Some students find Math a very hard subject so here on BoardStudy, we have shared class 12 Math Chapter 6 Application of Derivatives notes. We have covered every topic in a simple and easy way so anyone can understand the chapter and perform well in exam.
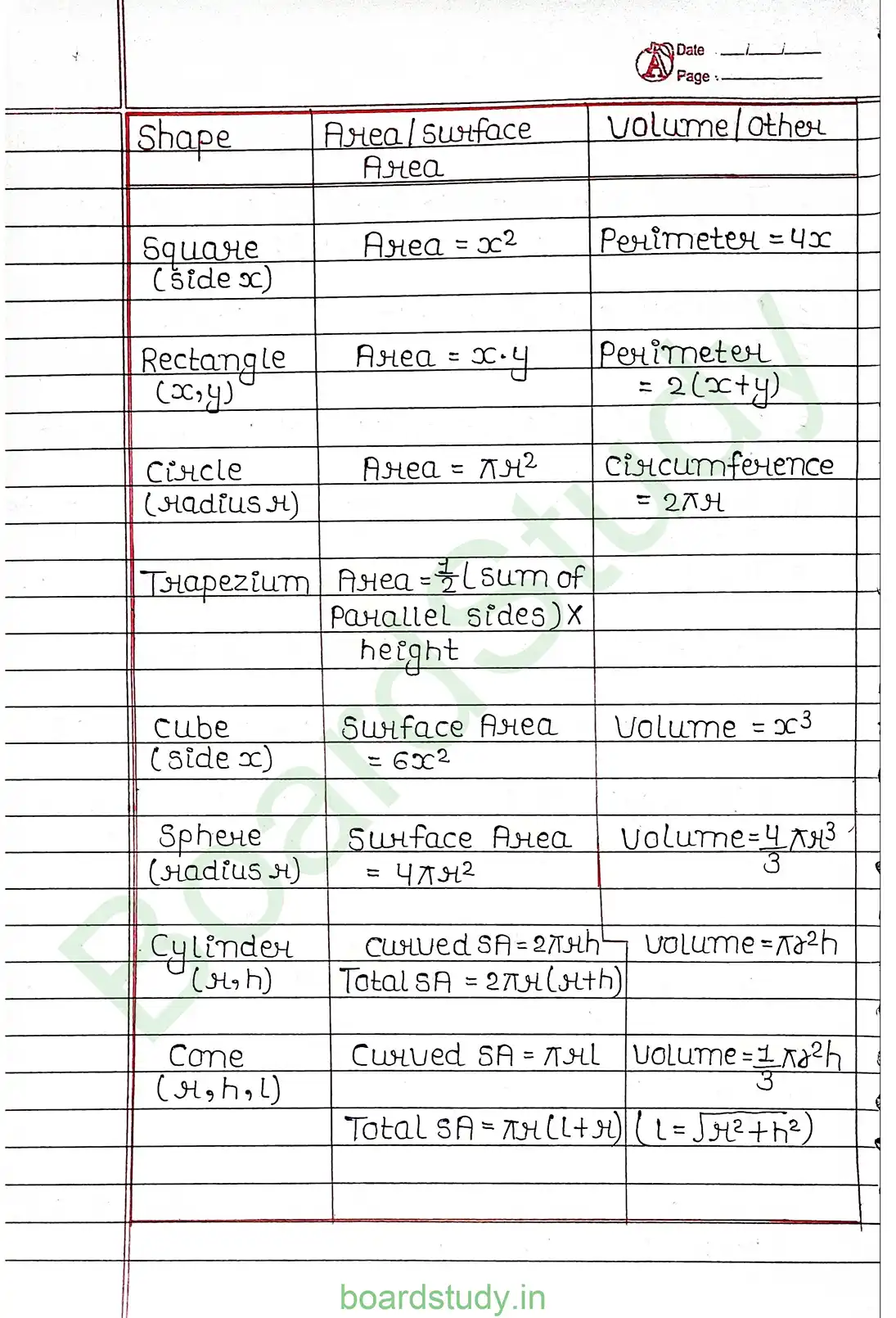
Notes are very clean and colourful written by BoardStudy subject matter experts. Every important concept, formula, diagram and derivation is shared in Application of Derivatives notes that will help you solve the problem. These notes are designed to make complex topics easier which will definitely boost the students’ confidence during the exam.
