Here we have shared class 12 Chemistry Aldehydes, Ketones, and Carboxylic Acids Notes. The Aldehydes, Ketones, and Carboxylic Acids notes is a best resources for students who are preparing for their board exam because it compile the entire lesson into short and includes every important topics.
With the help of Aldehydes, Ketones, and Carboxylic Acids notes students can understand the chapter in a better way. Notes are prepared by very experience teachers in an organised way so students can rely on this notes for their exam preparation.
Class 12 Chemistry Aldehydes, Ketones, and Carboxylic Acids Handwritten Notes
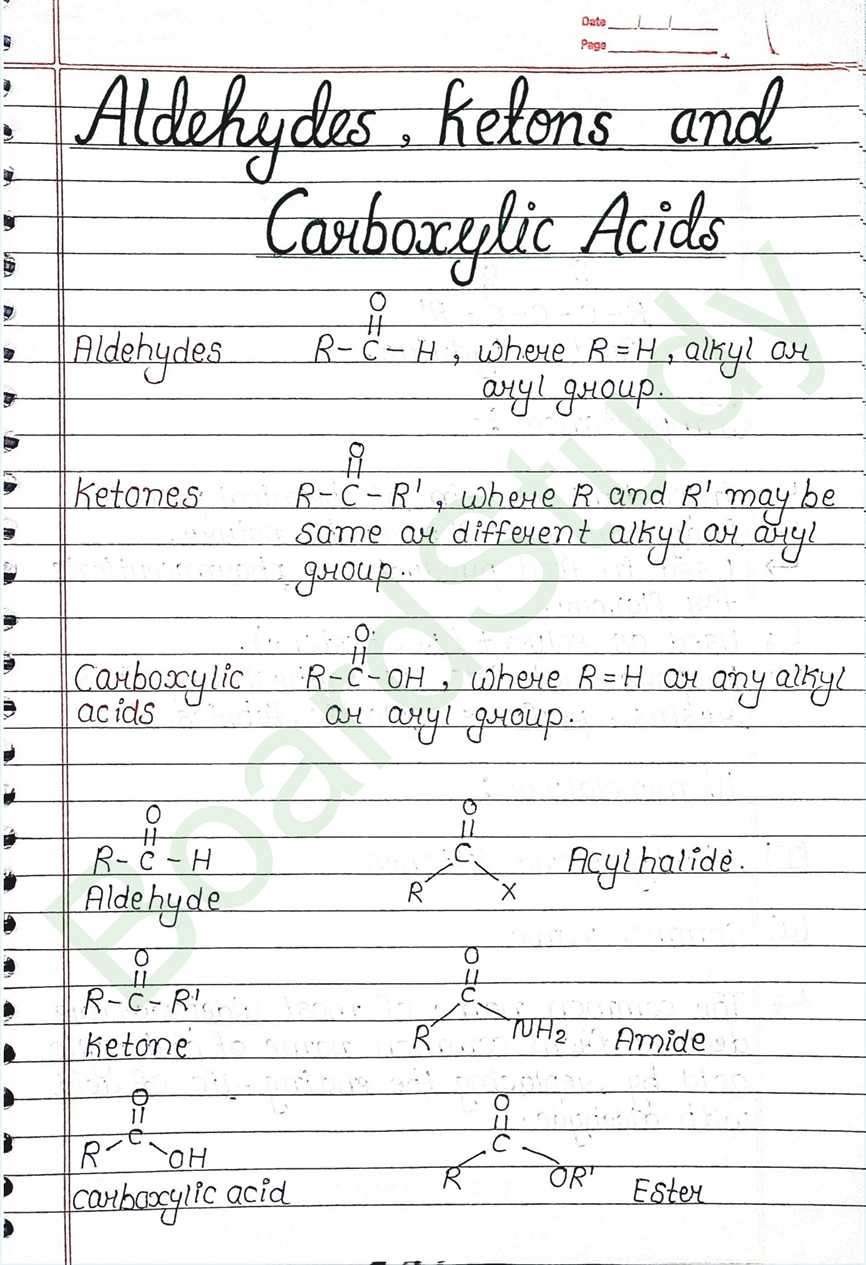

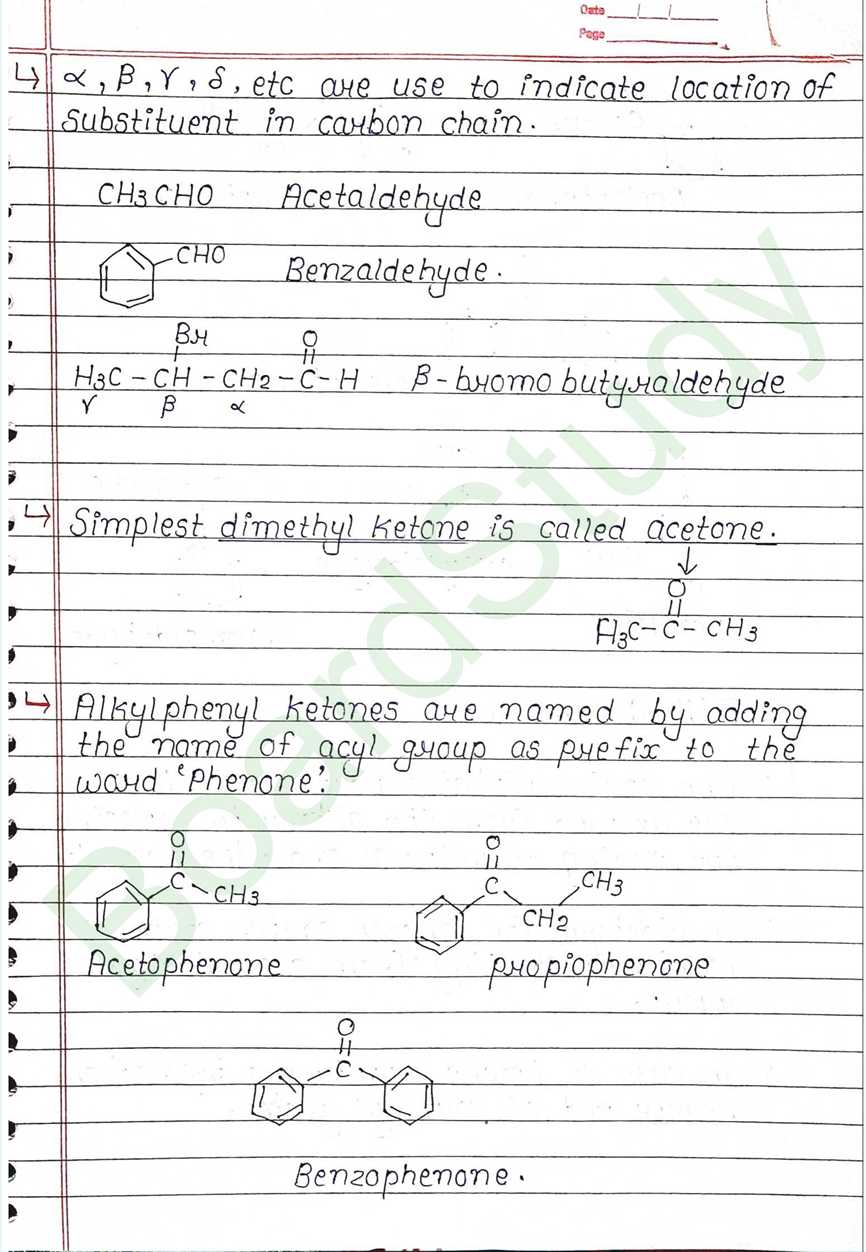
