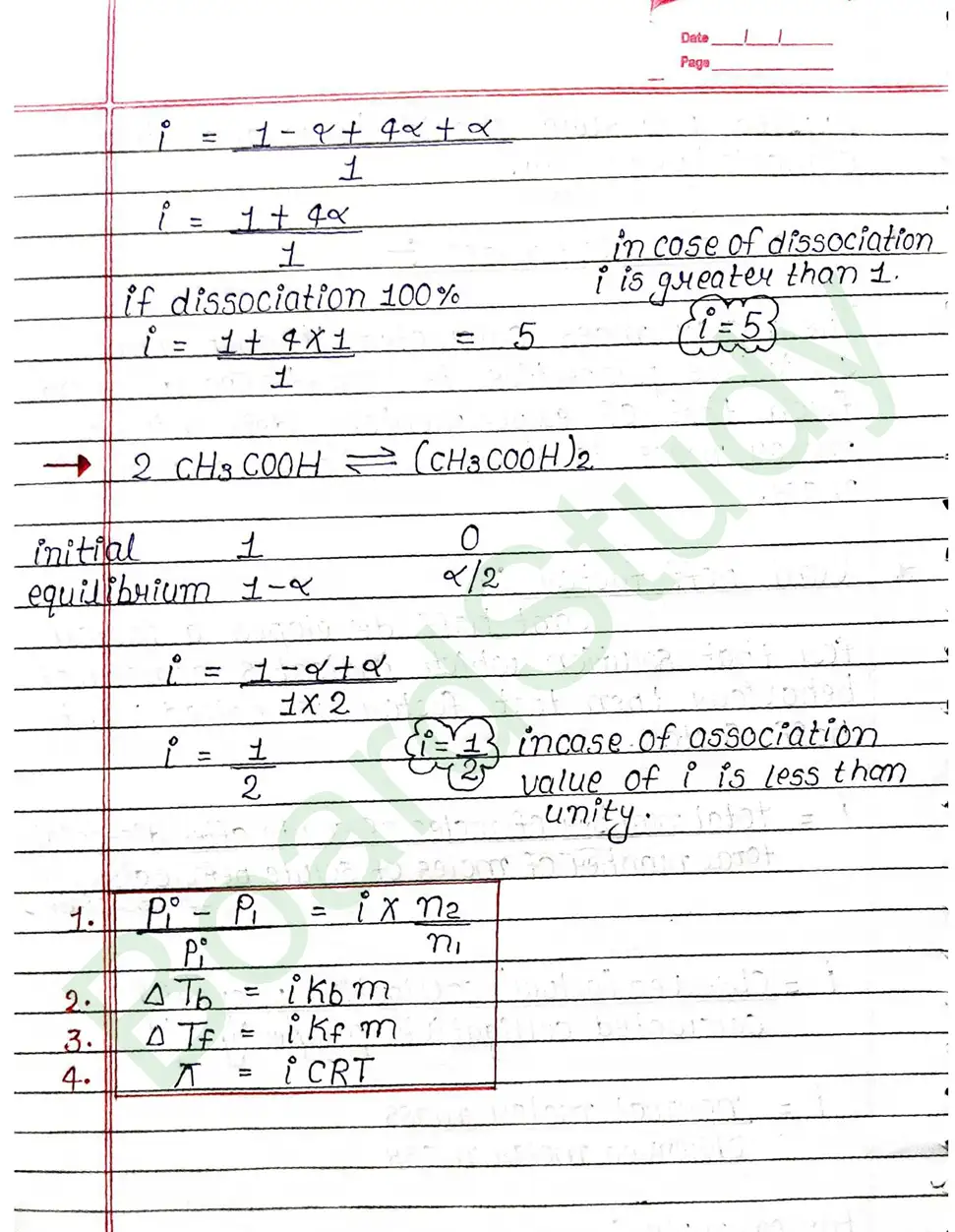
Colligative properties of solution: That property of solution which depends on number of particles of solute but it does not depend on nature of solute is known as colligative property of solution.
- Relative lowering of vapour pressure.
- Elevation in boiling point.
- Depression in freezing point.
- Osmotic pressure of Solution
Osmotic Pressure: Osmotic pressure is the minimum pressure that must be applied to a solution to stop the flow of pure solvent into the solution through a semipermeable membrane.
Features of Notes
- Students can use Solutions notes for last minute revision.
- In the last few days of exam students feel very stress due to pressure of exam. Notes will be very helpful for managing the stress in the last days of exam.
- All notes are totally free of cost and students can access notes anytime on our for totally free of cost.
- Solutions Notes PDF are created very carefully so you can rely on this notes.
Summary
| Chapter | Solutions |
| Chapter Number | 1 |
| Subject | Chemistry |
| Class | 12 |
| Medium | English |
FAQ
What is Molarity ?
The number of moles of solute dissolved in one liter of solution is called molarity.
What is mass fraction ?
The ratio of mass of a component to the total mass of the mixture is called mass fraction.
Are these notes sufficient for board exam?
Solutions handwritten notes are created by topper’s and expert teacher keeping board exam in mind so you can score maximum in board exam.
Are Solutions Handwritten notes according to NCERT latest syllabus?
Yes notes are created according to the NCERT latest syllabus.
How can i download Solutions Notes PDF?
For downloading Solutions Notes PDF click on Download PDF button.

heyy can you tell me, this notes of pcb is enough for boards! reply assp
yes
Thank you very much 😊
thank you so much
doing great work
thanku veryyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyy veryyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyy muchhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhhh
these are extremely helpful and perfect notes