Application of Derivatives Handwritten Notes PDF





Chapter 5: Continuity and Differentiability Notes
Chapter 7: Integrals
Other Subjects:
Class 12 Physics Notes PDF
Class 12 Chemistry Notes PDF
Key Points
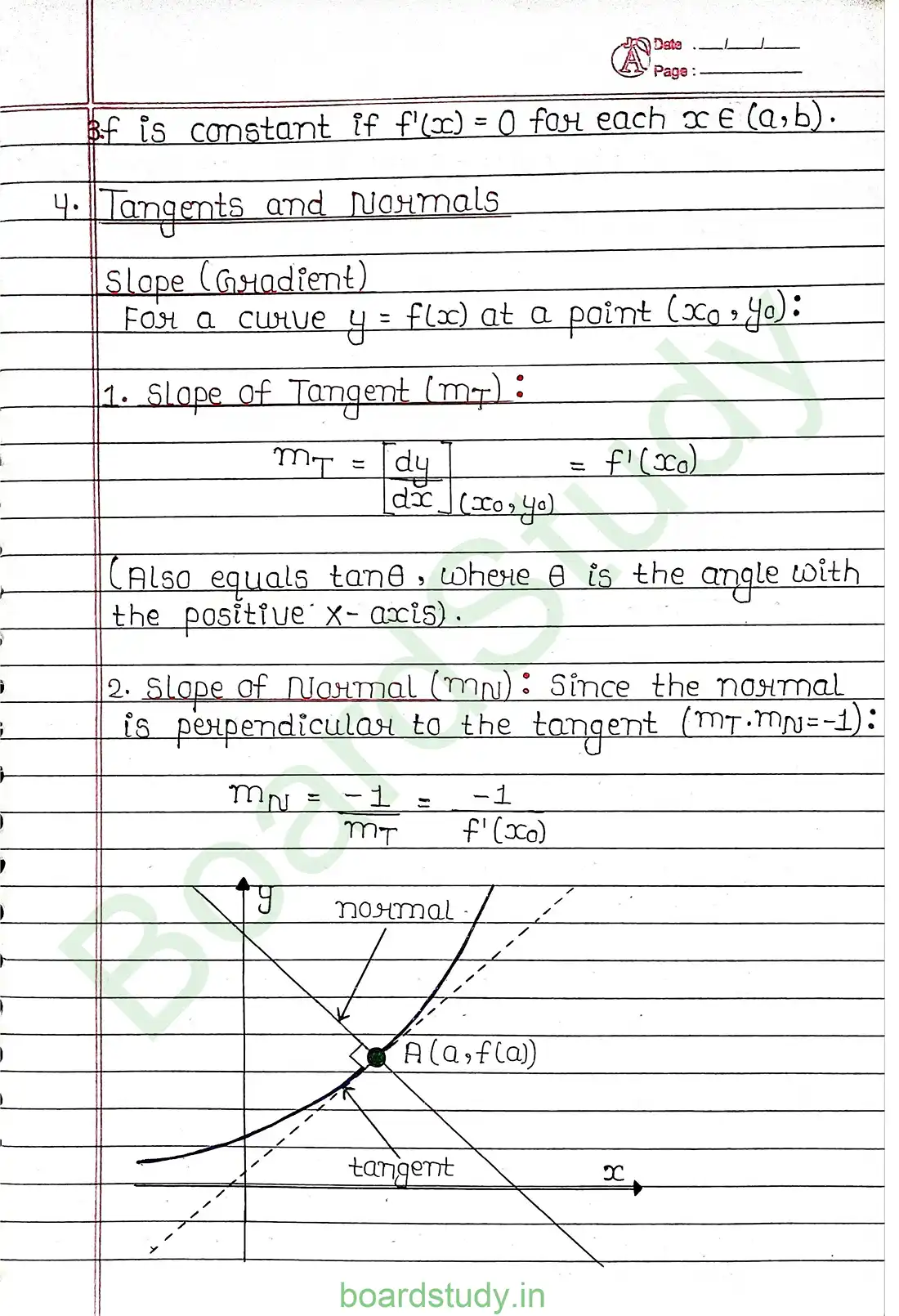
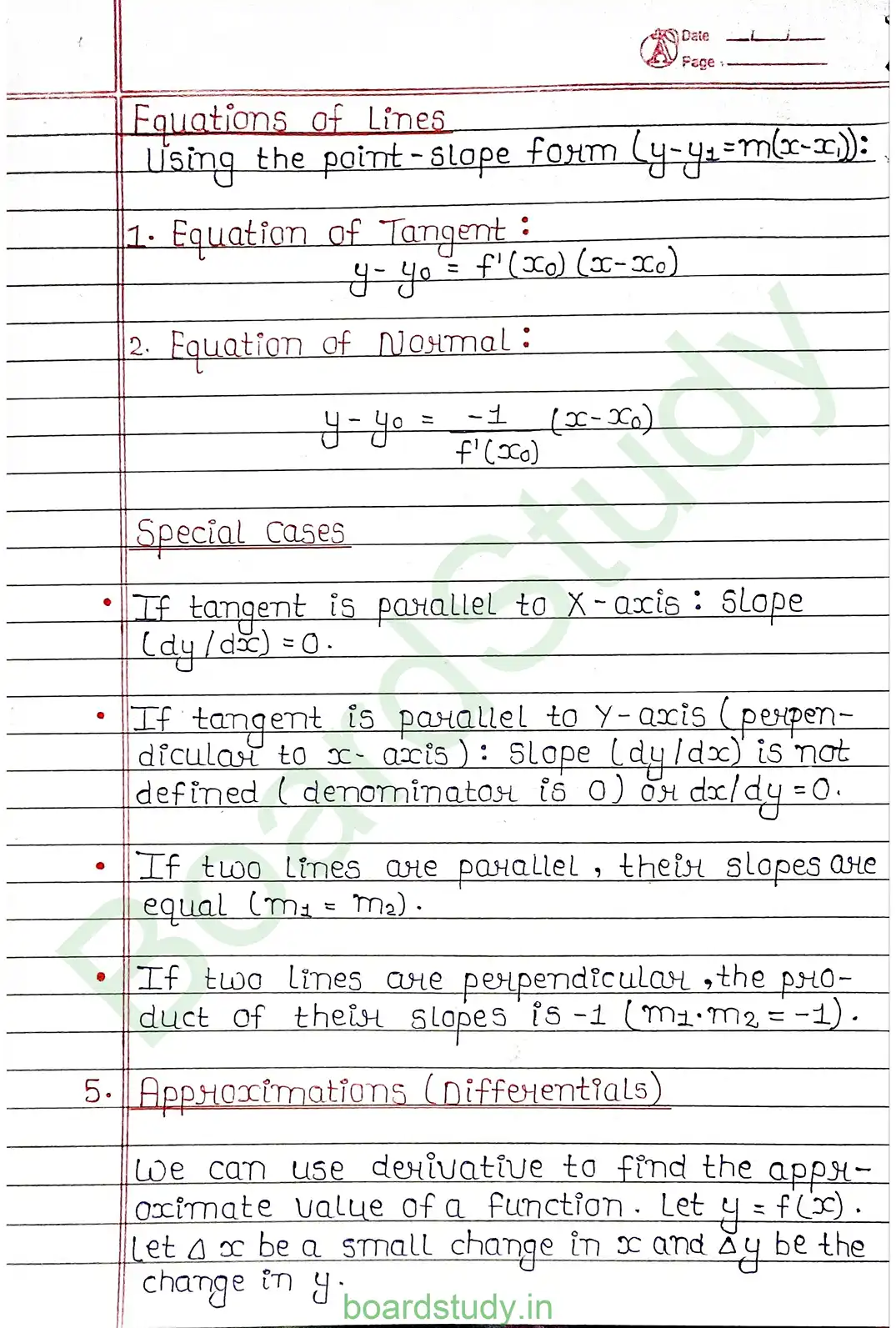
Application of Derivatives If a quantity y varies with another quantity x, satisfying some rule (y=f(x)), then dx/dy (or f'(x)) represents the rate of change of y with respect to x at x=x0. OR, f'(x0) represent the rate change of y with respect to x at x=x0