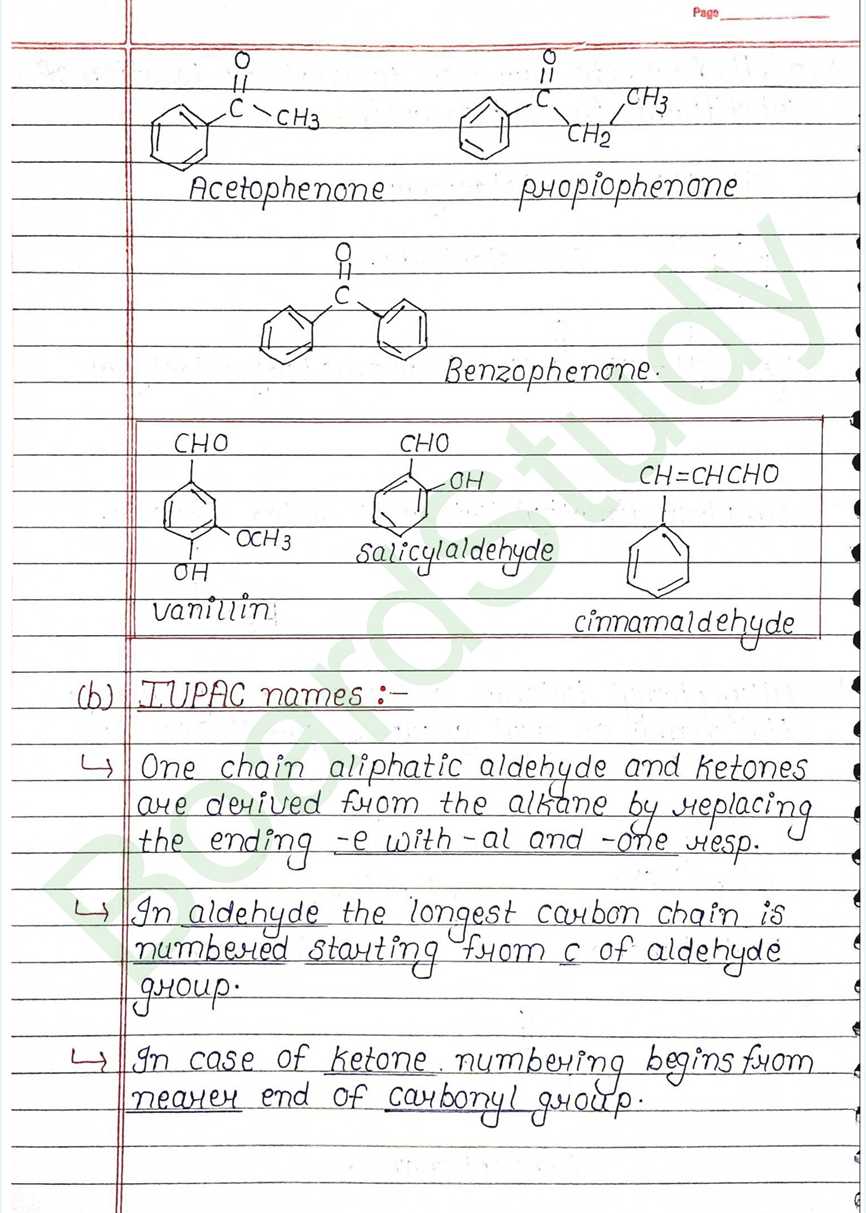
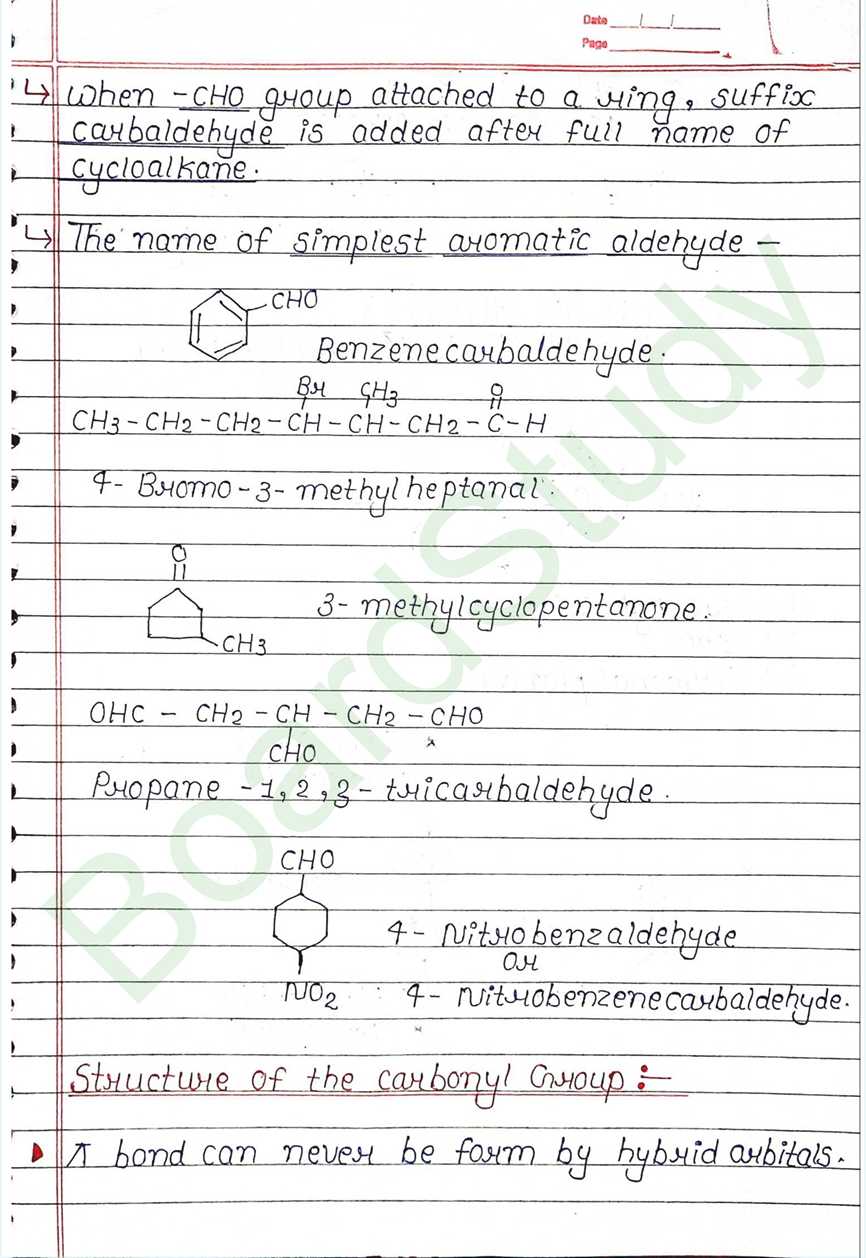
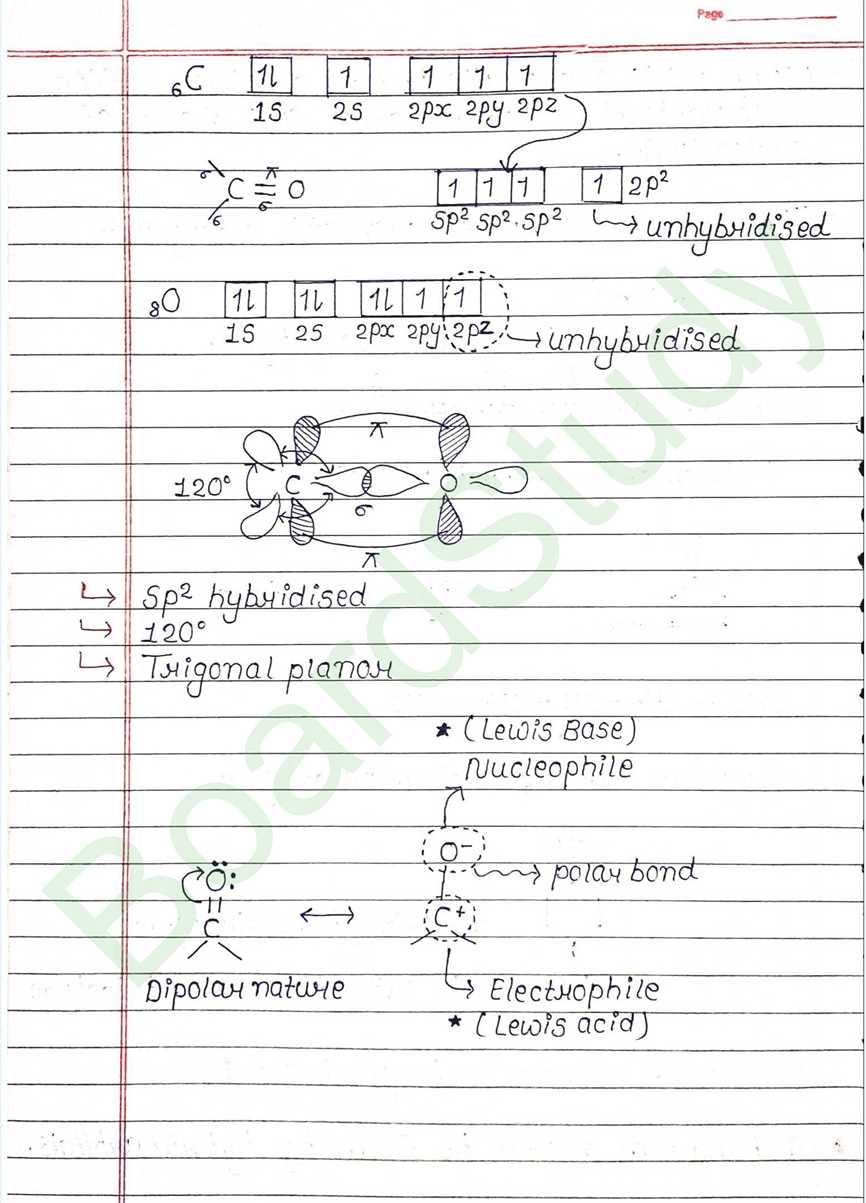
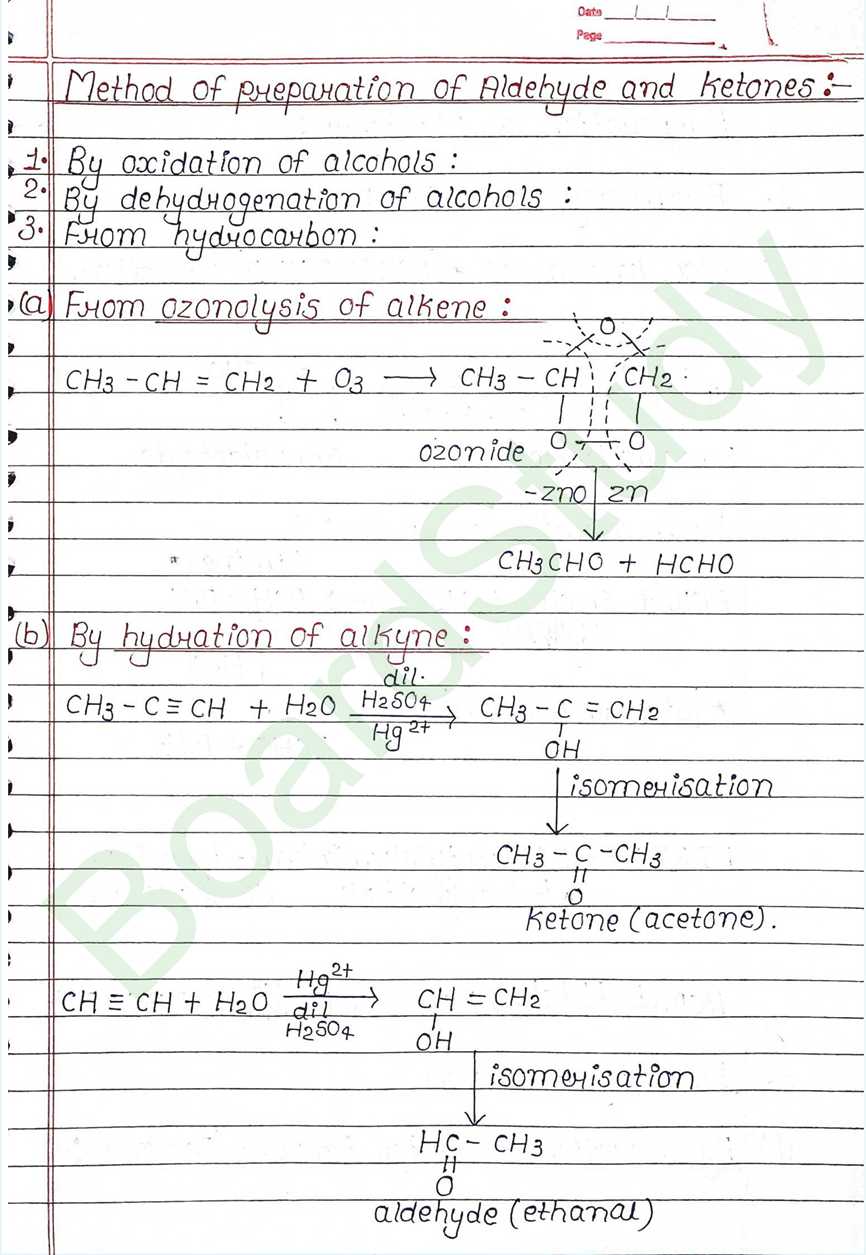
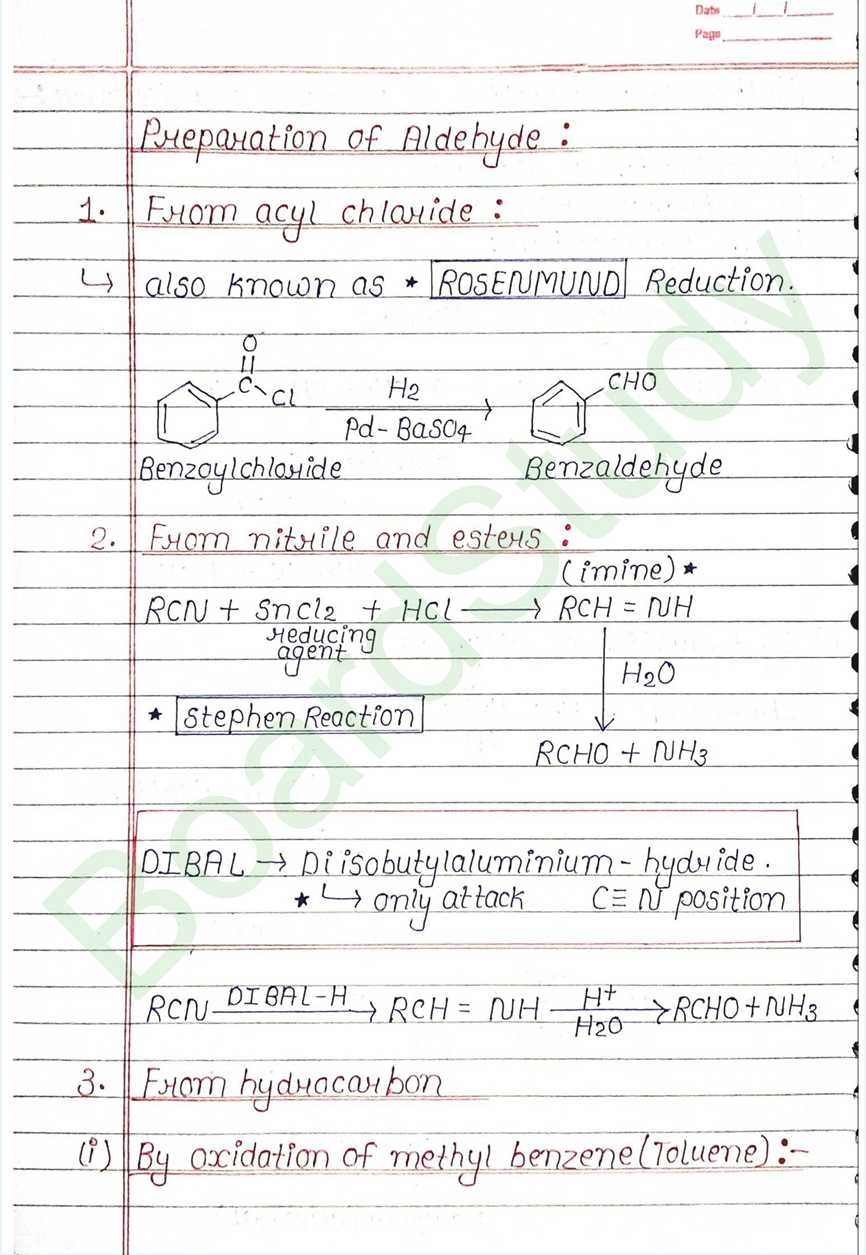
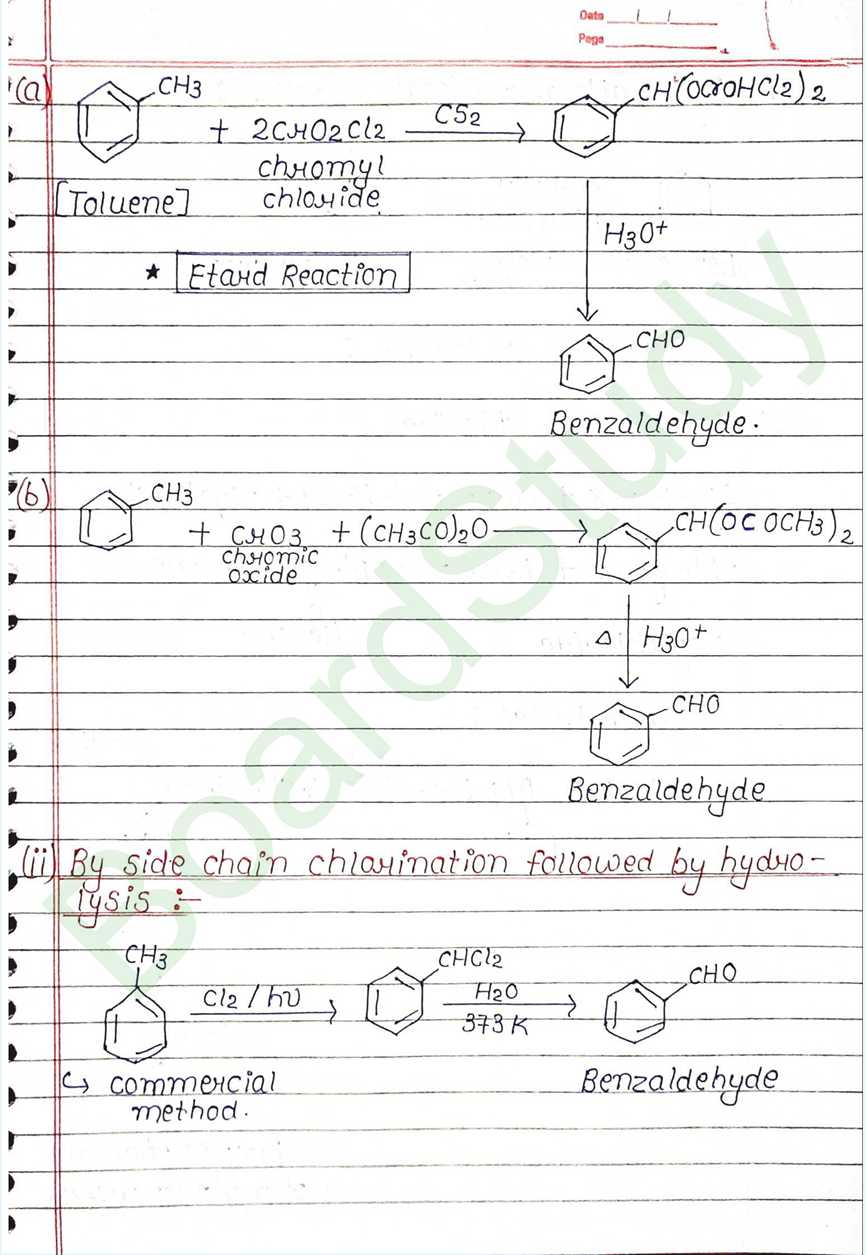

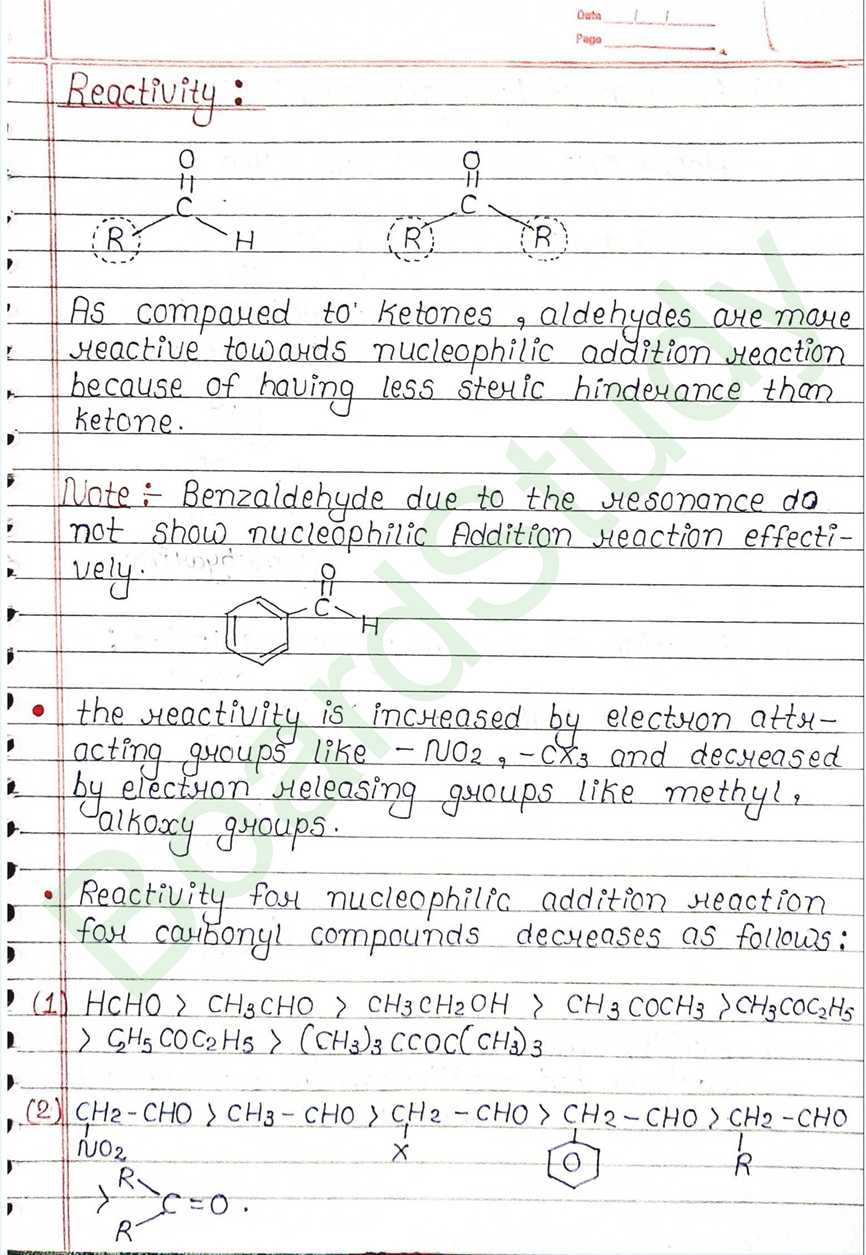
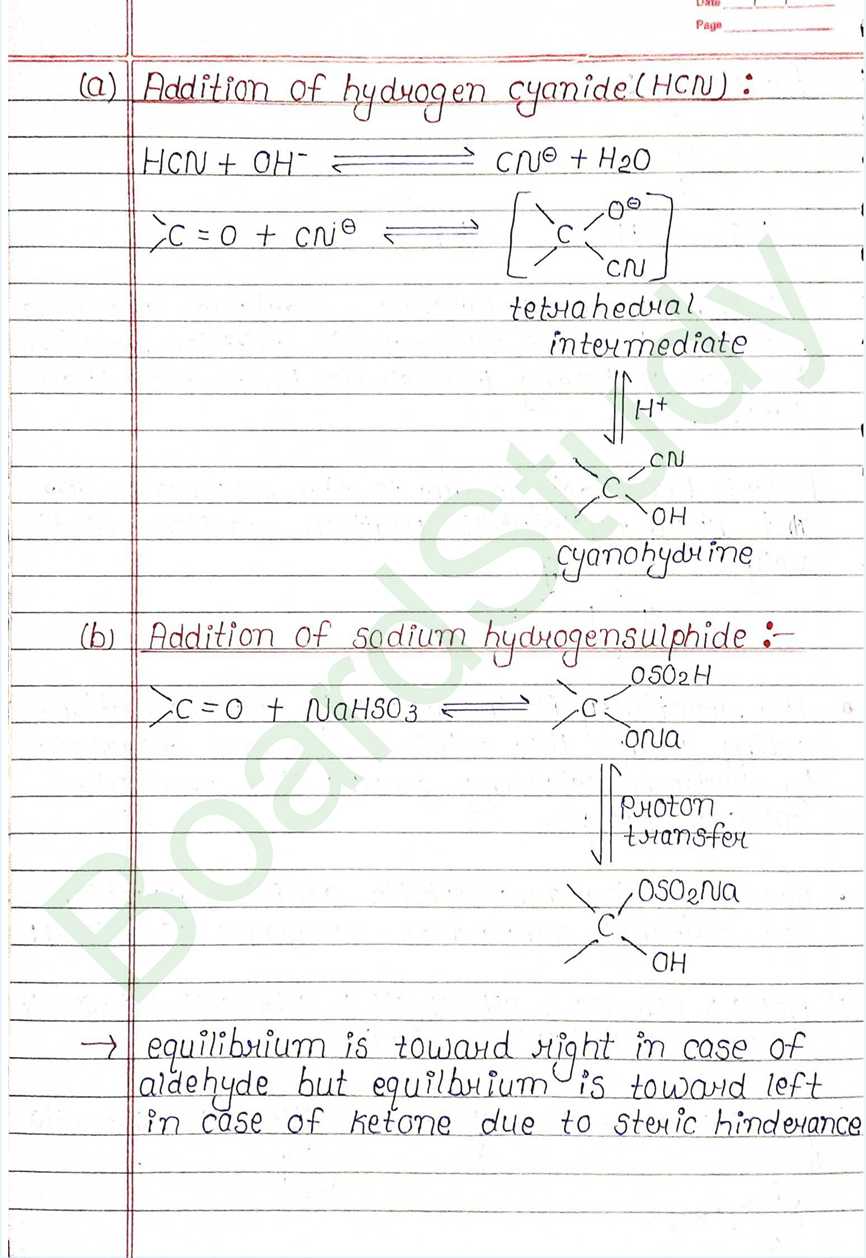
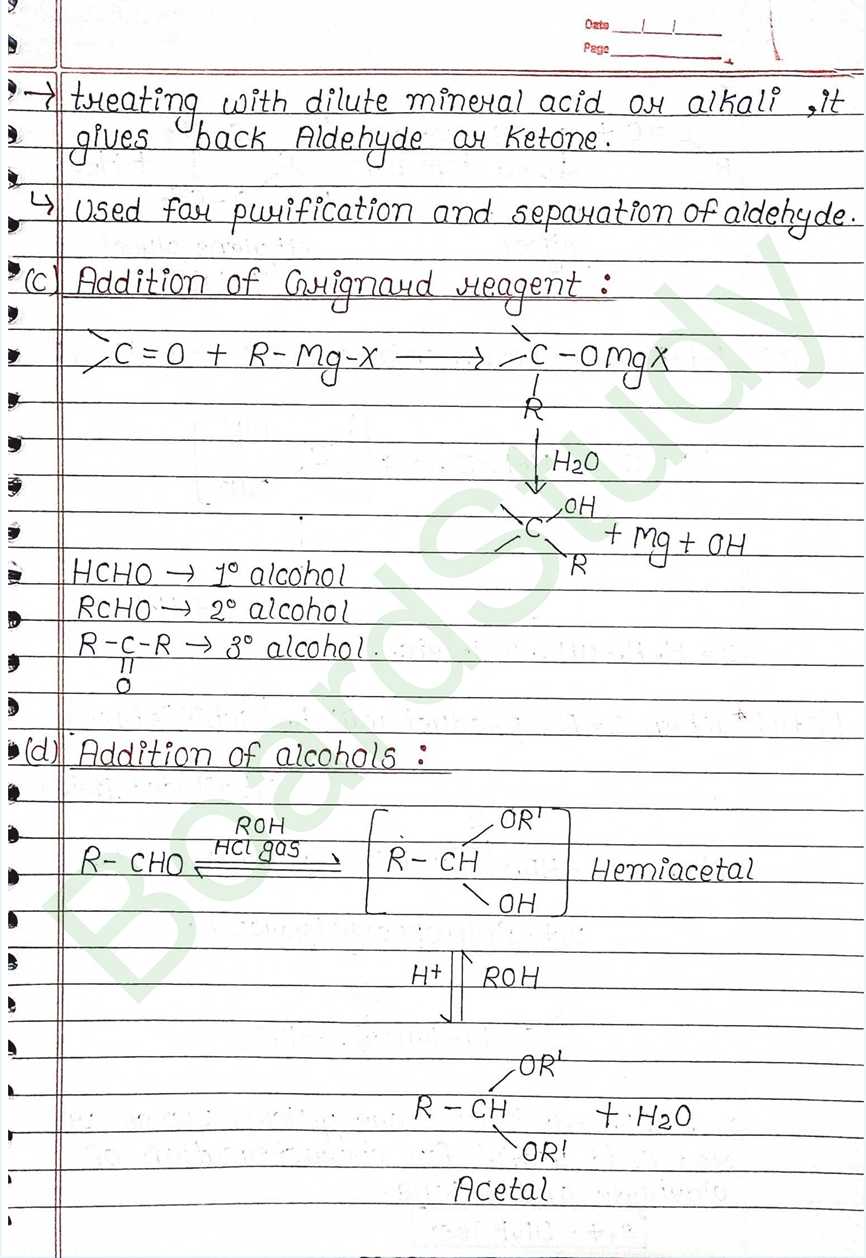




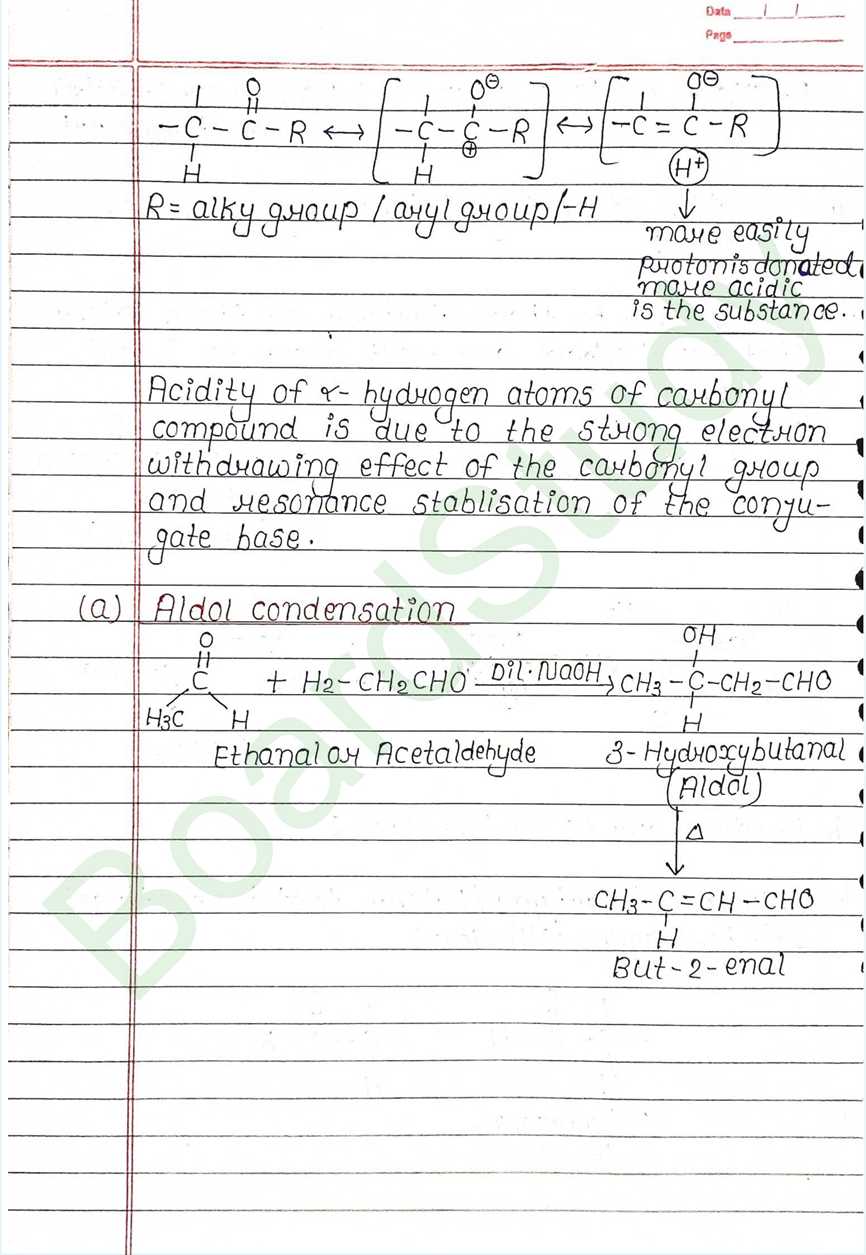












Next Chapter: Amines
Previous Chapter: Alcohols, Phenols, and Ethers
Other Subjects:
Class 12 Biology Notes
Class 12 Physics Notes
Students can access this notes anytime on our website for free of cost. If you found notes helpful, you can also help your friends by sharing with them.