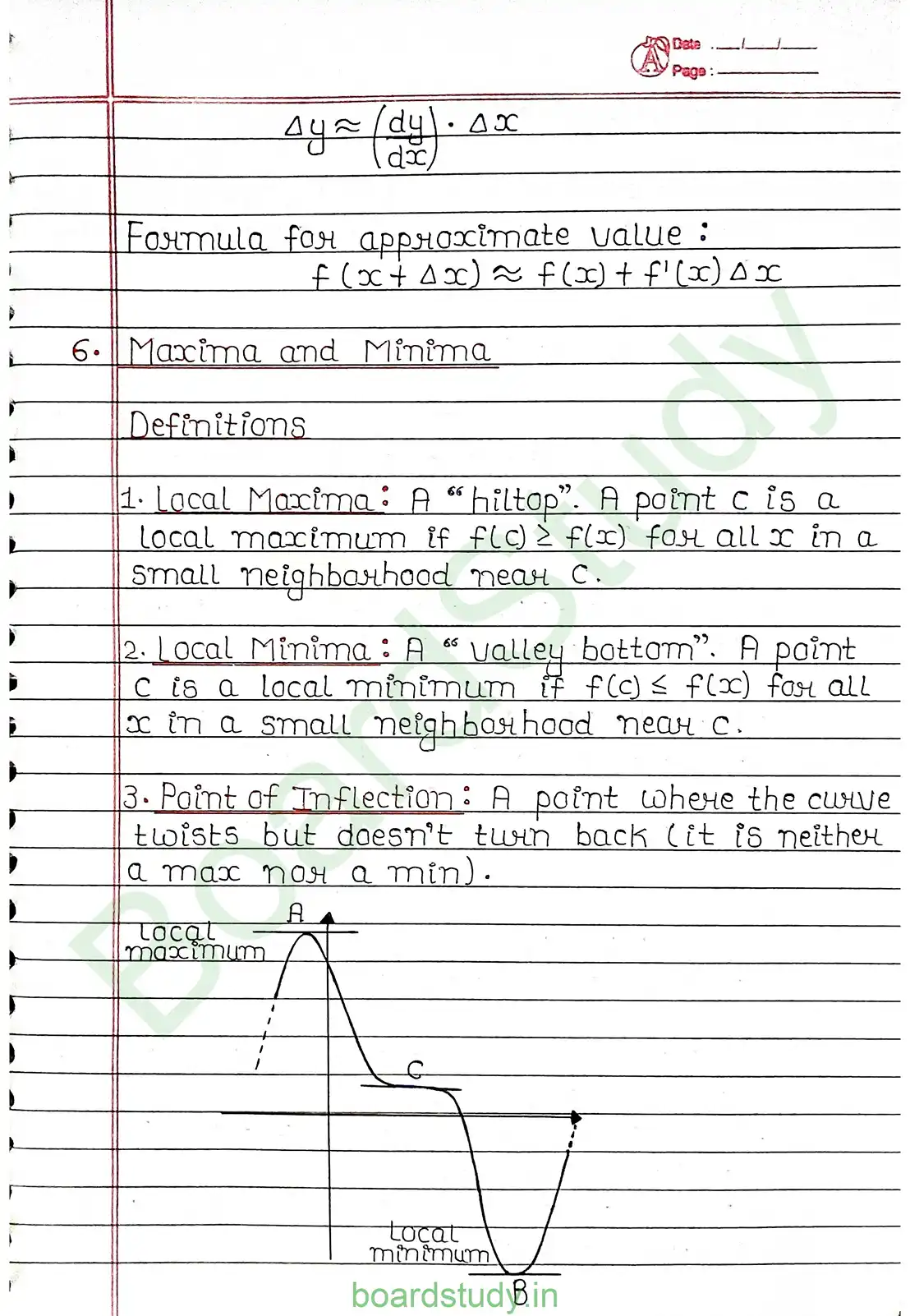
Maxima and Minima
Let f be a function defined on an interval I. Then
(i) f have maximum value in I if there exists a point c in I such that, f(c)>f(x) ∀ x ∈ I. The number f(c) is called max. value of f in I. Point c is called a point of max. value of f in I.
(ii) f have minimum value in I if there exists a point c in I such that, f(c)<f(x) ∀ x ∈ I. The number f(c) is called max. value of f in I. Point c is called a point of min. value of f in I.
(iii) f have an extreme value in I, if there exists a point c in I such that f(c) is either a maximum value or a minimum value of f in I. The number f(c) is called an extreme value of f in I. The point c is called an extreme point.
Local Maxima and local minima Let f be a real valued function and let c be an interior point in the domain of f. Then,
(a) c is called a point of local maxima if there is an h>0 such that, f(c)>f(x) ∀ x ∈ (c-h, c+h). The value of f(c) is called local max. value of f.
(b) c is called a point of local minima if there is an h>0 such that, f(c)<f(x) ∀ x ∈ (c-h, c+h). The value of f(c) is called local min. value of f.