Key Points: Aldehydes, Ketones, and Carboxylic Acids Notes PDF
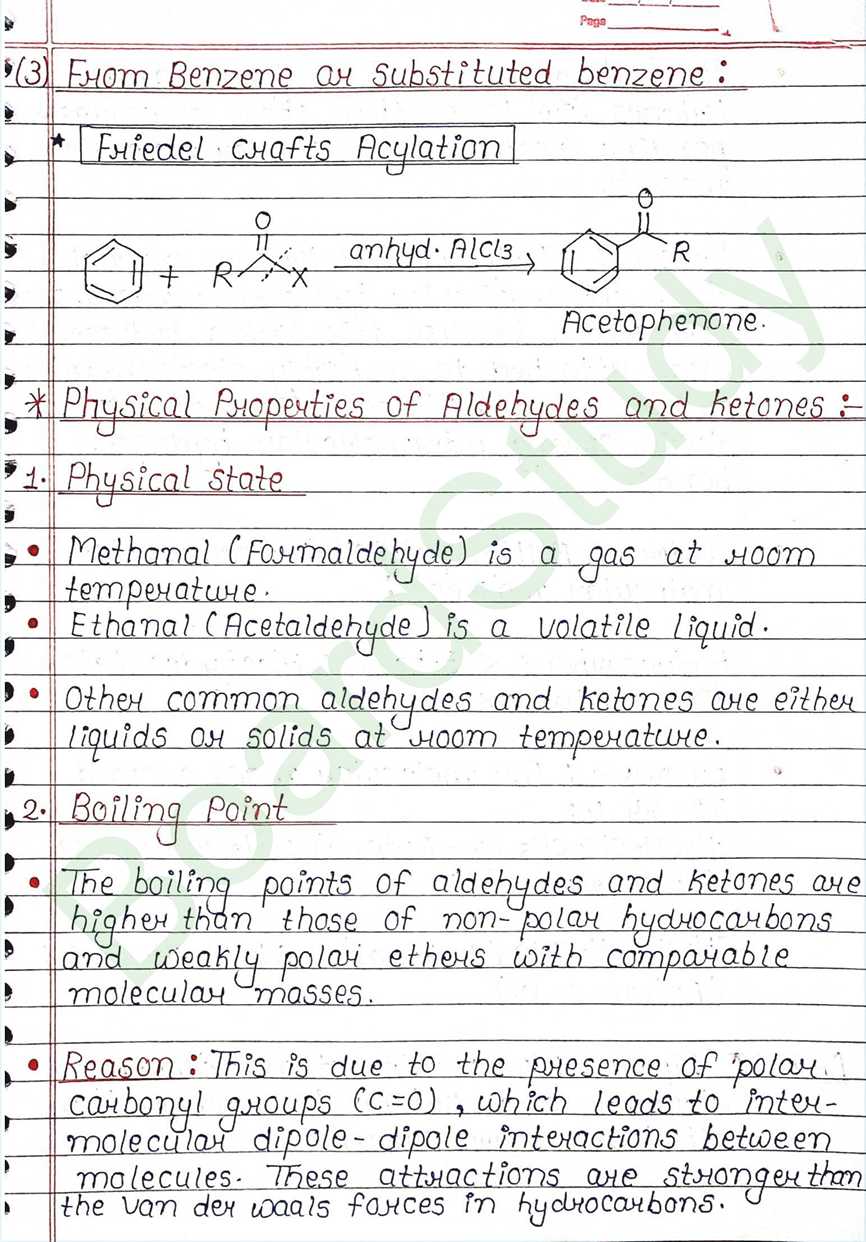
Physical Properties of Aldehydes and ketones:
- Physical state:
- Methanal (Formaldehyde) is a gas at room temperature.
- Ethanal (Acetaldehyde) is a volatile liquid.
- Other common aldehydes and ketones are either liquids or solids at room temperature.
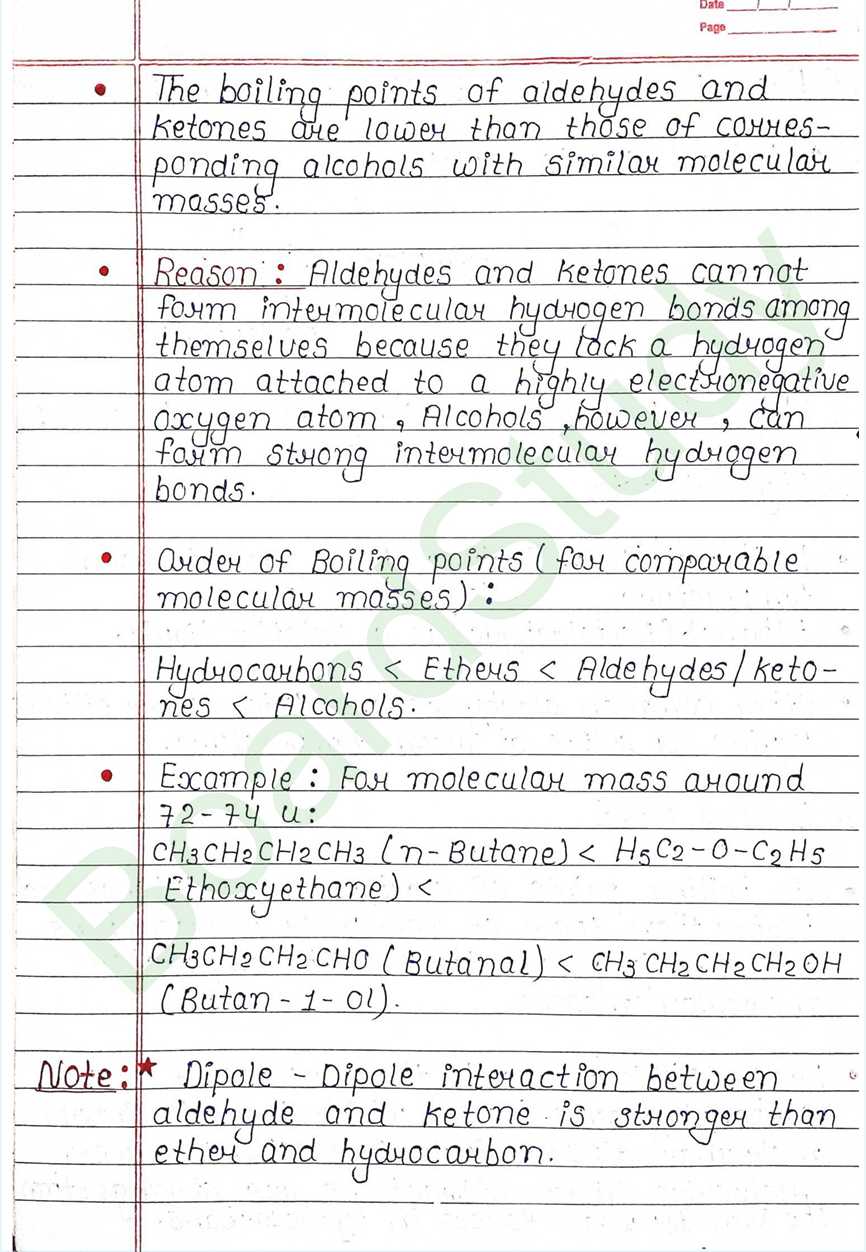
- Boiling Point:
- The Boiling poit of higher than those of non-polar hydrocarbons and weakly polar ethers with comparable molecular masses.
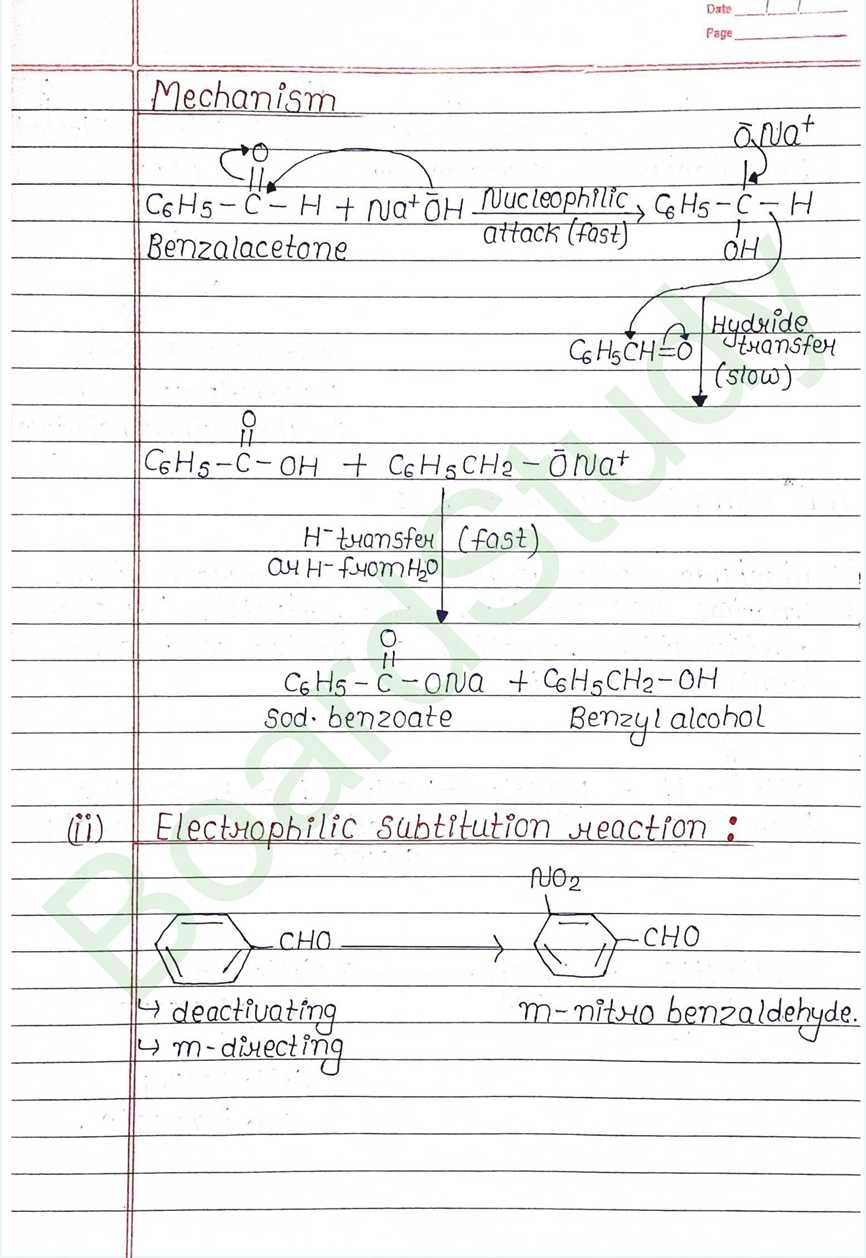
Cannizzaro reaction:
- aldehyde which do not have α hydrogen atom.
- undergo self oxidation and reduction (disproportionation) reaction on heated with concentrated alkali.
Uses of Aldehydes and ketones:
- Solvents
- Formalin (formaldehyde 40%) – preserve biological specimen.
- HCHO in bakelite.
- Flavouring and sweetning agent.
Carboxylic Acids: Organic compounds containing the carboxyl function group COOH.
Fatty Acids: Higher aliphatic carboxylic (c12 to C8) found in natural fats as esters of glycerol.