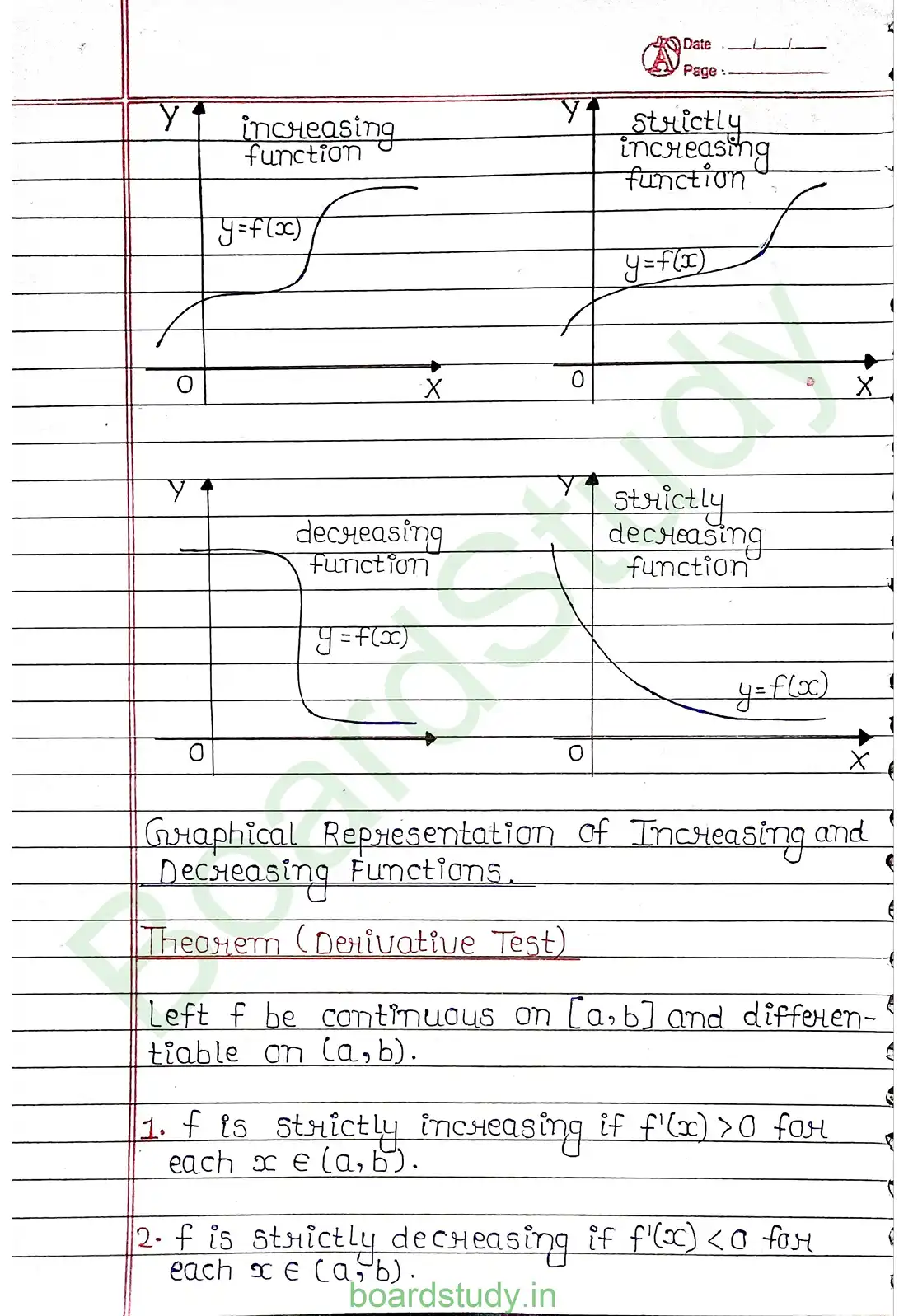
Turning points: The points at which a function changes its nature from decreasing to increasing or vice versa are called turning points.
Critical points: A point c in the domain of a function f at which either f'(c)=0 or f is not differentiable, is called critical point of f.
First derivative test: Let f be a function defined on an open interval I. Let f be continuous at a critical point c in I. Then,
- If f'(x) changes sign from +ve to -ve as x increases through c, then c is a point of local maxima.
- If f'(x) changes sign from -ve to +ve as x increases through c, then c is a point of local minima.
- If f'(x) does not change sign as x increases through c then c is neither a point of local maxima nor a point of local minima. Such a point is called point of inflection.
Benefits of Notes
- Application of Derivatives Notes are crafted by BoardStudy expert. All concepts and diagrams are included in notes.
- Our revision notes make a complex topic very simple. By using our notes, students can quickly revise Application of Derivatives chapter.
- In the last few days of exam, students feel very stressed due to the pressure of exam. Application of Derivatives Notes will be very helpful for managing the stress in the last days of the exam.
Summary
| Chapter | Application of Derivatives |
| Chapter Number | 6 |
| Subject | Math |
| Class | 12 |
| Medium | English |