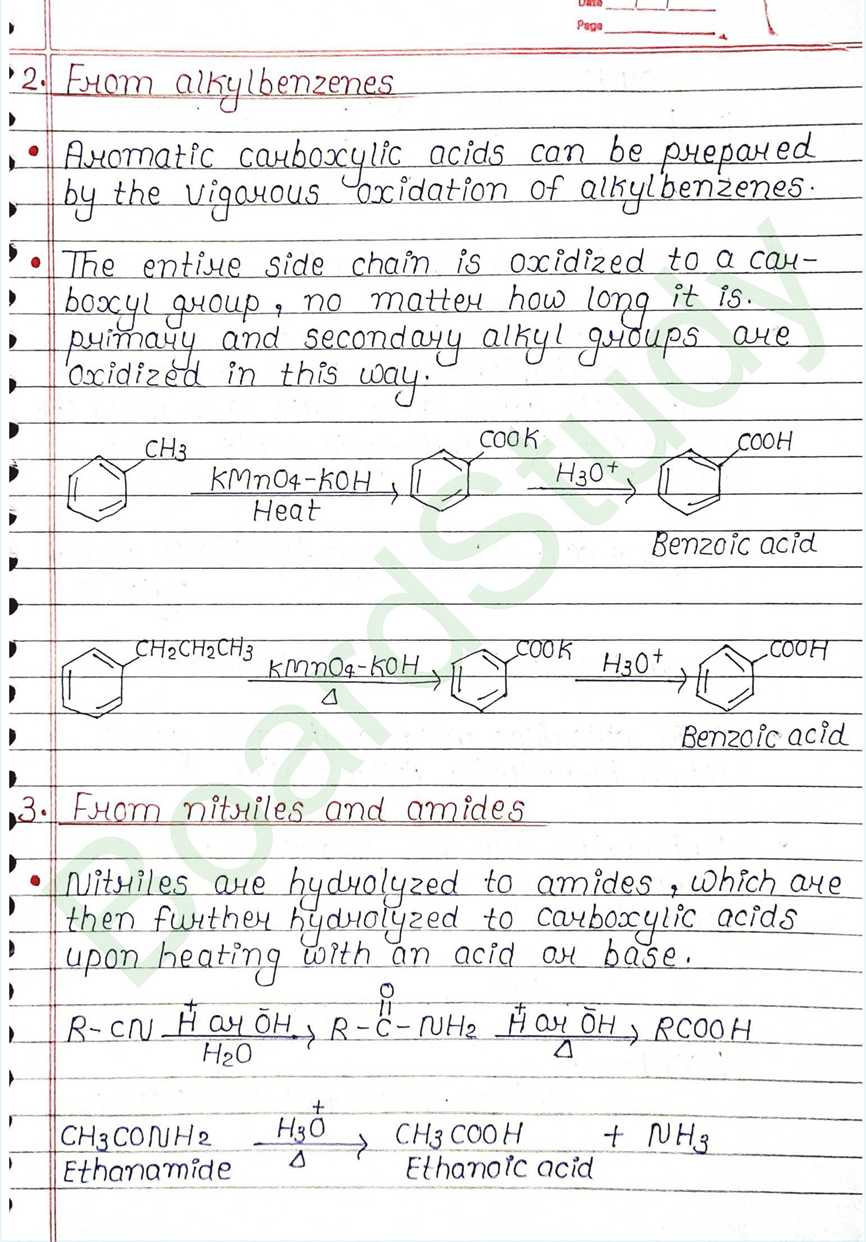
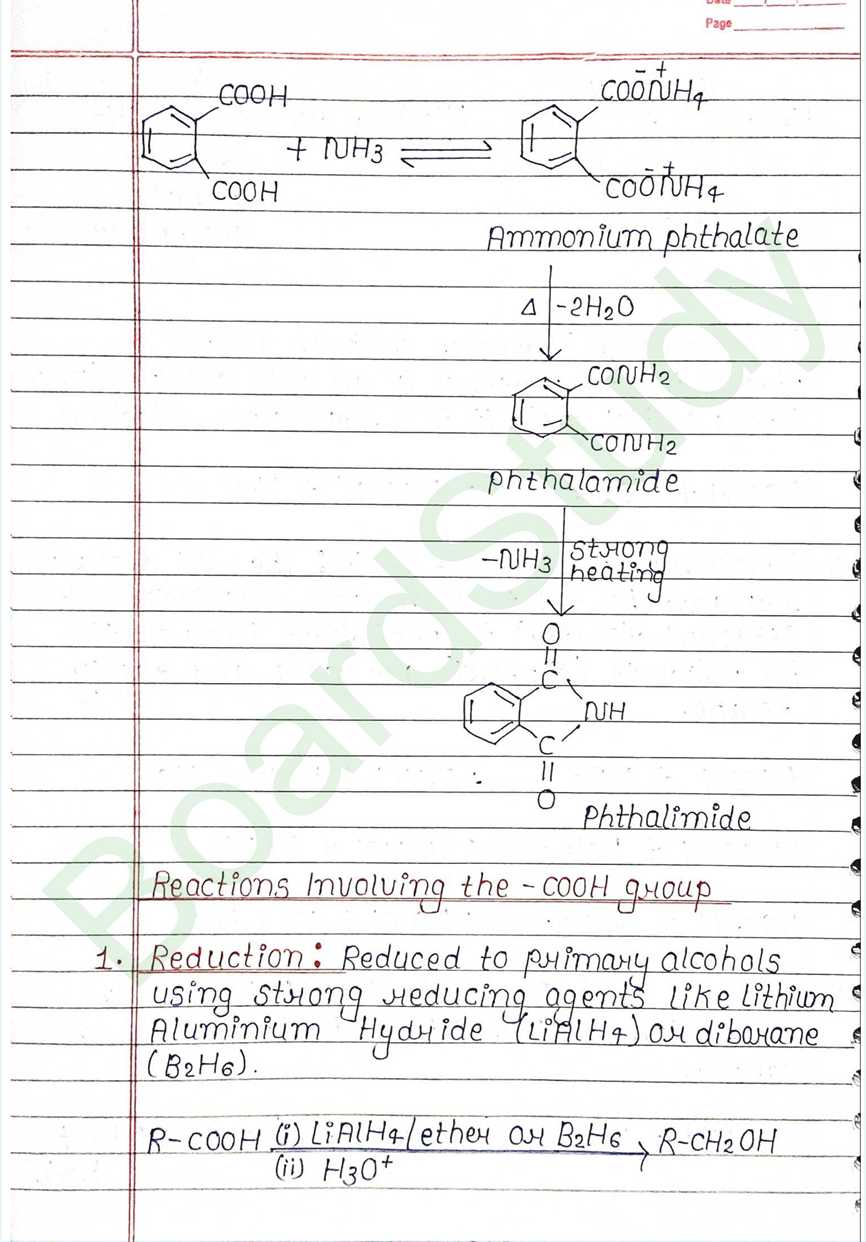
From alkylbenzenes
- Aromatic carboxylic acids can be prepared by the vigorous oxidation of alkylbenzenes.
- The entire side chain is oxidized to a carboxyl group, no matter how long it is.
- primary and secondary alkyl groups are Oxidized in this way.
Boiling point : carboxylic acids have higher boiling points than aldehydes, ketones and even alcohols of comparable masses.
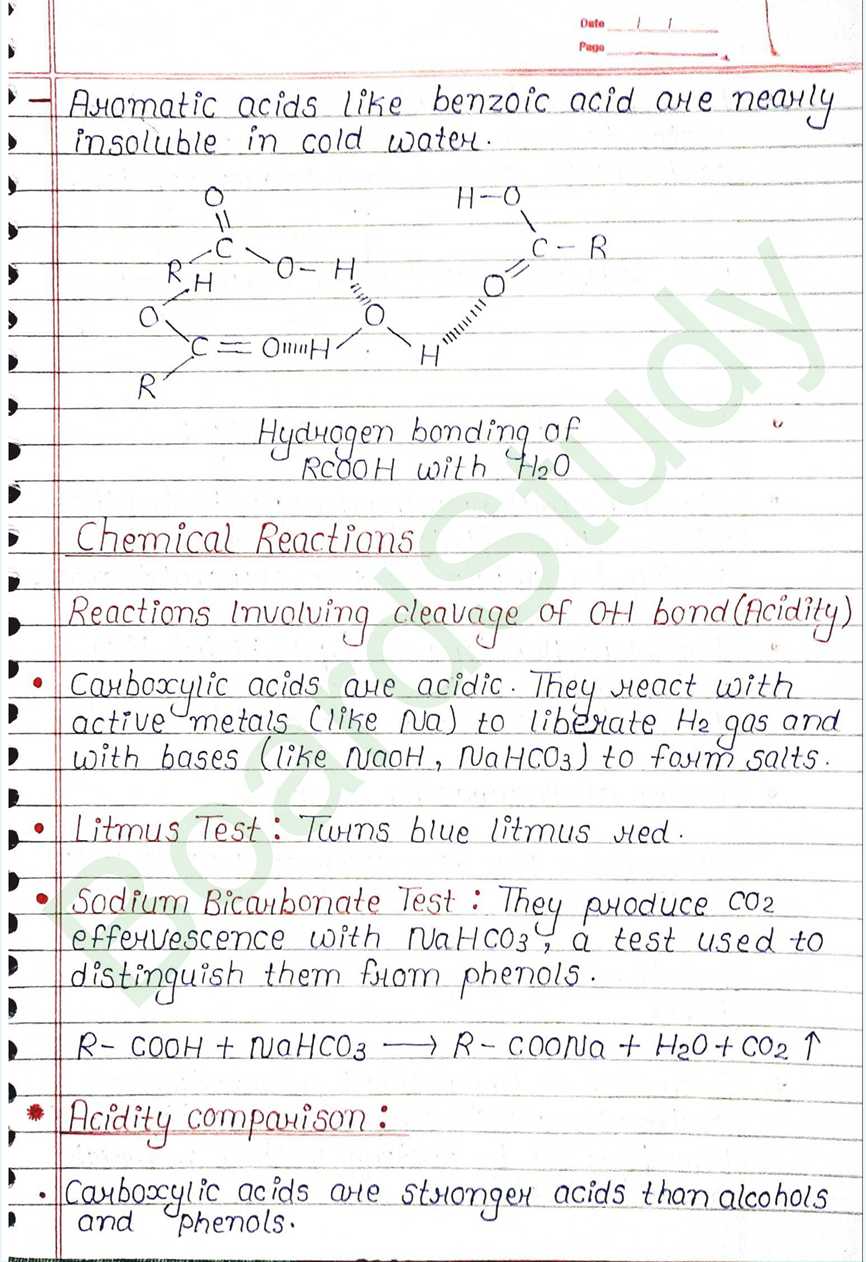
Solubility:
- Simple aliphatic carboxylic acids (up to 4 carbons) are miscible in water due to hydrogen bonding with water molecules
- Solubility decreases as the size of the alkyl group increases because the hydrophobic part of the molecule become larger.
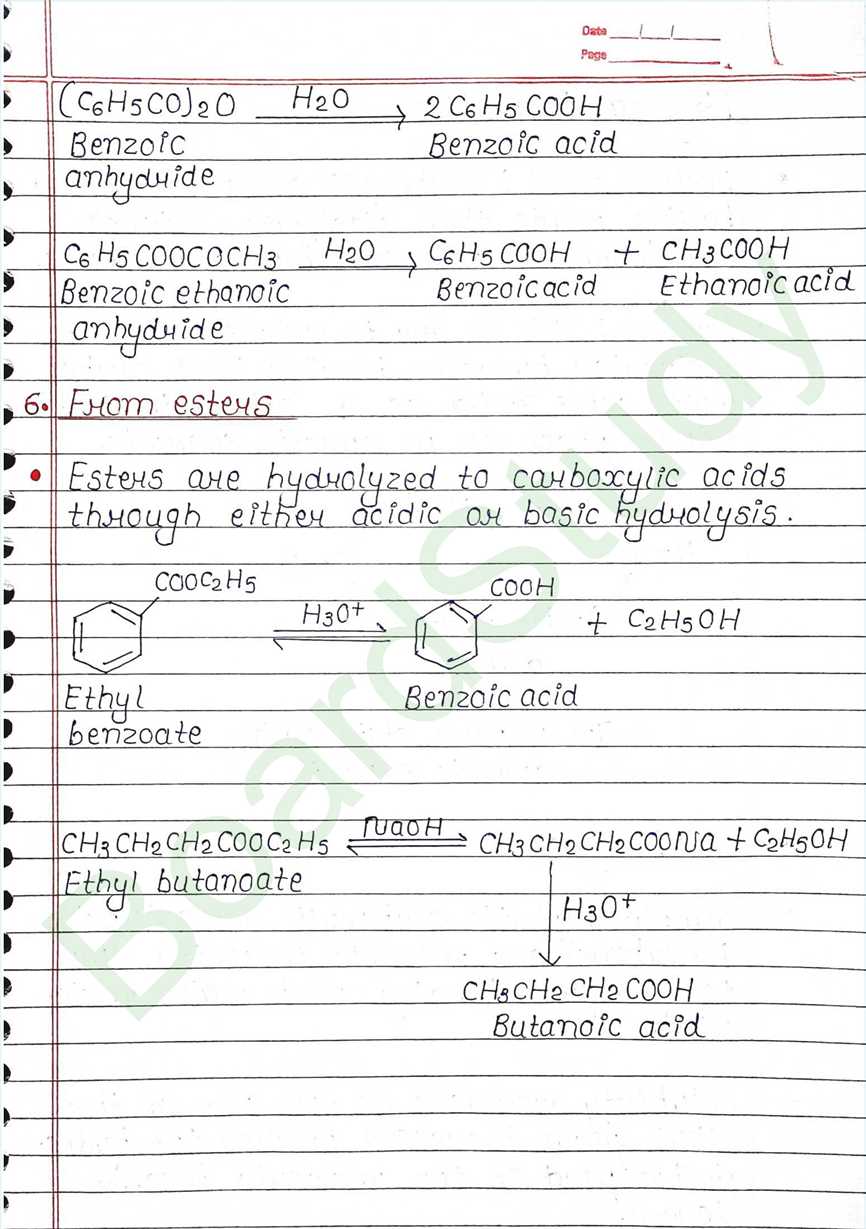
Reactions Involving the – COOH group
1. Reduction: Reduced to primary alcohols. using strong reducing agents like Lithium Aluminium Hydride (LiAlH4) or diborane (B2H6).
2. Decarboxylation: Removal of CO₂ from the molecule Sodium salts of acids are heated with sodalime (NaOH + CaO) to form hydro- carbons with one less carbon atom.
Hell-Volhard – zelinsky (HvZ) Reaction :
Carboxylic acids having an α-hydrogen are halogenated at the α position on treatment with chlorine or bromine in the presence Of a small amount of red phosphorus.
Ring Substitution (Aromatic Acids):
- The carboxyl group is a deactivating and meta- directing group for electrophilic substitution reactions.
- Friedel-crafts reactions do not occur because the COOH group deactivates the ring and the catalyst (AlCl3) gets bonded to the carboxyl group.
Uses of Carboxylic Acids :
- Methanoic acid : Used in rubber, textile, and leather industries.
- Ethanoic acid : Used as a solvent and as vinegar in the food industry.
- Hexanedioic acid (Adipic acid) : Used to manufacture nylon-6,6.
- Sodium Benzoate : Used as a food preservative.
- High fatty acids : Used to make soaps and detergents.
Features of Notes
- Students can use Aldehydes, Ketones, and Carboxylic Acids notes for last minute revision.
- In the last few days of exam students feel very stress due to pressure of exam. Notes will be very helpful for managing the stress in the last days of exam.
- All notes are totally free of cost and students can access notes anytime on our for totally free of cost.
- Aldehydes, Ketones, and Carboxylic Acids Notes PDF are created very carefully so you can rely on this notes.
Summary
| Chapter | Aldehydes, Ketones, and Carboxylic Acids |
| Chapter Number | 8 |
| Subject | Chemistry |
| Class | 12 |
| Medium | English |
FAQ
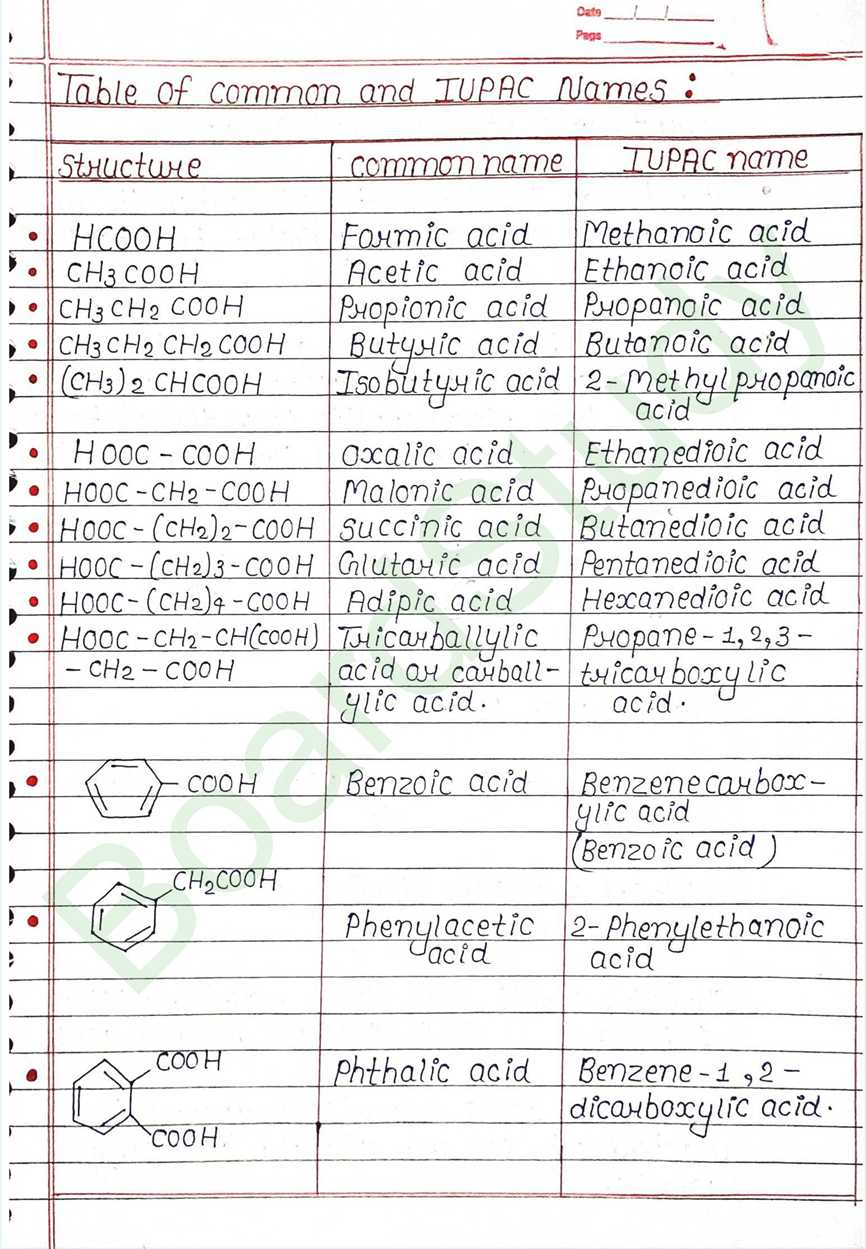
What is IUPAC Names ?
IUPAC Names: Derived by replacing the -e from the parent alkane’s name with -oic acid. The carboxyl carbon is always numbered 1
What is Boiling Point ?
The Boiling poit of higher than those of non-polar hydrocarbons and weakly polar ethers with comparable molecular masses.
Are these notes sufficient for board exam?
Aldehydes, Ketones, and Carboxylic Acids handwritten notes are created by topper’s and expert teacher keeping board exam in mind so you can score maximum in board exam.
Are Haloalkanes and Aldehydes, Ketones, and Carboxylic Acids notes according to NCERT latest syllabus?
Yes notes are created according to the NCERT latest syllabus.
How can i download Aldehydes, Ketones, and Carboxylic Acids Notes PDF?
For downloading Aldehydes, Ketones, and Carboxylic Notes PDF click on Download PDF button.
